Mesothelium and Mesothelioma
Mesothelium
Mesothelioma is a cancer that is specific to a particular type of tissue. This tissue is called "mesothelium."
Mesothelium is not an organ (like liver, kidneys or heart) but more a protective tissue that surrounds or lines body cavities. One type that you may have heard of is the pericardium. This is the sheath of tissue that surrounds and protects the heart and major arteries.
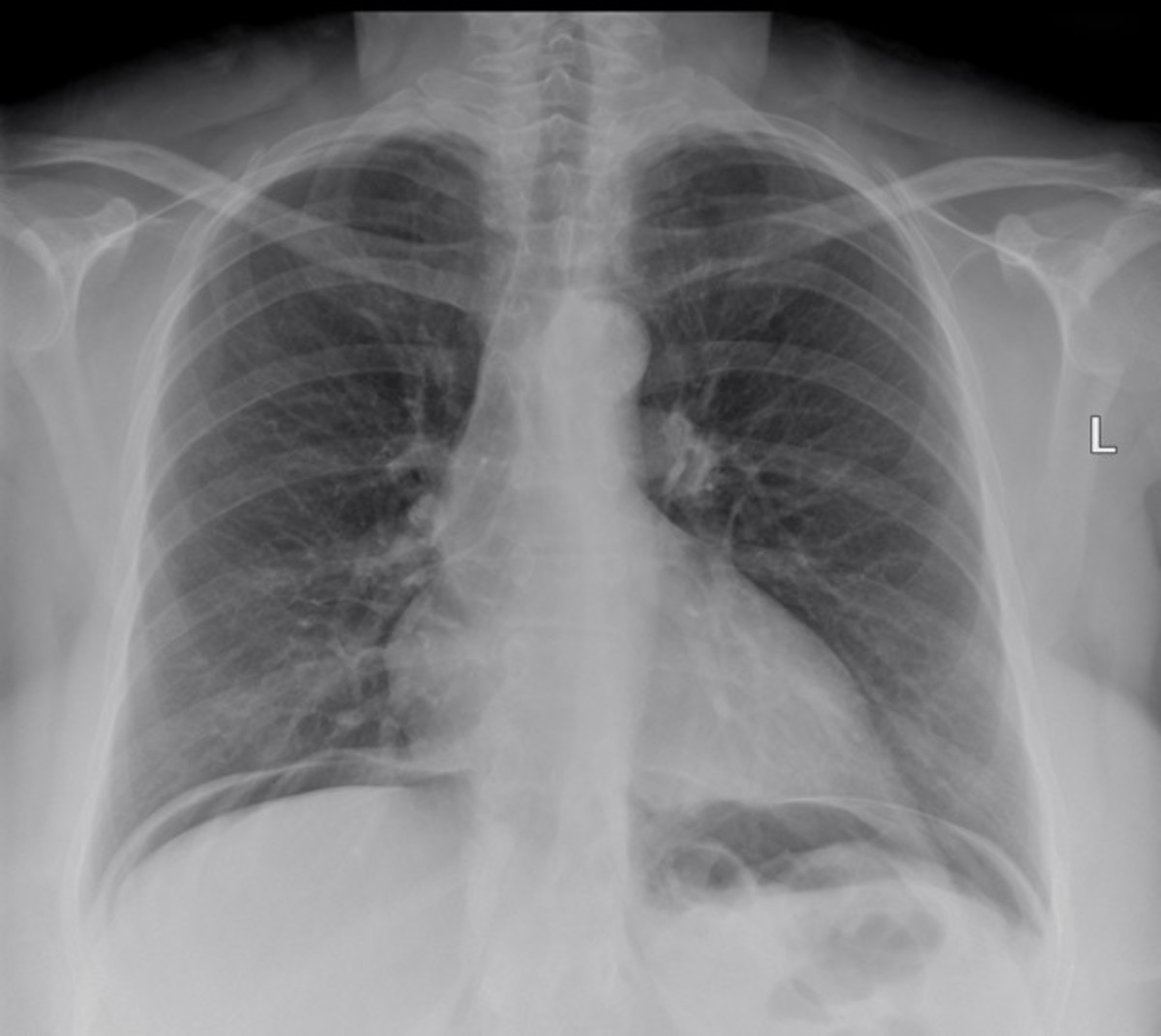
Oddly, one that is not often named is the pleura. This is the membranous tissue that surrounds the lungs in the thoracic cavity. It is odd that it is not mentioned in the context of mesothelioma as the pleura is the tissue most often associated with the disease.
