Prostate Cancer Facts

Prostate Information
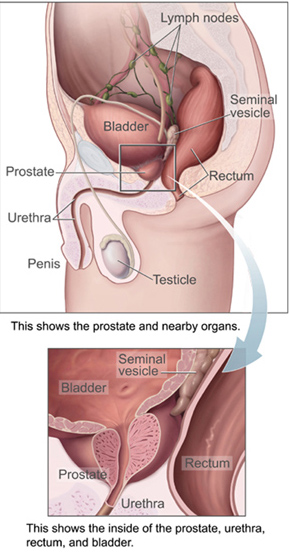
A man’s prostate is a small gland that is shaped like a small walnut. It is located between the bladder and the penis, just in front of the rectum. It produces seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. A prostate exam is usually done on a man of fifty years of age. If there is a family history of prostate cancer an exam may be performed as early as forty years of age.
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men. It is typically a slow growing cancer and it is initially confined to the gland. If the cancer is growing slowly it may only need minimal or sometimes no treatment. There are some aggressive types of cancer that spread quickly. The earlier any cancer is detected the better the chance for successful treatment. By age 80 roughly half of all men have prostate cancer. African American men tend to be diagnosed at a younger age.
Symptoms of Prostate Problems
There are some specific symptoms that occur when there is an infection or cancer in the prostate, including:
- Getting up several times at night to urinate
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Pain or burning with urination
- Painful ejaculation
- Frequently having pain or stiffness in the lower back, hips, pelvic or rectal area or in the upper thighs
Prostate Examination
A prostate exam will help your doctor (typically a urologist) diagnose an inflamed or an enlarged prostate. The exam usually involves:
- Digital rectal exam (DRE) where the doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to examine the prostate.
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, which is a blood test that is analysed for PSA for higher levels in the blood. Higher levels can mean infection or cancer.
- Dribbling of urine
If there is an abnormality in the DRE or lude:PSA test there are other types of tests that may be ordered, and they include:
- A transrectal ultrasound may be ordered, which means a small probe will be inserted into the rectum that uses sound waves to create a picture of the prostate gland.
- A collection of prostate tissue, which is a procedure done with a thin needle to collect tissue that will be analysed in a lab.
- MRI fusions are being increasingly used as they assist in a prostate biopsy.
Mayo Clinic leverages MRI-TRUS fusion technology that fuses images from an MRI scan and a transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) creating a very precise 360-degree prostate may that improves the accuracy of a prostate biopsy.
The first medical center in the U.S. approved to use C-11 choline PET scanning to help detect recurrent prostate cancer was Mayo Clinic. This scan allows for more precise targeting of cancer cells and it allows for faster follow up treatment.
Signs and Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer Treatment
When a man is diagnosed with prostate cancer the first thing is to determine the level of aggressiveness of the cell. Depending on the patient’s age a decision will be made as to what treatment is appropriate. If the cells are not very aggressive and the man is elderly no treatment may be warranted.
The Gleason score is used to grade the cells. The Gleason score ranges from 2 to 10. A score between 8 and 10 is a very aggressive cancer. A score of 2 is a nonaggressive cancer. Additionally, genomic testing is being used more often to get a more accurate risk assessment and to detect aggressive cancers.
Radiation is the most common type of prostate cancer treatment for early diagnoses. Three types of radiation used to treat cancer include:
- External beam radiation therapy
- Brachytherapy (internal radiation)
- Combination of external beam therapy and brachytherapy radiation
If surgery is required, then the prostate gland and some surrounding tissue is removed, along with a few lymph nodes. There are many ways to perform a radical prostatectomy. A robot assist may be used where instruments are attached to a mechanical device (robot) and this is inserted through the abdomen using several small incisions. The surgeon is sitting at a console and uses hand controls to guide the robot. The prostate gland may be removed through an incision in the lower abdomen.
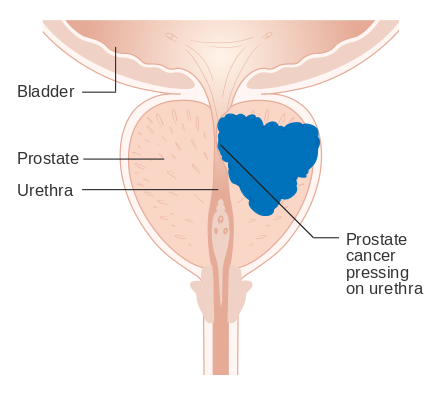
Prostate Pressing on Uretha
Testing for Aggressive Cancers
Once the stage of the cancer is determined a doctor may recommend further tests if the cancer is aggressive and if the doctor suspects the cancer has spread beyond the prostate. Some of the possible testing include:
- Ultrasound
- Bone scan
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: What to expect
Risk Factor For Prostate Cancer
The primary risk factors for prostate cancers are:
- Age
- Family history
- Obesity
- Age above 70 years
Conclusions
Prostate cancer in men over 50 years is the most common when there is a family history. Sometimes the cancer is not aggressive and if the man is older there may be no surgery or other treatment required. Any aggressive cancer receives treatment. The tests for prostate cancers are very good at identifying an aggressive versus a non-aggressive cancer. Prostate cancer is more easily diagnosed than it once was and the treatments are very good.
References
This content is accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge and does not substitute for diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, prescription, and/or dietary advice from a licensed health professional. Drugs, supplements, and natural remedies may have dangerous side effects. If pregnant or nursing, consult with a qualified provider on an individual basis. Seek immediate help if you are experiencing a medical emergency.
© 2020 Pamela Oglesby