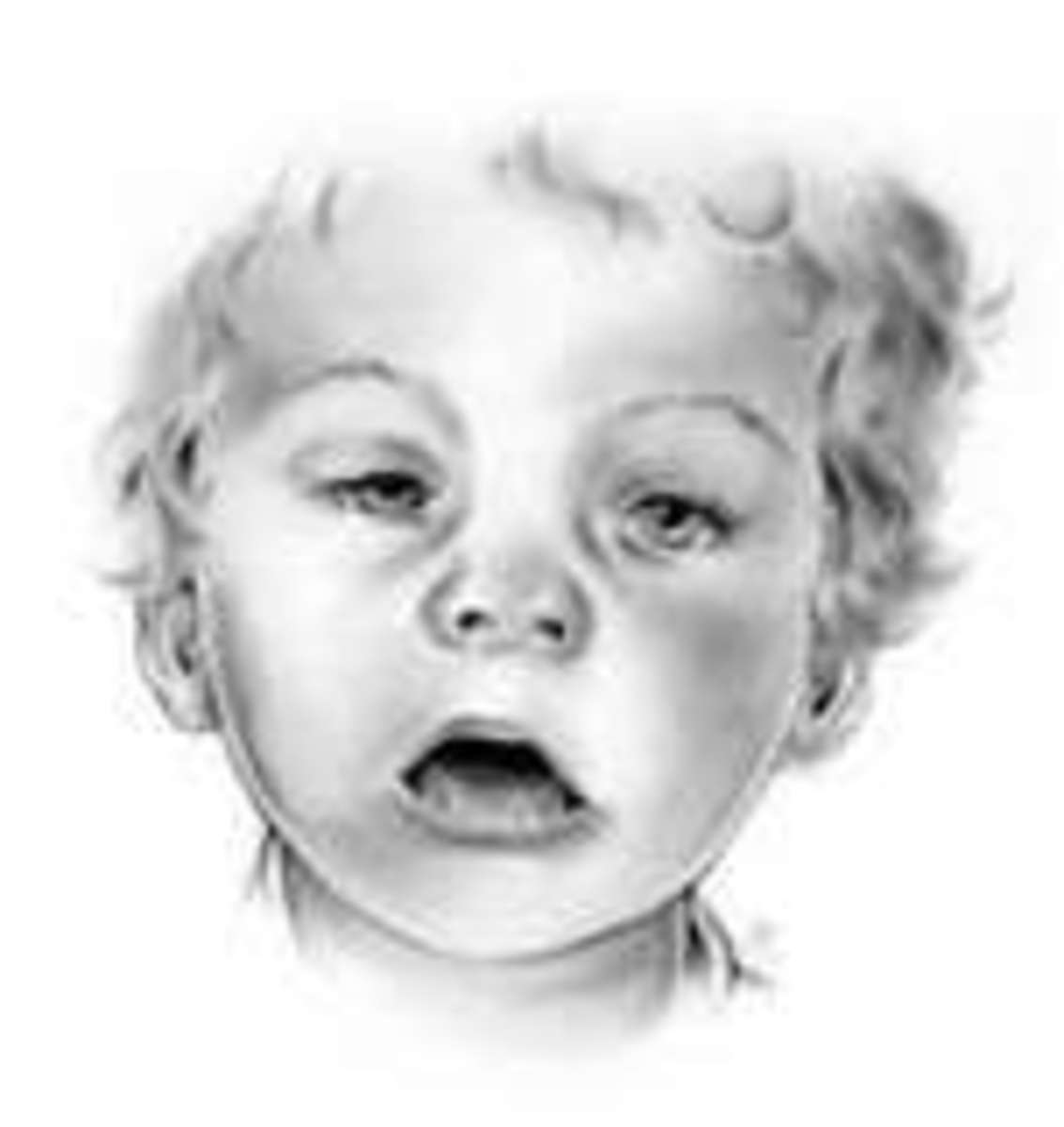
Mental Birth Defects: Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders

Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
Do you know anyone with FASD?
