Proteus And Escherichia Coli Infections: Clinical Presentations, Diagnosis And Treatment
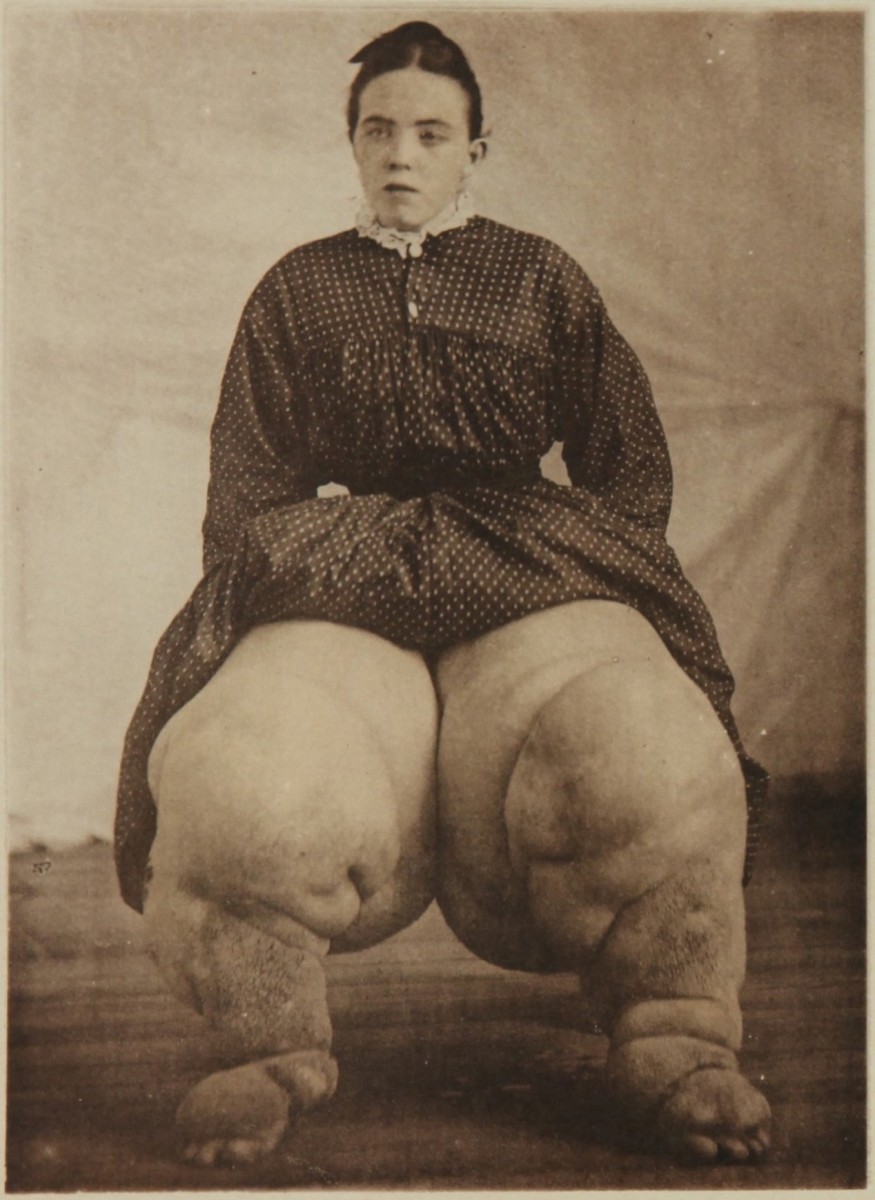
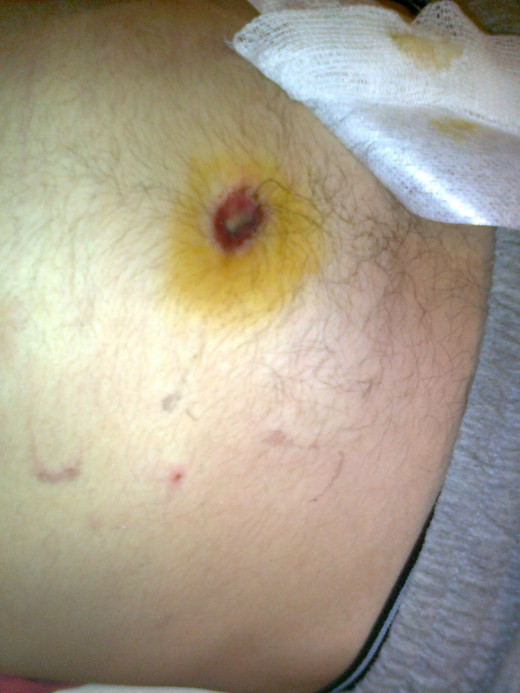
Omphalitis: A Common Proteus Infection
Proteus Infections
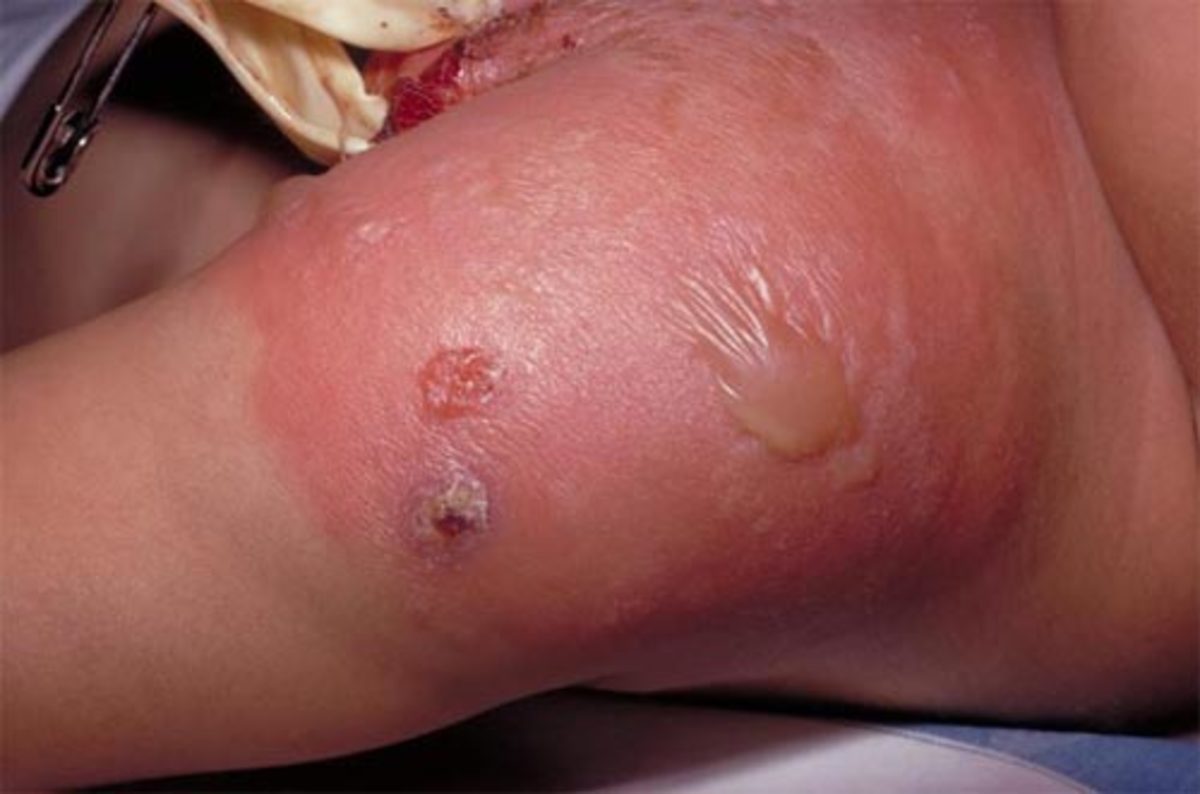
The genus proteus has four species which are pathogenic to man: P. mirabilis, P. vulgaris, P. morganii and P. rettgeri. Proteus mirabilis is the most common species, accounting for 70 to 90% of the total. The organisms are widely distributed in nature in the soil, water and in the intestinal tract of man and animals. They may cause superinfection in areas of tissue damage, especially in subjects treated with antibiotics. Exudative inflammatory lesions are produced.
