Peritoneal Mesothelioma: An Asbestos Related Cancer
What is peritoneal mesothelioma?
It is a tumor associated with asbestos exposure. Most (70%) cases of mesothelioma occur in the chest region on the pleura covering the lungs and is known as pleural mesothelioma. Peritoneal mesothelioma is less common comprising of around 30% of the total cases and it occurs in the abdominal region.There is difficulty in early diagnosis as the symptoms are confused with other benign conditions of the digestive system. The diagnosis at an advanced stage when the disease is widespread limits treatment options. Advances in treatment by chemotherapy and surgery have led to better survival in patients.
The increase in the incidence of peritoneal mesothelioma is related to asbestos mining which peaked in the 1970's. The asbestos-related activities have stopped but exposure in the past is largely responsible for peritoneal mesothelioma.
Peritoneum
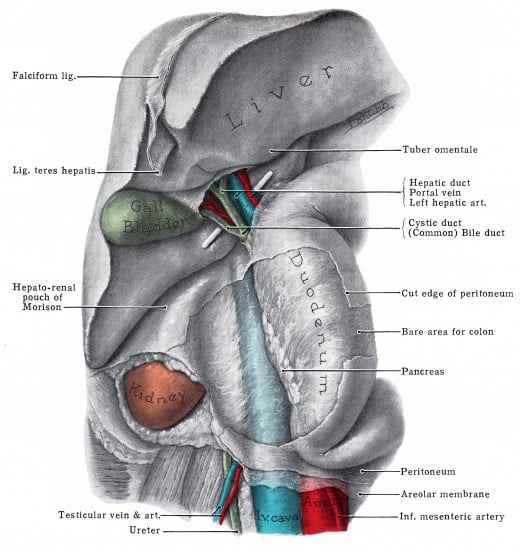
The Peritoneum
As the name implies peritoneal mesothelioma arises from the peritoneum.The peritoneum is a very thin membrane lining the abdominal cavity and it supports the various organs in the abdomen. Apart from support for the organs in the abdomen, it provides a path for the nerves, blood vessels and lymph vessels to these organs. It also releases a lubricating fluid which helps these organs to slide over each other when there is any physical movement.There are two layers of this peritoneum-
1) Visceral peritoneum (Outer Layer)
2 ) Parietal peritoneum (Inner Layer)
The mesothelial cells make the mesothelium which covers the internal organs and this mesothelium in the abdomen and pelvis is known as the peritoneum.
Rarely mesothelioma can occur in the membrane around the heart ( pericardium) or membrane around the testes (tunica vaginalis).
Cause of peritoneal mesothelioma
Asbestos exposure causes peritoneal mesothelioma.The association between asbestos and peritoneal mesothelioma has been found in many studies. Asbestos causes irritation of the peritoneal lining which covers the abdominal structures. This causes the mesothelial cells in the peritoneum to undergo cycles of damage and repair. This causes a release of certain chemical substances from the body which are called cytokines. This by a complex cascade of events promotes tumorigenesis. Oxygen free radicles are also liberated and this causes damage to DNA. This causes alterations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Very rarely mesothelioma may develop in patients who receive radiotherapy.
People who worked in the construction or transport industry in the past when asbestos was not banned have a risk of exposure to asbestos. The time period between exposure to asbestos and mesothelioma to develop may vary between 20 to 60 years.
So peritoneal mesothelioma is more common in elderly with 80% of the cases being reported in people over 65 years of age.
Asbestos is strongly related to the causation of peritoneal mesothelioma

Clinical presentation of peritonial mesothelioma
Peritoneal mesothelioma develops in patients with heavier exposure to airborne asbestos fibers. The latent period between asbestos exposure and disease development is about 20-30 years. In pleural mesothelioma, this gap between exposure and development of pleural mesothelioma is 30-40 years. A study was done at Washington Cancer Institute showed that the presenting clinical symptoms of peritoneal mesothelioma may be as follows-
1) Abdominal pain (33%)
2) Increasing abdominal girth (31%)
3) New onset hernia (12%)
4) Abdominal pain (5%)
The remaining 19% of the patients may present with loss of appetite, breathing difficulty, fever or a mass in the abdomen.
