Oral Cancer - Causes, Symptoms and Diagnosis
What is Oral Cancer
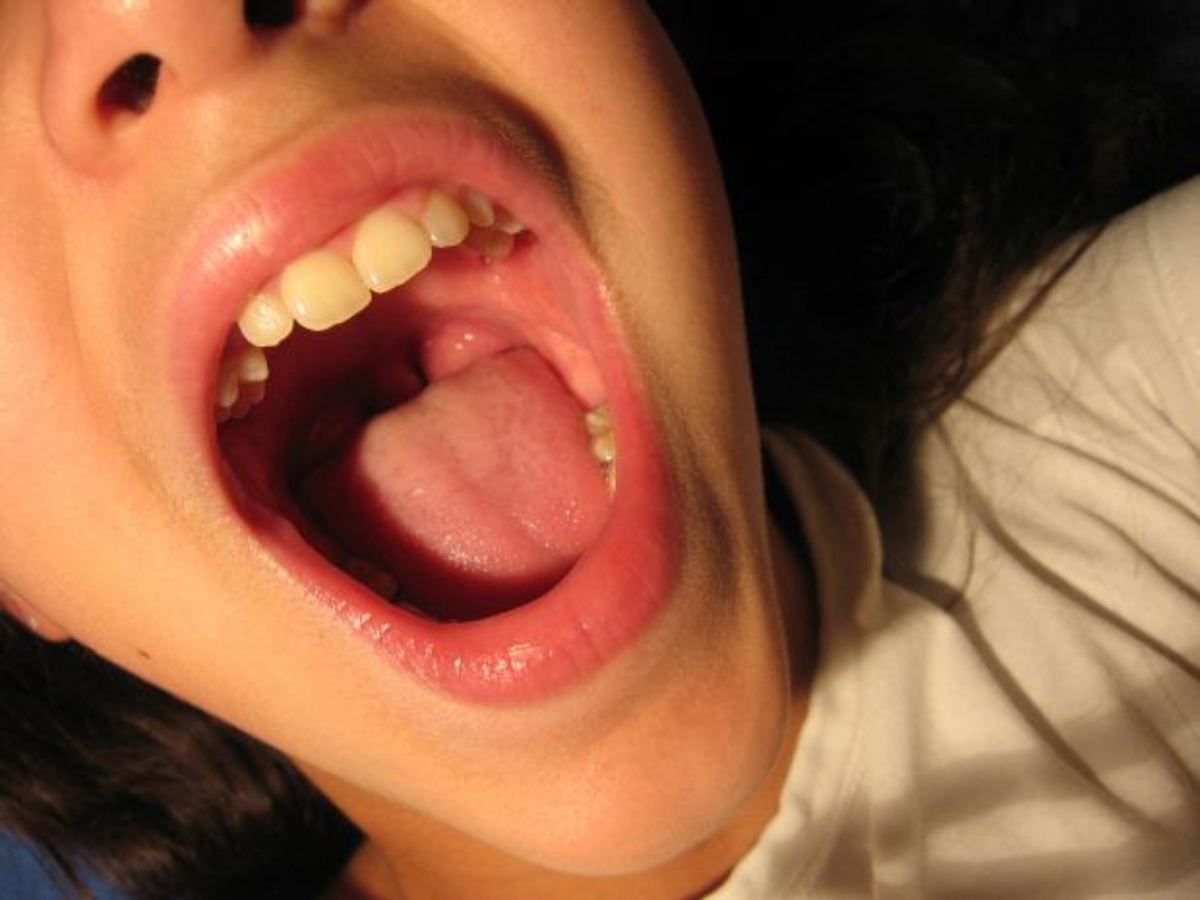
Oral Cancer refers to the uncontrollable growth of cells that invade and cause damage to the surrounding tissue. It is the cancer of the oral cavity or oropharynx. Oral cancer can develop in any part of the oral cavity which includes cancer of the mouth, lips, tongue, cheeks, gums and teeth, tonsils and throat. Oral cancer can prove to be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated at an early stage. It is the sixth most common cancer among men. Oral or mouth cancer most commonly involves the tongue. These are malignant and tend to spread rapidly.
The death rate for oral cancer is quite higher in the United States. Nearly about 36,000 Americans are diagnosed with oral cancer every year, resulting in over 8,000 deaths. The overall 1-year survival rate for patients with all stages of oral cancer is 81%. The 5 & 10-year survival rates are 56% and 41%, respectively.
Risk Factors and Causes of Oral Cancer
The risk factors responsible for the development of oral cancer include the following:
- Smoking – Smokers are six times more likely to develop oral cancer than non-smokers.