Common sites of infection are skin, ears, mastoid, sinuses, eyes, peritoneal cavity, bone, urinary tract, meninges, lungs and blood stream. Urinary tract infection is the most frequent and it is more common in obstructive uropathy, urolithiasis and diabetes. The normal urinary tract is seldom infected. Proteus infection makes the urine alkaline. Since it splits urea to release ammonia. Blood stream invasion may result from the primary lesions. Urinary instrumentation may trigger off bacteremic spread. Bacteremia leads to high fever, chills, rigor and metastatic abscesses and these are indistinguishable from those of other bacteremias. Blood may show leukocytosis and rarely thrombocytopenia. Endotoxic shock is particularly common.
In the newborn, the umbilical stump may be colonized by proteus which may lead to bacteremia and septic meningitis.
Diagnosis: It is established by isolating and identifying the organism from urine, blood or local lesions.
Treatment: Proteus mirabilis is sensitive to high doses of penicillin, ampicillin, kenamucin, gentamicin, chloramphenicol and cephalosporins. Ampicillin in a dose of 0.5g every 6 hours is quite effective in the treatment of urinary infections.
Antibiotic combinations are necessary for treating bacteremia and other systemic infections. Ampicillin, 6 to 12g + kanamycin 15 mg/Kg/day or penicillin G, 20 mega units + gentamycin 5mg/Kg/day are quite effective in most of the cases.
Treatment Of Escherichia Coli Infections (E.Coli)

Infectious Diseases
Escherichia Coli Infections (E.Coli)
Escherichia coli belongs to the group Enterobacteriaceae and it is found as a commensal in the intestinal tract of normal man. When the normal anatomical and immunological barriers are disrupted, it spreads to other areas to produce local lesions and bacteremia.
Epidemiology: Classification of the strains of E.Coli is based on their somatic (O), flagellar (H) or the capsular (K) antigens. All the strains are capable of producing disease in man. Some strains produce endotoxins which is responsible for diarrhea in infants and adults. Infection may spread directly to other regions from the bowel-lumen from the upper respiratory tract by aspiration, or by fecal oral contamination. The organisms may enter the blood stream from these primary sites. Invasion is predisposed to be debility, recumbency and prolonged antibiotic therapy. In the newborn, fecal contamination and lack of maternal antibodies favour infection. Escherichia coli produces suppurative lesions. In most situations, the bacterial flora is mixed and bacteroids and other anaerobic organisms give a fecal odour to the exudates.
Clinical presentations:
- Urinary tract infections
- Peritonitis
- Septicemia
- Neonatal infections: Bacteremia and meningitis
- Biliary tract disease: Ascending cholangitis, cholecystitis, rarely septic thrombophlebitis (pylephlebitis) of the portal veins and pyogenic abscesses in the liver.
- Gastroenteritis: Outbreaks of gastroenteritis in children’s nurseries may be due to enterotoxigenic strains of E. coli (ETEC). They produce a toxin which causes diarrhea. Dehydration and electrolyte depletion occur early and the condition carries a heavy mortality. Escherichia may cause diarrhea in new immigrants and travelers who use contaminated good and water (traveller’s diarrhea).
Other lesions: Escherichia coli may produce abscesses in various tissues. Gas formation occurs in tissues and this gives rise to creptius. Pyemia occurs due to hematogenous spread. Osteomyelitis, meningitis and brain abscess occur metastatically.
Laboratory diagnosis: It is based on the isolation of E.Coli in cultures obtained from suitable materials. The infection produces neutrophil leukocytosis.
Treatment: Sulfonamides, ampicillin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, aminoglycosides, polymyxin-B, cephalosporins, cotrimoxazole, nitrofurantoin and nalidixic acid are all effective. Urinary tract infection may be treated with sulfonamides, but serious systemic illness requires parenteral ampicillin in high doses even up to 150 mg/Kg body weight per day. Abscesses have to be incised and drained.
Prevention: Since E.Coli infections in adults are nosocomial, their incidence can be reduced by restricting the use of indwelling catheters, isolation of infected patients and judicious use of antimicrobial agents. As Escherichia coli transfers the resistance to antibiotics to other enteric bacterial like Salmonella through “R” factors, the extensive and indiscriminate use of multiple antibiotics for diarrheal diseases should be avoided.
© 2014 Funom Theophilus Makama