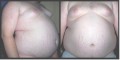
Obesity: The Health Significance Of Its Diagnosis And Treatment
Starvation: Going Without Food For Days Is Recommended In Severe Cases

Diagnosis
Clinical diagnosis is based on weight, physical appearance and measurement of skin fold thickness. Sophisticated methods are available to establish the diagnosis in a borderline case. Increase in weight occurring during pregnancy, fluid retention, hypothyroidism, hypothalamic lesions, and other endocrine disturbances should be differentiated from obesity due to nutritional causes. So also overweight may be caused by excessive muscular development in wrestlers, weight lifters and boxers.
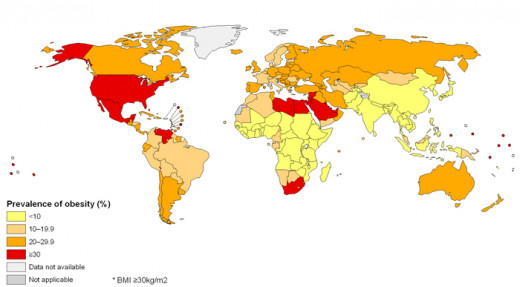
Mexico Is Now The World's Fattest Nation With 38%
Obese Woman Engaging In Simple Exercises

Treatment Of Dietary Obesity
Strong motivation of the patient is absolutely essential for successful management. Dietary regulation is the basis of modern therapy. Calorie intake should be reduced below the basal requirements and the patient has to be kept on negative energy belance over prolonged periods of time. The excess fat is catabolised and weight is lost.
On an average, daily intake has to be limited to 800 to 1000 calories. More drastic cuts on foods are frequently resented and result in non compliance. For optimal results, the diet should be acceptable, sufficient in volume and conforming to the general eating habits of the individual. Bulk is provided by adding liberal amounts of vegetables and low- caloric fruits. Clear instructions on the exact quantity of food and its timing are very essential. Regular follow up is necessary for proper motivation and assessment. Patients put on the subcaloric diets lose weight steadily after an initial latent period ranging from days to weeks. It is ideal to reduce the weight by 1 kg, a week. Vitamin and mineral supplementation is advisable, since the restricted diet may fail to meet these requirements. The major principles of dieting in a condition of obesity are as follows:
- Sugar, sweets, honey and similar high- caloric articles of food and alcohol are to be strictly avoided.
- Timing of the diet and the menu should be adjusted to conform to the occupation and dietary habits of the individuals
- When the optimum weight reduction has been achieved, graded increase in the diet can be made under-supervision, taking care not to restore the original weight and to ensure balance nutrition.
Global Obesity Epidermic
Exercise And Drugs
Exercise: Moderate exercise augments the beneficial effect of dieting. Walking slowly up to 4 to 5 Km, twice a day, swimming or games are ideal, depending upon individual preferences.
Drugs: Several drugs are available which reduce appetitie. These anorectic drugs have been employed on short- term basis when the patient is not able to resist the desire to eat. Diethyl propion 25 mg, 1 hour before meals and fensluramin 20 mg, twice daily increased up to 120 mg, per day are commonly used anorectic drugs. On a short term basis, there can be employed to help in weight reduction. Since there drugs cause dependence, they should preferably be with-drawn after 3 months of administration. Side effects include dryness of the mouth, abdominal pain, drowsiness, alopecia, mental depression, confusion and impotence. There drugs are contraindicated in patients with psychiatric illness.
When obesity is extreme and rapid weight reduction is desired, more drastic measures are employed. These include total starvation programmes and surgical procedures.
Total Starvation: This can be undertaken under strict supervision for 2 to 3 weeks. Only water, salts, and vitamins are allowed during this period. Complications include starvation ketosis, ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death. Due to these risks, total starvation should be undertaken only under exceptional circumstances. Wiring of the jaw to prevent ingestion of solid foods has been practiced in persons unable to undertake total starvation. Follow up treatment consists of subcaloric feeding.
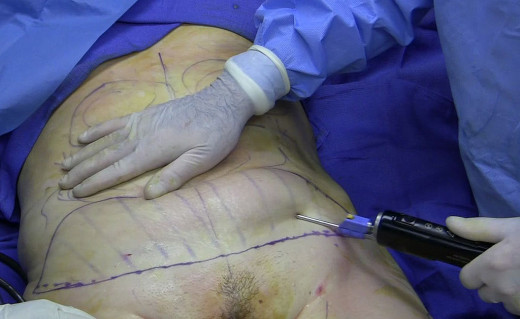
Liposuction Procedure
Surgical Measures
Surgical measures done to procude short-circuiting of digestive and absorptive portions of the intestines have been in vogue for severe cases. The procedures include jejuno-ileal bypass and gastric bypass. Gastric complication has been tried with a view to reduce the capacity of the stomach. Extirpation of excessive fat and plastic surgical procedures to remove redundant skin folds remaining after achieving weight loss help to correct cosmetic disability and also to augment the effects of dietary treatment.
In general, loss of weight up to 5 to 10 kg is easy but further reduction and maintenance of the optimal weight demand great motivation on the part of the patient and skill on the part of the physician. Once the optimum weight is reached, the patient should slowly increase the diet to prevent further weight loss, and try to adhere to the optimum weight. Even an occasional dietary excess results in rapid weight gain. All the complications of obesity can be arrested and may even regress if normal weight is maintained for long periods.
Secondary obesity should be treated by adopting dietary measures and giving due attention to the primary cause.
© 2014 Funom Theophilus Makama