- Excessive chewing of tobacco – Use of tobacco products increase the risk of cancer of the cheek, gums, and lining of the lips.
- Excessive consumption of alcohol – Regular alcoholic drinkers are six times more likely to develop oral cancer than non-drinkers or those drinking occasionally.
- Excessive exposure to sun, especially at the young age
- Family history of cancer
Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cancer
The symptoms associated with oral cancer include the following:
- Bleeding in the mouth
- A lump in the neck
- Loosening of teeth
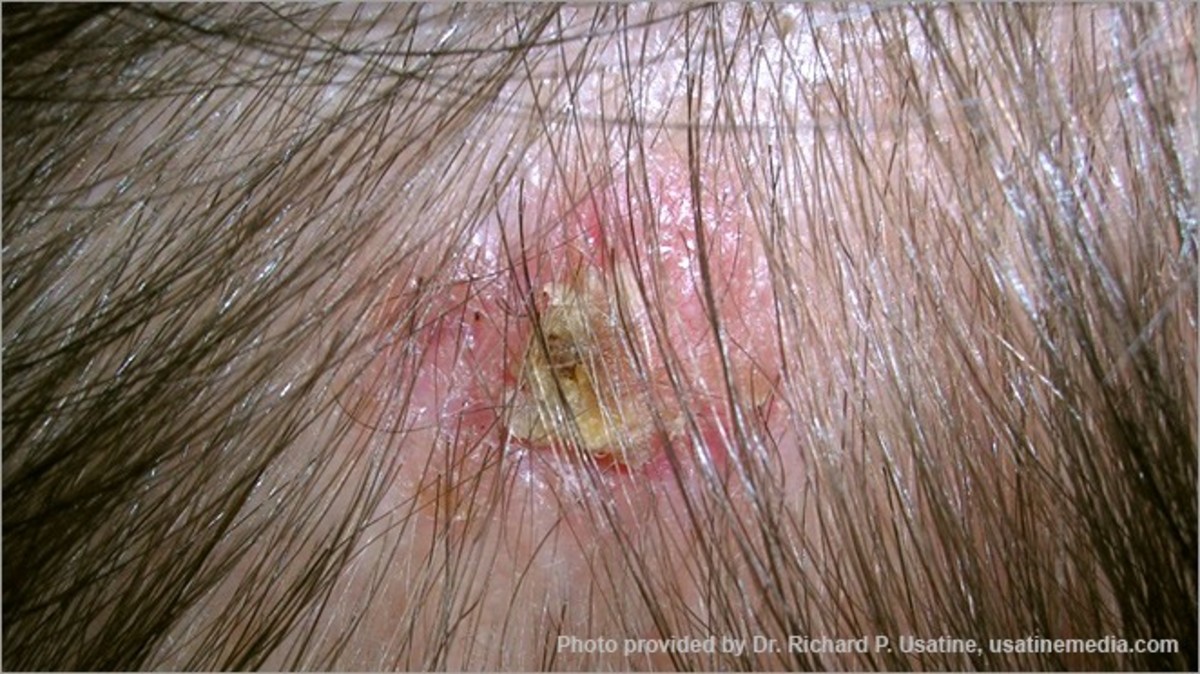
- White or red patches in the mouth or on lips
- Pain in ear
- Pain or tenderness in any area of the face, mouth or neck
- Difficulty in chewing or swallowing
- Difficulty in speaking clearly
- Excessive weight loss
Anyone with these symptoms must see a doctor so that problem, if any, can be diagnosed and treated as early as possible. Regular checkups can detect the early stages of oral cancer or conditions that may lead to oral cancer.
Diagnosis of Oral Cancer
For diagnosing oral cancer, an oral cancer screening examination is performed by the dentist or doctor for visibility of any red or white patches, lumps, loosening of teeth, swelling or any other problem. More specifically, your dentist will feel for any lumps or irregular tissue changes in your neck, head, face, and oral cavity. The floor of your mouth and lymph nodes in your neck are also examined. Your tongue is also pulled out gently so that the doctor can carefully check the sides and underneath.
If the examination shows an abnormal area, then a small sample of the tissue may be removed and sent for the tests like biopsy, endoscopy, imaging studies and further testing. These tests are conducted in order to know whether the abnormal area is cancerous or not.
These tests are necessary to detect oral cancer at an early stage, before it can get spread to the surrounding tissues. Oral cancer needs to be diagnosed and treated at an early stage otherwise it can prove to be life-threatening.