Two other mesthelium are the peritoneum and mesentery. These two membranes are located in the abdominal cavity where they suspend segments of the small intestine from the rear of the abdomen.
There is one final mesothelium tissue which is present in human reproductive areas, but this is almost never the site of cancer.
What the Tissue Does
Because the human body is "riddled" with cavities it is important that organs within these cavities have structural support and a means of sliding past other organs without injury. The heart and lungs do not simply float in the thoracic cavity, they are suspended there with connective tissue. These organs also need to move around, in a limited range of motion, in the thoracic cavity without causing damage or being damaged as they move around other organs. The mesothelium helps in this as it is both tough and slippery.
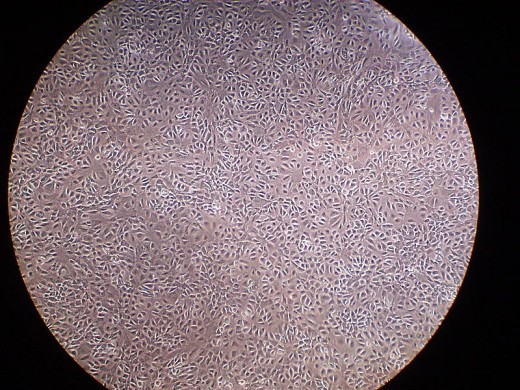
Cell Structure of Mesothelium
Mesothelial cells are flat and typically comprise a single layer of cellular tissue.
The cells are both flattened in cross section and joined to each other in a regular "cobblestone" pattern. The cells also feature tiny filaments and pockets that retain fluids. These fluids aid the body's ability to allow organs to slide past one another without undo friction and harm.
Mesothelium tissues have a number of important functions all related to its cellular structure:
- to separate and support the organs
- to provide a white-blood cell permeable barrier
- to aid in allowing organs to slide past one another without injury
In other words this tissue plays a supporting role in organ location and separation along with providing structural support to those organs around various locations in the body.
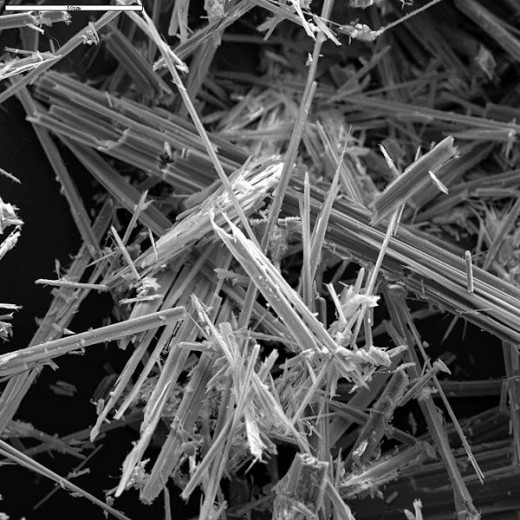

Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is cancerous growth of mesotheliumic tissue.
Most often this form of cancer affects the pleura mesothelium in the chest cavity, but it can also affect the pericardium and the abdominal cavity.
Because it does not directly affect the lungs it is not a lung cancer. Rather it is a cancer that affects the connective/protective tissue of the chest cavity by causing uncontrolled replication in the cells that make up the protective tissue. Those tissues can also experience morphed growth in that they replicate normally, but with abnormal structure.
Smoking does not cause mesothelioma, but once the disease has taken hold smoking exacerbates its symptoms.
The direct result of this uncontrolled or morphed growth is an increase in the amount of lubricating fluid produced by the mesothelium. This fluid, in turn, presses in upon the lungs causing shortness of breath. Over time a buildup of this fluid or of the mesothelium itself can interfere with lung function.