FASD: An Overview
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders are a range of conditions caused by the consumption of alcohol during pregnancy. Like Down syndrome, FASD is a developmental, lifetime condition with no cure that affects one’s behavior, learning capabilities, attention span and memory as well as introducing a variety of physical issues. These can range from abnormal facial features, problems with the central nervous system, and low height and weight. Someone suffering with FASD typically has a combination of these problems (Facts about FASDs). Considering that it is so easily preventable, FASD occurs at a startlingly high rate in North America, at 9.1 cases per 1,000 births. It’s the most common form of preventable brain injury (Mclachlan). Interestingly enough, according to Evaluating the Psycholegal Abilities of Young Offenders with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder, “…[F]indings suggest individuals with FASD (largely ARND) are overrepresented in criminal justice settings, with estimates ranging from 10% to 23%” (Mclachlan). FASD appears to be correlated with criminal activity.
The Spectrum of Disorders
FASD is a far-reaching term to describe the variety of physical and mental conditions caused by prenatal alcohol consumption. It encompasses several different subsets, including Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS), Partial Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (pFAS), and Alcohol Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder (ARND). FAS is the most extensive and severe level of FASD, affecting the patient’s physical features and cognitive functions. pFAS is a less severe form of FAS’s impairments, while ARND retains FAS’s mental retardation without the physical indicators (Mclachlan).
- Mental Birth Defects: Down Syndrome
Some mental illnesses, such as depression and anxiety, develop long after a baby is born. Others, like Down Syndrome, begin in the safest place in the world: its mother's womb.
Prevent FASD - Don't Drink During Pregnancy
Do you know anyone who drinks or has drank during pregnancy?
Symptoms of Fetal Alcohol Syndromes
Symptoms of FASD typically include abnormal facial features, a small head size, low weight and height, poor coordination, hyperactive behavior, poor attention span, poor memory, learning disabilities, speech and language delays, low IQ or intellectual disabilities, poor reasoning and judgment skills, vision or hearing problems, and problems with the heart, kidneys or bones (Facts about FASDs). This list is far from extensive; it only includes visible symptoms. Far more happens on a cognitive level.
FASD results in a variety of learning, social and behavioral difficulties. Similar to Down syndrome, those with FASD can suffer developmental delays, including issues with speech, causing stuttering and stammering. Processing and thinking skills especially suffer; this can make abstract concepts such as math extremely challenging. Applying previously learned knowledge is also difficult, due to the abnormal learning curve that can often frustrate teachers. One day a student with FASD may be making progress, the next he might appear to forget how to apply what he just learned (A Closer Look at Fetal Alcohol Syndrome). A student with FASD might memorize a formula or process for solving a problem well enough, but the next day he or she may struggle to incorporate the formula or process.

Living With a Fetal Alcohol Disorder
These mental challenges mean that FASD patients must be placed in special education programs as soon as possible; even young infants can be helped to foster better motor and intellectual development. Once they hit preschool, individualized education programs can be beneficial to help with the variety of developmental and language delays. Placement in special education programs continues into elementary school and beyond; it incorporates small classroom sizes and an increased level of individual attention. Unfortunately, while remedial education may prevent further deterioration, it has not been shown to further increase the mental capabilities of children with FASD. Patients tend to reach their academic peak at a high school level. Sadly, many with FASD will graduate from high school incapable of basic life skills like managing money, driving a car and holding a job (A Closer Look at Fetal Alcohol Syndrome).
Clearly, Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders have vast repercussions on victims’ minds, affecting their capacity to lead normal, independent lives. They often require parental or caregiver supervision throughout their entire lives. Because it is so easily preventable, it is particularly painful to see someone with FASD. Hopefully, with further research and time, progress can be made towards treating this disease.
- Emotional Intelligence: The Key to Success in Romance, the Workplace, and Life
What is emotional intelligence? How does it affect your workplace, love life and interpersonal relationships, and is it possible to improve upon what emotional intelligence you already have?
Works Cited
"A Closer Look at Fetal Alcohol Syndrome." A Closer Look at Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. Texas
Department of Family and Protective Services. Web. 13 Dec. 2014. <https://www.dfps.state.tx.us/Adoption_and_Foster_Care/About_Our_Children/Disabilities/fetal_alcohol.asp#learning>.
Mclachlan, Kaitlyn, Ronald Roesch, Jodi L. Viljoen, and Kevin S. Douglas. "Evaluating the
Psycholegal Abilities of Young Offenders With Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder." Law and Human Behavior (2012). PsycARTICLES. Web. 13 Dec. 2014.
"Facts about FASDs." Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 3 Sept. 2014. Web. 13 Dec.
2014.
© 2015 Nu Vew