Miscarriage symptoms: Early Signs of Miscarriage
Miscarriage or Spontaneous Abortion
Miscarriage, called by doctors spontaneous abortion, can be defined as the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks of gestation.
It is estimated that up to 20 percent of all pregnancies end in miscarriage; but the actual number may be even higher. That is because many miscarriages occur very early, before a woman even knows that she is pregnant. Miscarriage early in pregnancy can occur days or weeks after the embryo or fetus has actually died.
What are the signs of miscarriage?
Early symptoms of a miscarriage include:
- Vaginal bleeding that may be light or heavy, constant or irregular. Although sometimes spotting is harmless, but it may be a sign of something more serious. Up to 25 percent of all pregnant women experience bleeding or spotting at some point in pregnancy, so bleeding alone does not necessary mean that you are having a miscarriage. Bleeding with pain is a sign that miscarriage is more likely.
- Cramping, abdominal pain, and lower backache. Pain may start a few hours to several days after bleeding has begun.
- Blood clots or tissue passing from the vagina.
It's fairly common to have brown discharge and it isn't necessarily a sign of a problem with the pregnancy. Unfortunately, it is estimated that about half of women who experience bleeding will have a miscarriage. However, there may be other reasons for those symptoms. Call your doctor to schedule and appointment to check whether or not everything is OK. Also, read about early pregnancy symptoms and ectopic pregnancy symptoms.
How is miscarriage diagnosed?
Call your doctor's office if you experience bleeding and pain. The doctor will examine you depending on the stage of your pregnancy.
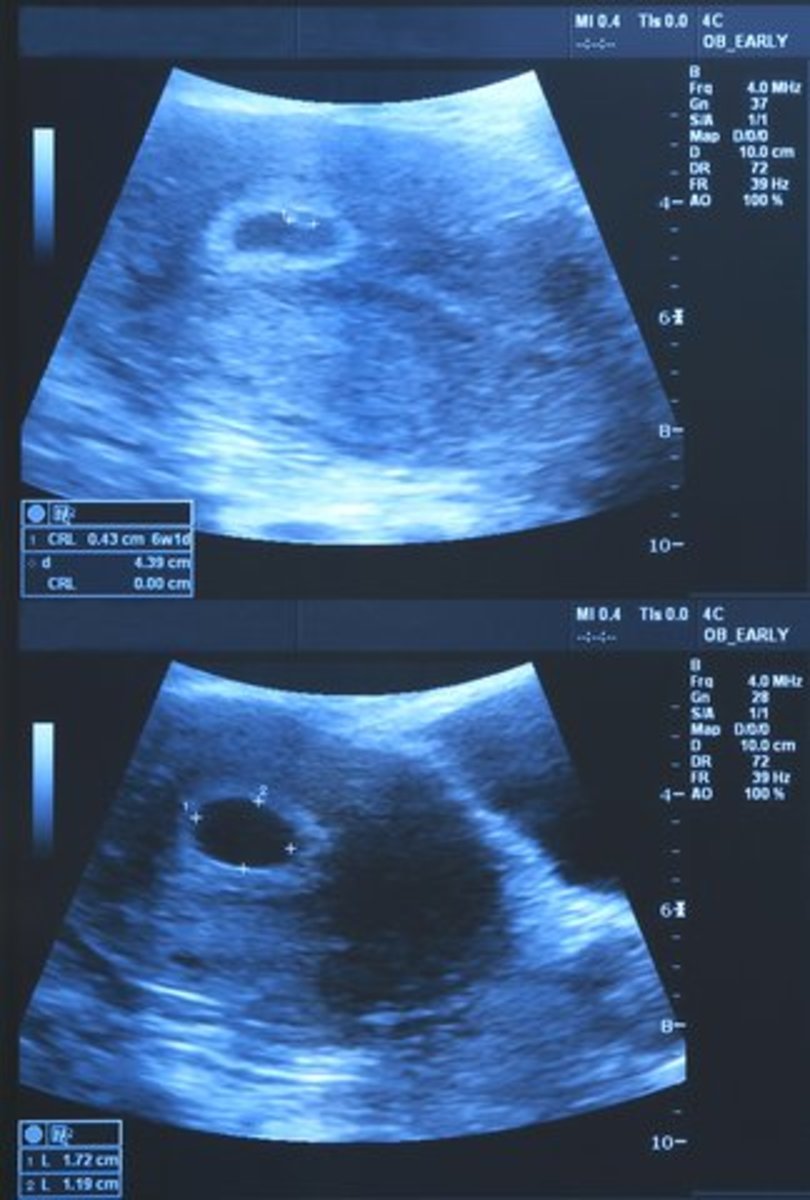
In the early stages, he or she may test your hormones or do the ultrasound to check for the heartbeat. During an ultrasound your doctor will to try to determine if there is a live fetus inside the uterus by looking at the sac that surrounds the fetus or checking the fetal heartbeat. If the fetus is there but is is not alive, this is called a missed abortion.
