Thoracic Outlet Syndrome #3 - Treatment 1
Introduction
The treatment of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome is almost similar to that for Cervical Discogenic Syndromes. Anyway the treatment depends upon the underlying pathology. The treatment of patients suffering from Thoracic Outlet Syndrome may be listed as follows.
- Rest
- Medications for the symptoms.
- Medications if there is Vessel Involvement.
- Surgical Intervention.
- Application of Cold or/and Heat Modalities.
- Immobilization.
- Mobilization.
- Scapular Exercises.
- Cervical Traction.
- Postural Corrective Exercises.
- Strengthening Exercises.
- Stretching of Pectoral Muscles.
- Guidance on Activities of Daily Living.
- Psychological Intervention.
- Breathing Exercises
1. Rest
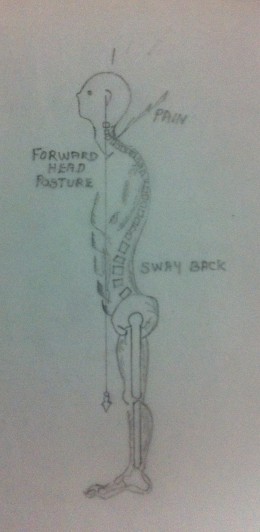
When the pain is acute, rest is very essential. Rest, in the strict sense, means avoiding or minimizing any activity that may aggravate the symptoms. Avoiding or minimizing activities like excessive driving, carrying out excessive work at the computer, improper way of doing activities of daily living or any activity that may aggravate the symptoms are desirable. Bed rest or reclining in a comfortable may be helpful to reduce the intensity of the symptoms. Keeping the head in a comfortable position may relieve the symptoms to certain extent. While on supine lying avoid pillows and use a small pillow under the head while side lying so that hanging down of head may be prevented. Sleeping on the stomach must be avoided because it can lead to hyper abduction syndrome initiating the symptoms of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome.
Medications for symptoms
Medications are given mainly to relieve the symptoms. The medicines usually prescribed are
- Non Steroid Anti Inflammatory Drugs
- Oral Corticosteroids
- Epidural Steroid Injunctions
- Muscle Relaxants
- Analgesics.
3. Medications if there is Vessel Involvement
It is estimated that about 3-5% of all Thoracic Outlet Syndrome cases are Venous in nature whereas less than 1% is Arterial in nature. From the above data it is clear that the Thoracic Outlet Syndrome due to Venous and Arterial pathology is very rare. There may be congenital narrowing or blockage of the Subclavian Vein or/and Artery. The patients with the congenital defect of narrowing of the blood vessel do have the tendency of having blood clots frequently, if the upper limbs are over used. If there is a blockage of blood vessels by a clot, treatment with medicine is urgently needed to dissolve the clot. For this purpose, Anticoagulants are used. Such treatment is continued for a period of time so that the formation of further clots may be avoided.
4. Surgical Intervention
If there is compression on the Blood Ve or Brachial Plexus, surgical intervention is needed e.g. removal of interfering Cervical Rib, repairing of mal- united or non-united Collar Bone or removal of thickened callous formation after the fracture of Collar Bone. Other surgical procedures are also done to relieve the pressure or compression on the anatomical structures that emerge through the Thoracic Outlet. Some are of the view that early surgical intervention is better than late because early intervention prevents the degeneration of the Brachial Plexus so that the effectiveness of postoperative physiotherapy is increased. But some are of the view that surgical intervention is resorted to only when there is obvious physical lesion. Sometimes there is a chance that the condition may deteriorate. Damage to the Long Thoracic Nerve or/and the Brachial Plexus is a possibility. The patient needs a well and careful appraisal preoperatively.
5. Application of Cold or/and Heat Modalities
a. Ice Application –Cryotherapy- Cryotherapy is highly beneficial in the acute stage. Usually, the pain is aggravated due to a phenomenon called protective muscle spasm. On the application of ice, the protective muscle spasm is relieved and hence the pain is also relieved. Ice is also has analgesic effect. It increases the arterial blood supply in the deep tissues. It prevents the formation of oedema. It also prevents the formation of histamine like by products. Crushed ice cubes wrapped in a thick towel is placed on the painful areas for 20 minutes. Remove the ice for 10 minutes. Again apply it for 20 minutes. This procedure is repeated twice or thrice a day. Never apply ice directly to the skin as it may cause ice burns.
b. Heat Application -Once the acute stage has subsided, heat application is preferred. As in the case of Cryotherapy, heat also relieves the protective muscle spasm and hence the pain is also relieved. It increases the blood supply .It helps in washing out the accumulated toxins and speeds up the healing process. It is more or less sedative and soothing. Even if the protective muscle spasm and the pain is relieved (either by Cryotherapy or Heat Application), they do not have any effect on the deeply situated anatomical structures. Hence suitable therapeutic exercise programs must be carried out along with Cold and Heat Application. Once Cold or Heat is applied the pain is relieved so that the exercise program may be carried out comfortably without any stress or strain. Hot water fomentation or Moist Heat is very much beneficial as it relieves the muscular spasm and the pain. Superficial Heating Modalities like Infrared Radiation (IRR) and Deep Heating Modalities like Short Wave Diathermy (SWD), Ultra Sound Therapy (UST) e. t. c. are very useful. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulater (TENS), an Electrotherapy modality is very useful to relieve pain.