These symptoms are non specific and may be present in a variety of medical conditions, so the diagnosis may often be delayed. Patients may have bowel obstruction, perforation of bowel, ascites and may require emergency surgery.
Peritoneal mesothelioma presentation may be similar to other cancers arising from the peritoneum. These may include pseudomyxoma peritonei, ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer and peritoneal sarcomatosis.
Investigations for peritoneal mesothelioma
Blood Test
A blood test is not a diagnostic test for mesothelioma but it provides information regarding the effects of the tumour on blood cells, liver and kidney.
X-ray
X-ray of the abdomen may show fluid and thickening. A X-ray chest should also be done to rule out lung involvement.
CT scan
A CT scan will provide accurate information regarding the size and location of the tumour(s) in the abdomen. It will also show the spread of the cancer to the other organs. A CT guided biopsy of the tumour may be taken to confirm the diagnosis.
MRI Scan
A MRI scan is best for soft tissue tumours and may be required during the work up of the disease. Patients with a pacemaker or other metallic implants in their body should inform the medical team regarding these to the medical team.
PET Scan
A PET scan is an advanced imaging technique which may be used in patients if there is a diagnostic dilemma.
Biopsy
A small part of the thickened tissue is removed from the body and examined under a microscope to see if there are any abnormal or cancer cells. A biopsy is the diagnostic test for most cancers. It helps us to determine the presence or absence of mesothelioma. The type of mesothelioma may also be determined from the cell type which may be epithelioid, sarcomatoid or biphasic.
CT guided Biopsy
A biopsy may be taken under CT guidance where the thickened tissue is visualised using an CT scan and the needle to take biopsy is inserted using this imaging technique. The procedure is usually done under some sort of local anaesthesia to numb the pain of the needle prick.
Laparoscopy
A camera attached to a thin tube is inserted in the abdomen by a very small incision in the stomach and a biopsy is taken from the tissue under direct visualisation.
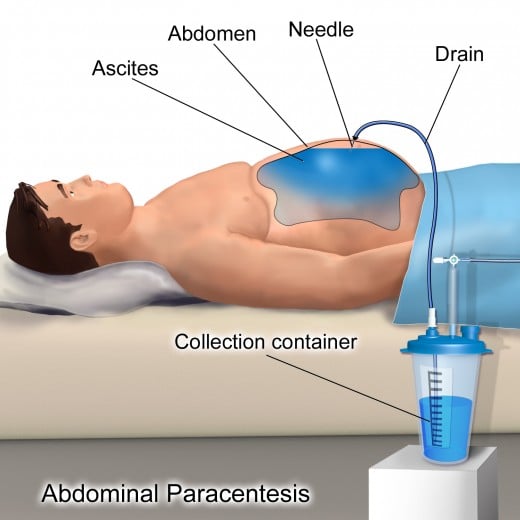
Paracentesis
Peritoneal mesothelioma may be a cause of fluid collection in the abdomen. This fluid is aspirated from the abdomen using a fine needle and examined under a microscope for mesothelioma cells. This procedure is known as a diagnostic peritoneal tap. If the fluid collection in the abdomen due to peritoneal mesothelioma is causing symptoms like abdominal pain or respiratory difficulty due to a bloated and tense abdomen then also we can aspirate fluid from the abdomen to relieve the symptoms. This is called a therapeutic tap in peritoneal mesothelioma.
The investigations used for the diagnosis of peritoneal mesothelioma are also used for the staging of the disease. Staging helps us to objectively quantify the spread of the cancer in the body.
Parcentesis in peritoneal mesothelioma is both diagnostic and therapeutic
Treatment of Peritoneal Mesothelioma
The treatment regimen a patient receives is determined by-
- Extent of the spread of the disease as described by its stage.
- Age and fitness of the patient at diagnosis.
-
Patient and his family's decision regarding the treatment options available.
