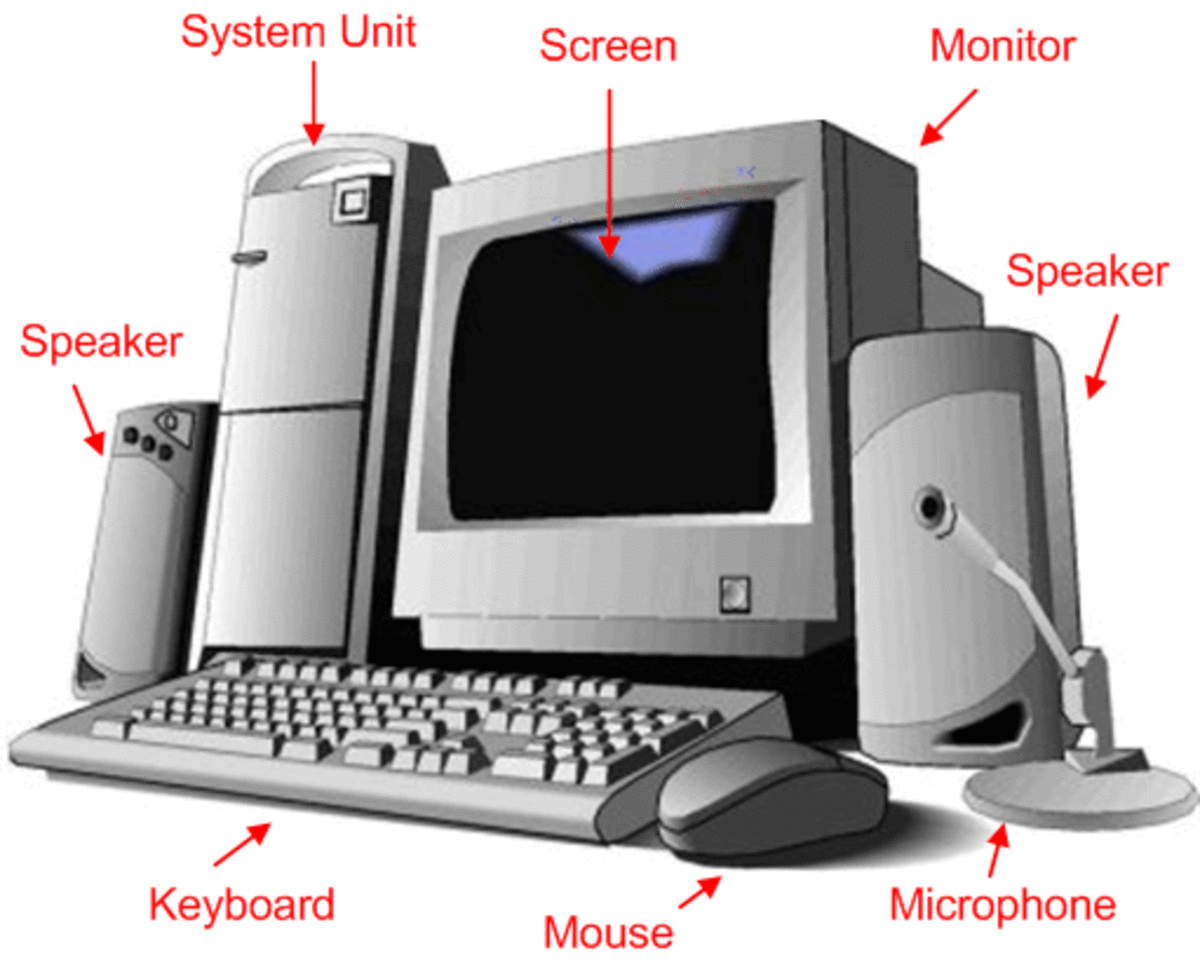
Ergonomics Tips for Computer Use

Most Hubbers spend a lot time sitting in front of a computer hammering computer keyboard and at the same time thinking critically about how best to join their words in order to come up with yet other quality, high scoring useful hub.
With long hours of computer use a number of health and safety issues related to vision, body aches and pain can arise. Problems related to prolonged use of computers are called Repetitive Strain Injuries (RSI).
This implies damage to vision, muscles, nerves, tendon or other soft tissues caused by repetitive or continuous work over a long period of time and especially where some force is applied however minimal it is for example in typing. To prevent RSI, computer users should apply and follow the laws and principles of working with computers otherwise called Ergonomics.