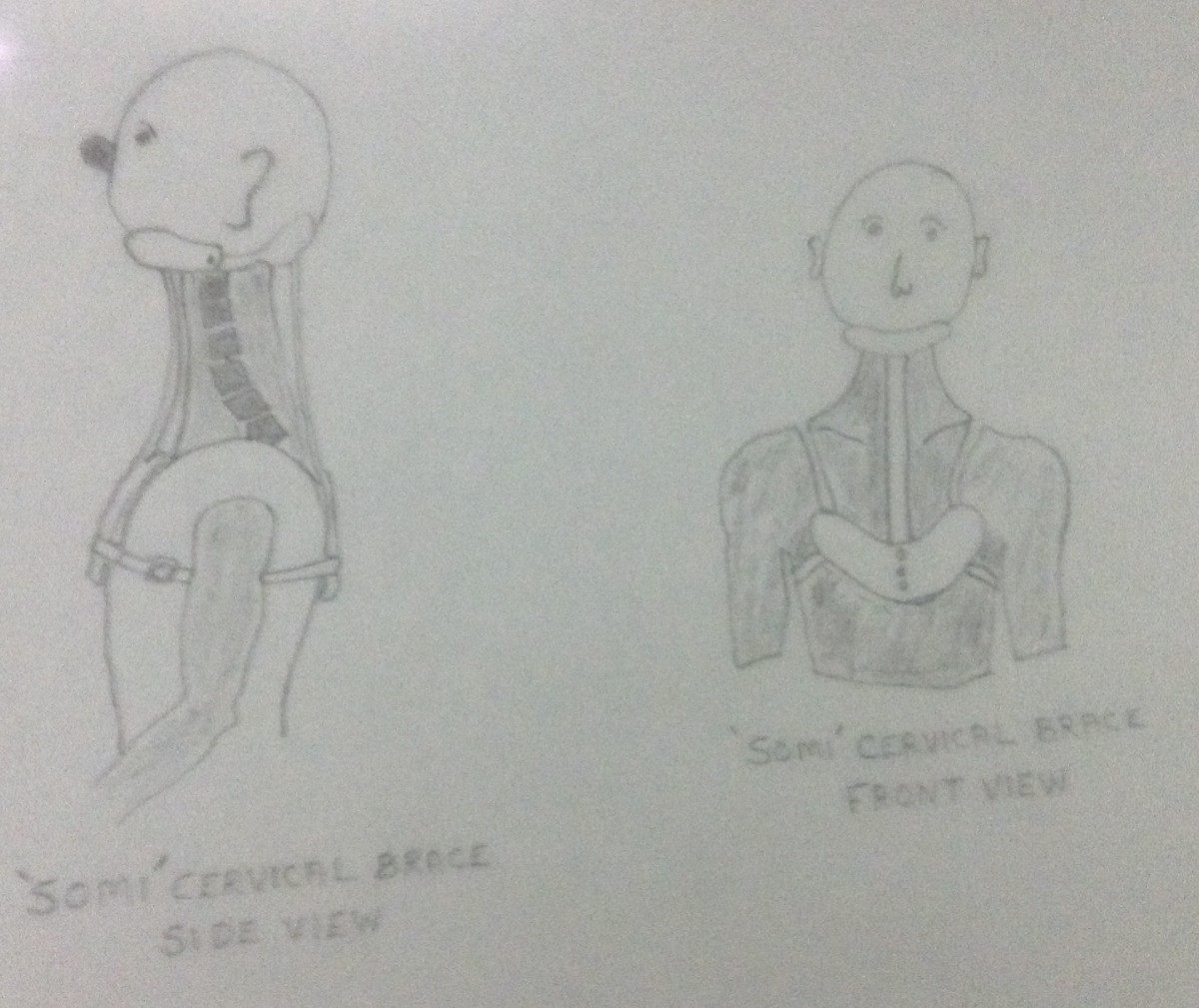

6. Immobilization
In the acute stage with severe pain a cervical collar or a cervical brace is used to immobilize the cervical spine in the normal position. Not only the cervical collar or brace immobilizes the cervical spine but it also keeps the head in the correct postural position. It places and maintains the head directly above the centre of gravity and hence it corrects the ‘forward head posture’ of the patient to some extent. It provides rest to the neck by restricting its movements in all directions. It decreases the lordosis of the cervical spine. It also gives a stretch to the cervical spine and the soft tissues around it. But prolonged use of cervical collar is contraindicated. It is to be noted that within one week of its use it becomes addictive and depending on it develops. Prolonged use may lead to the weakening of the neck muscles and limitation of movements of neck and shoulders. Hence a careful and judicious use of cervical collar or brace is very important.