In the later stages of the pregnancy, in addition to an ultrasound, she or he will do a pelvic exam to see whether your cervix has started to dilate. If the cervix is dilated - it is called threatened abortion — you will probably not have a miscarriage, but it is not certain.
Your obstetrician is going to examine the membranes surrounding the fetus. If they have ruptured, and cervix is dilated, you are going to have a miscarriage.
What causes miscarriage?
More than 80 percent of miscarriages occur in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. At least half of these early miscarriages are thought to be caused by abnormalities with the fetus's chromosomes.
- Miscarriage is NOT caused by physical activity, working out, drinking a glass of wine, having sex, working, or lifting heavy objects. Nausea and vomiting in early pregnancy, even if severe, will not cause a miscarriage. (In fact, evidence shows that women who have these symptoms are less likely to miscarry.) It is also unlikely that a fall, a blow, or a sudden fright can cause miscarriage.
- Many of these miscarriages are caused by chromosome problems. These chromosome defects are not usually inherited from the parents, but are due to errors that occur as the fertilized egg begins to divide. Because of these chromosome abnormalities, the fetus would not have been able to develop into a normal baby.
- Another factor that increases the risk of miscarriage are any health issues that the mother is experiencing. These include infections, chronic diseases such as diabetes or high blood pressure, and problems with the immune system. Such miscarriages typically happen later in the pregnancy.
- If the woman has any abnormalities of the uterus or cervix, they also increase her risk for a miscarriage. For example, so-called cervical incompetence, in which the cervix begins to dilate too early in pregnancy. This type of miscarriage almost always occurs in the second trimester.
Recurrent or repeated miscarriage is defined as three or more miscarriages in a row. The causes of this are similar as those for a single miscarriage. There are some tests that can be done to identify the specific problem for recurrent miscarriage, but they are expensive and the treatment options are somewhat limited. Despite repeated miscarriages, many couples go on to have a successful pregnancy later.
Risk factors for miscarriage
- Woman's age, especially if you are 35 or older
- Father's age (35 or older)
- Recurring miscarriages (three or more).
- PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome)
- Diabetes or an autoimmune disease
- Certain bacterial or viral infections during pregnancy.
- A blood-clotting disorder
- A T-shaped uterus or other structural problem with the uterus
- A history of pregnancy with a birth defect.
- A physical injury.
- Exposure to dangerous chemicals before or during pregnancy.
What about pregnancy after miscarriage?
The good news is that the majority of women who have had a miscarriage will go on to have successful pregnancies in the future. Even women who experience repeated miscarriages (three or more in a row) have a 70 to 85 percent chance of carrying another pregnancy to term. It is usually advised, however, to wait a few months before becoming pregnant again.
Additional Reading
- Very Early Pregnancy Symptoms: 15 Early Signs and Symptoms of Pregnancy
Of course, the most surefire sign of pregnancy is the positive pregnancy test ;-) although even that may not be 100% reliable. But even before you take a test or miss a period you may suspect that you may... - Baby Heartbeat Monitor Allows You To Listen To Your Unborn Baby Sounds
After suffering a miscarriage at 10 weeks, my husband and I found out we were expecting again a few months later. Since I was so worried about the possibility of another miscarriage),I decided to rent a baby heartbeat monitor, also known as fetal dop - What not to eat when pregnant: Foods to avoid while pregnant
When you are pregnant you are eating for two: you and your unborn baby. Everything you consume, passes into the placenta, so your unborn baby gets it too. And apart from knowing what to eat, it is equally... - How to get pregnant fast: Some best tips for getting pregnant quickly
Many people when they finally decide it’s the right time for them to have kids, want the pregnancy to happen as fast as possible. Trying to conceive can be an exiting time in your life, but it can also...