Sunburn Basics: Red Skin After the Fun
How much do you know about sunburn?
It’s not enough that you wear a cap outside. The sun with all its might can burn your skin even before you realize it. Sunburn is often regarded as a minor skin reaction to sunlight. But the fact is excessive exposure to sunlight is dangerous. In excessive exposure to Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the leading cause of non-malignant skin tumors. Furthermore, the risk of melanoma increases when the person gets more than 5 sunburns in his lifetime. Statistics show that 42% of people get sunburn at least every year. This is surprising considering the amount of sunburn products in the market.
What is sunburn?
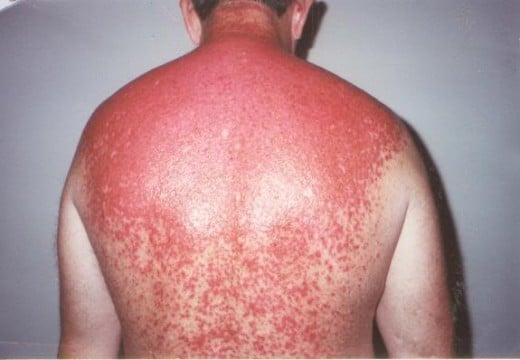
Sunburn or erythma is the one of the most visible signs of exposure to UV radiation. Once UV touches your skin, it damages the outermost layer of the skin (epidermis). This is when redness kicks in. As the body tries to repair itself, white blood cells remove damaged skin cells and new ones are produced. In the process, the affected area may feel itchy and will peel.
Though the most common cause of sunburn is sun light, other artificial UV sources also cause this skin damage. Tanning lamps, welding arcs and UV germicidal irradiation are artificial sources of UV light that can result in sunburn after excessive exposure.
Signs of sunburn
Skin becomes red, swollen and warm to the touch. Contrary to popular belief, the skin turns red not because your skin gets burnt. Rather, the immune system of the body kicks in and sends blood and antibodies to the affected area. This also causes the sunburned area to feel warmer to the touch. In addition, sunburn-damaged skin may be painful. This is due to the damage to the skin. Some individuals may also feel fatigued, or even dizzy depending on the extent of their burn.
Treatments for Sunburn
According to the AmericanAcademy of Dermatology (AAD) mild sunburn can be treated with cold baths. This will help soothe the affected area. Hydrocortisone creams can also help the skin heal faster but do be cautious with the topical preparations that you use. Some ingredients may do you more harm than good. For the pain and swelling, over-the counter pain reliever or aspirin can be used.
However, if the burn is more severe, the person must be brought to the hospital at once and must be treated as an emergency. Blistering, fever and headaches usually accompany severe sunburn. Severe sunburn treatment MUST be left to the medical professionals. Don’t use any home sunburn remedies in such cases.
Sunburn Tips
- Use sun block whenever you go out SPF of 15 is good enough but higher is better
- Reapply sun screen every 2 hours or as instructed
- Use appropriate clothing and accessories like hats and caps
- Avoid direct sunlight (especially from 10 AM to 4 PM)
- Moisturize your skin regularly to avoid dryness
- Use medically approve sunburn products
- Pat dry your skin rather than rubbing a towel
- Don't just put topical creams for pain
Exposure to sunlight is inevitable. Moreover the effects of UV radiation compounds every time you get exposed to the sun. More than just protecting yourself from the heat, you should protect your self from the effects of the harmful radiation.