Mesothelioma is quite dangerous as it can indirectly affect the lungs to the point that they case to function.
Mesothelioma is also very difficult to treat.
Symptoms
Symptoms include shortness of breath and weight loss. Less common symptoms include chest pain, fatigue, abdominal pain, bowel function problems, and even jaundice.
Because the two primary symptoms are more often associated with lung cancer or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), mesothelioma can only be determined by biopsy of the connective tissue which requires a thoracoscopy where a tissue sample can be procured.
Once the sample is taken it must be examined under a microscope for an accurate diagnosis.
Chest X-Rays and C.T. scans are not accurate in determining mesothelioma, but can be used as a guide to full diagnosis via biopsy.
Cause
Though not all mesothelioma is caused by asbestos exposure this far and away the most common factor. Inhalation of silicon dust has also been implicated along with exposure to radiation.
Types of Mesothelioma
Roughly seventy-four percent of cases are pleural (chest) mesothelioma with fifteen to twenty percent peritoneum (abdomen), and between five and seven percent in the pericardium.
Treatment
A variety of treatment options are available including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. No single therapy is particularly successful so treatment typically involves a combination of therapies. Pleural mesothelioma is easier to treat and those patients will enjoy a longer survival rate than those with abdominal or pericardia mesothelioma.
To date no single therapy is particularly successful so, for example, surgery has a very poor success rate with an average survival of just less than one year. Radiation therapy alone has an even less encouraging survival rate.
However surgery and radiation therapy combined can provide survival rates of five years or better. Unfortunately there is not a great deal of data on this combination treatment as of yet.
Despite its ubiquitous presence in the public lexicon, mesothelioma is a rare form of cancer. For that reason less is known about it than, say, lung or brain cancer.
Chemotherapy has the best prognosis with survival rates ranging from ten months and up. When combined with surgery survival rates improve slightly.
Survival Rates and Age
Survival rates in the young are much better than with an older patient, but this is not so much a factor of age as one of additional disease.
A younger victim has a better prognosis simply because he or she is less likely to have other contributing conditions such as diabetes, reduced liver or kidney function, hypertension (high blood pressure) or heart disease.
However, because the disease resulting from asbestos exposure can take as long as forty years to develop, cases of mesothelioma in the young are exceedingly rare.
A positive outlook is a contributing factor to a good survival rate. Apparently not allowing the disease to "win" can drastically increase the survival rate.
Survival Rates in Years
Although advanced (stage 4) mesothelioma is typically given a survival rate of just less than a year (ten to eleven months) there are exceptions.
Australian Paul Kraus has had the disease since 1997 and continues to survive while routinely rejecting traditional therapies. Others have survived the disease well past the ten year mark. There are also two elderly women who display mesothelioma remission.
Survival Rates and the Future
As little as one year ago the mean survival rate of mesothelioma was four to eighteen months. However, survival rates continue to climb as more and more is learned about both the disease and how to treat it.
Over time this trend is almost certain to continue.
Wrapping Up
Despite the fact that most of us hear about this disease on an almost daily basis it is actually quite rare.
Fewer than three thousand cases per year are diagnosed in the United States. This means that the likelihood of being diagnosed with mesothelioma is less than one thousandth of one percent.
This is both good and bad news. The rarity of the disease means it is highly unlikely that you or someone you know will contract it. But it also means that research for cure and prevention will be difficult due to its rarity.
Keep Heart
Perhaps the best defense for this disease seems to be to keep a positive attitude and to take good care of yourself. Paul Krause uses a regimen of sound diet and vitamin therapy.
Research has shown that patients with this disease fare much better if they take good care of themselves by staying physically fit by eating healthily.
Disclaimer
The author was not compensated in any way, either monetarily, with discounts, or freebies by any of the companies mentioned.
Though the author does make a small profit for the word count of this article none of that comes directly from the manufacturers mentioned. The author also stands to make a small profit from advertising attached to this article.
The author has no control over either the advertising or the contents of those ads.