Surgery
DEBULKING SURGERY
Peritoneal mesothelioma is mostly discovered at an advanced stage which means it has already spread throughout the body. So the surgical option aims at debulking or reducing the size of the tumour. This will help in reducing the pressure symptoms the tumour causes by its mass effect on the other vital organs. It can help in preventing the further spread of the tumour but is mostly done as a palliative treatment. A palliative treatment aims at reducing the patient's suffering and improving the quality of life, but it cannot cure the disease.
PERITONECTOMY Or CYTOREDUCTIVE SURGERY
In a few patients where the cancer is not in an advanced stage an operation known as peritonectomy or cytoreductive surgery is done. In this operation the surgeon will remove parts of the peritoneum from which the peritoneal mesothelioma tumour arises. Here the aim is to completely remove the tumour from the body and increase the life expectancy of the patient.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a way to treat cancers where a anti-cancer drug is given to kill or shrink the cancer cells of the peritoneal mesothelioma. The basic aim is to keep this tumour under control. The anti-cancer drug may be injected through a vein. This needs to be done weekly or every two to three weeks over a period of time.If the anti-cancer drugs are injected directly in the abdomen it is called intra peritoneal chemotherapy for peritoneal mesothelioma
It may be used as the sole treatment for peritoneal mesothelioma or it may be used in combination with surgery both in the intraoperative and postoperative period.
HIPEC
It is heated intraoperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC). The chemotherapy drugs are heated to 42°C and inserted in the abdomen for 60-90 minutes during the operation.
EPIC
It is early postoperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy given in the postoperative period. Ii is directly delivered in the abdomen through a thin tube.
Palliative Care
This type of treatment does not intend to cure the peritoneal mesothelioma and is meant for alleviating the pain and suffering of people with terminal illness.
It includes paracentesis, debulking surgery and chemotherapy.
Questions What Should I Ask My Doctor About Peritoneal Mesothelioma
What is the treatment plan for my disease and why?
How long should I undergo treatment?
How will it affect my daily routine?
How much the treatment cost?
Am I likely to have pain from mesothelioma?
Is there a risk of developing peritoneal mesothelioma among other members of my family?
What are the risks and possible side effects of both surgery and chemotherapy for peritoneal mesothelioma?
Can I claim compensation for my disease?
Conclusion
Peritoneal mesothelioma is a rare disease with atypical clinical presentation. So it is often diagnosed late and in advanced stages. For the treatment of the disease surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy is the only option.
References
- Welch LS, Acherman YIZ, Haile E, et al. Asbestos and peritoneal mesothelioma among college-educated men. Int J Occup Environ Health 2005;11:254-8
- Yang H, Bocchetta M, Kroczynska B, et al. TNF-alpha inhibits asbestos-induced cytotoxicity via a NF-kappaB-dependent pathway, a possible mechanism for asbestos-induced oncogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006;103:10397-402.
- Pott F, Ziem U, Reiffer FJ, et al. Carcinogenicity studies on fibres, metal compounds, and some other dusts in rats. Exp Pathol 1987;32: 129-52.
- Shatos MA, Doherty JM, Marsh JP, et al. Prevention of asbestos induced cell death in rat lung fibroblasts and alveolar macrophages by scavengers of active oxygen species. Environ Res 1987;44:103-16
- Shivapurkar N, Wiethege T, Wistuba II, et al. Presence of simian virus 40 sequences in malignant mesotheliomas and mesothelial cell proliferations. J Cell Biochem 1999;76:181
- Cell death in rat lung fibroblasts and alveolar macrophages by scavengers of active oxygen species. Environ Res 1987;44:103-16.
- Moyer VD, Cistulli CA, Vaslet CA, et al. Oxygen radicals and asbestos carcinogenesis. Environ Health Perspect 1994;102(Suppl 10): 131-6.
- Chahinian AP, Pajak TF, Holland JF, et al. Diffuse malignant mesothelioma. Prospective evaluation of 69 patients. Ann Intern Med 1982;96:746-55
- Acherman YIZ, Welch LS, Bromley CM, et al. Clinical presentation of peritoneal mesothelioma. Tumori 2003;89:269-73.