Nanotechnology in Health: Intelligent Delivery Systems for Making Chemotherapy Effective and Safe
Cancer Plays Havoc, Chemotherapy Faces Challenges
Cancer has been one of the major health problems around the globe. Global demographic statistics has predicted increasing cancer incidences in coming decades, with 420 million new cases each year expected by 2025. Current cancer treatments include surgical intervention, radiation and chemotherapeutic drugs. A major problem limiting the success of majority of currently used anticancer agents is their non-specificity or non-selectivity towards tumor cells and tissues. This has resulted in dominant side effects of these drugs in healthy tissues and organs. In cancer treatment, therapeutically active concentration of drug in tumor tissue is achieved at the expense of contamination of the rest of the body. This non-specificity or non-selectivity towards tumor cells and tissues creates toxicological problems that erect obstacles to effective chemotherapy. Moreover, most of the anticancer drugs are poor aqueous soluble due to their hydrophobicity. This leads to their lower absorption from biological membranes and thus, affects their clinical efficacy. Delivering anticancer drugs selectively and precisely to tumor tissues in increased concentrations and enhancing their aqueous solubility are highly required for better treatment and management of cancer.
Nanotechnology is Replacing Conventional Dosage Forms
Conventional dosage forms faces several challenges such as non-specific distribution of drugs, inferior pharmacokinetics and efficacy of drugs even at large doses, lower oral bio-availability and stability issues. For the past few decades, nanotechnology has been widely employed in medicines, including cancer therapy. Nanotechnology exploits nano range carriers that efficiently address the issues associated with conventional dosage forms. Drug nano-carriers possess several attractive features like enhanced loading or solubilization of drugs as well as their selective delivery to the required disease sites. Furthermore, these nano-carriers are rich with reactive functional groups on their surfcaes, thus they can be chemically modified accordingly for achieving drugs increased internalization to the target cells, superior pharmacokinetics and their delayed clearance from biological system. These nano-carriers are such versatile that they release their loaded therapeutic contents “on demand” in a fair sustained manner in response to stimuli or remote actuation.
Nanotechnological Strategies for Improved Chemotherapy
To achieve better clinical outcomes of anticancer drugs for improved management and treatment of cancer without off-target adverse side effects, they are needed to be delivered specifically or selectively to the cancerous tissues in increased concentration. Nanotechnology uses multiple strategies via employment of versatile nano-carriers for making chemotherapy more effective and safe. The nano-carriers overcome the barriers that are associated with drugs due to their physico-chemical properties. These properties include low aqueous solubility and instability. Nano-carriers are capable of improving the solubility and stability of anticancer drugs, thus enhance their absorption across biological membrane. Moreover, some anticancer drugs get deactivated in biological systems due to harsh enzymatic environments. Nano-carriers protect them from such harsh biological environment, leading to improvement in their therapeutic efficacy.
Biological barriers are also their for reducing the efficacy of anticancer drugs. Some drugs get quickly cleared from the body, thus desired efficacy cannot be achieved despite increased doses. Nano-carriers can prolong their circulation time by avoiding their clearance through biological policing systems. Thus, increased anticancer effects for the drugs are achieved at their low doses, this in turn results in cost-effective chemotherapy without off-target side effects.
Anticancer Drugs are Blind but Nano-carriers are Intelligent
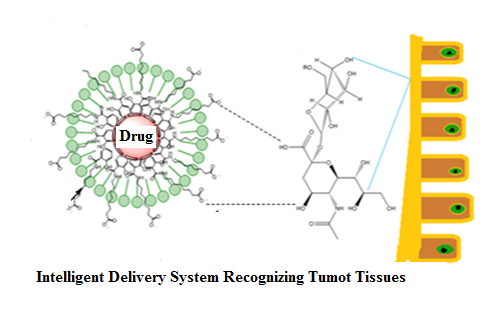
Anticancer drugs are blind and they cannot differentiate between healthy and cancerous tissues. In chemotherapy, minimum anticancer activity of the drugs is achieved at the massive contamination of the rest of the body. Ultimately, adverse side effects further deteriorate the condition of cancer patients. Nano-carriers are intelligent systems that can recognize the cancerous cells through their modification with a targeting ligand. The targeting ligand is a chemical that specifically recognizes a receptor that gets overexpress on the surface of cancer cells. Thus, surface engineering of nano-carriers with targeting ligands result in the selective delivery of anticancer drugs to the tumor or cancerous tissues, leading to accumulation of anticancer drugs in the cancer cells in increased concentration. As a result better anticancer activity is achieved in the vicinity of tumor tissues while minimizing their side effects on healthy tissues. Moreover, nano-carriers can also be directed to the cancer cells selectively through application of external or internal stimulus. for this purpose, the nano-carriers are made responsive to a specific external stimulus i.e. magnetic field, ultrasound or an internal stimulus such as pH or temperature changes in the cancer cells micro-environment, as a result the nano-carriers unload the encapsulated drug directly in cancer cells.
It is Not Over, More Exciting Nanotechnological Aspects Yet To Be Revealed
The novel aspects such designing of intelligent nano-carriers for reversing multi-drug resistance against anticancer drugs are also getting wider acceptance for improving chemotherapy. Controlled release nano-carriers are also emerging as novel tools for making chemotherapy effective through release of loaded drugs in a sustained manner which will result in the efficacy of drugs for a longer time with decreases doses and dosing frequency. Nanotechnology is also focusing the designing of super intelligent systems that would be used for chemotherapy and monitoring the progress of disease simultaneously. The smart nano-carriers are going to be the "magic bullets" for highly effective, safe and personalized chemotherapy in near future.