RSI are preventable and when they occur they can be solved by corrective measures. However, Hubbers should not ignore such problems and should seek immediate medical attention if such problems persist. Problems related to prolonged use of computers can be:-
- Experiencing discomfort
- Stiffness
- Pains and aches
- Eye strain
- Numbness
- Eye watering
Most hubbers will experience nearly all the above mentioned problems and you might not be aware until you change the siting position or the discomfort become too much. If you are working for long periods with a small sized computer that has a small screen chances of eye strain, fatigue, double vision and eye watering are high. Eye strain can eventually lead to pains and aches and when this happen individual productivity is reduced.
Ergonomics Tips For Computer Use
So how can we reduce or eliminate computer related health problems? Computer users should practice proper Ergonomics all the time. Here are such practices:-
- Always position computer monitor in such a way as to minimize glare and reflection on the screen when you are working. The room should have adequate light, reflection from the window can be avoided by turning the monitor to a different location or by use of blinds or curtains
- Take regular breaks from typing, working or using the computer at least a few minutes in an hour. Use the breaks to relax, take a glass of water or just stretch your muscles and body in general. Don’t take breaks because you have fatigue already instead take breaks at regular intervals.
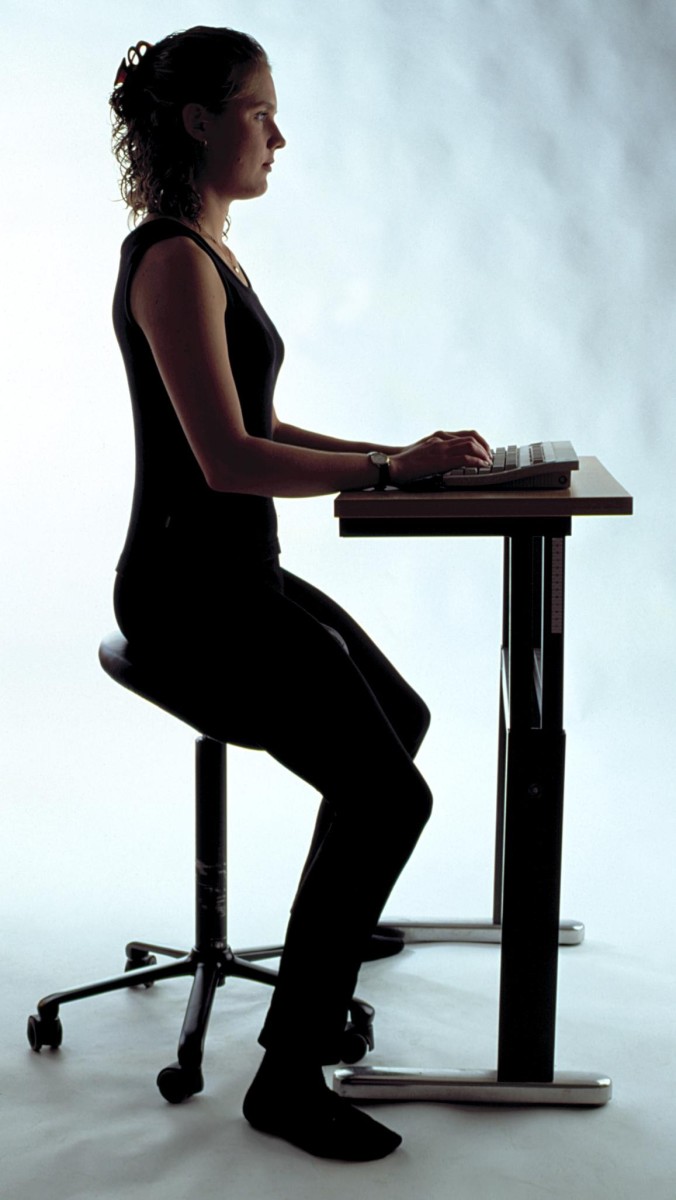
- A good posture and technique when using the mouse and keyboard is important. Relax and keep your body at a relaxed position without over stretching your wrist or fingers. It is recommended that forearms should be at the same level with the mouse and keyboard.
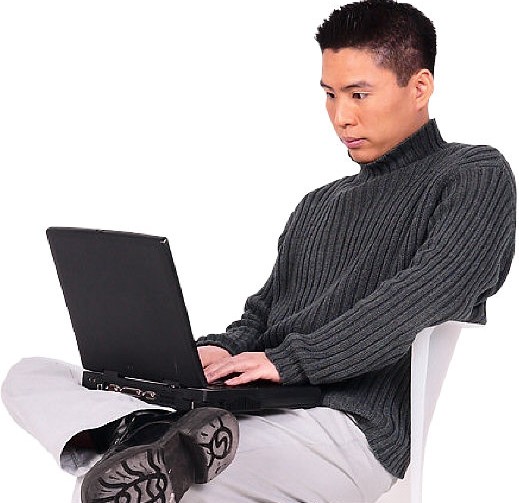

- Organize your work place such that the items you require frequently are closest to you and that you don’t have to over stretch reaching for them.
- Only place your hand on the mouse when you are using it and when you are not place your hands else where for example on your lap or better still do some hands and fingers exercises.
- Apply only the necessary pressure on the mouse. Avoid gripping the mouse too tightly and if you can, practice how to use the mouse with your opposite hand.
- Don’t receive telephone calls by placing the handset between your ear and shoulder while working as this can strain your shoulder and neck muscles. If you do receive frequent calls while typing or working on a computer it is a good idea to use telephone headsets.
- If your bifocal glasses are causing you to tilt backward in order to view the computer screen you may strain your shoulder and neck muscles. Get Optometrist advice about this, you may find that there are a number of options available.
- Adjust the chair position so that you have a comfortable view of the computer screen while maintaining a good comfortable sitting posture. Support yourself by use of footrest, armrest and a backrest that is self-adjustable to the back movement.
- The working area and furniture should provide enough space to work on and enough leg room.
- Learn and familiarize yourself with as many keyboard shortcuts as possible for your frequently used tasks to minimize overuse of the mouse.
- You can reduce eye strain by alternating between tasks for example between typing and proofreading.
This list of practices is not exhaustive. Following proper Ergonomics can go a long way in improving our productivity and quality of work, reduce injuries and increase satisfaction in our work. Apply proper working practices and eliminate RSI.