Treatment And Prophylaxis Of Herpes Genitalis And Health Implications Of Genital Warts And Molluscum Contagiosum
Urinary Retention In Herpes Genitalis

Treatment and Prophylaxis
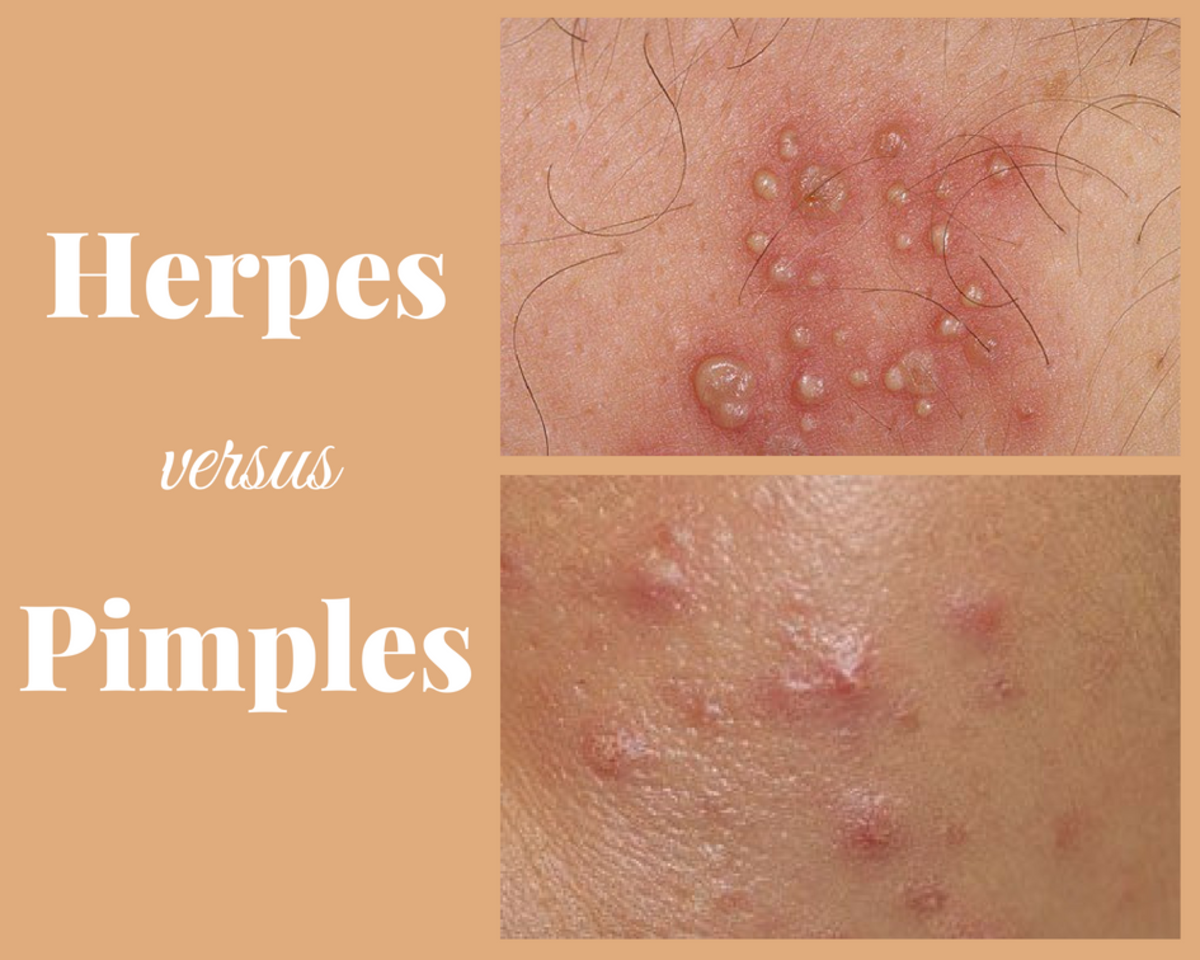
Antiviral drugs have been tried. Iodoxuridine dissolved in dimethyl sulphoxide has been used for local application, but the results are poor. Other newer drugs like vidarabine given intravenously in a dose of 5 to 15 mg/Kg/day for 10 days or acyclovir 5 mg/Kg given intravenously every 8 hourly for 5 days is effective.
Urinary retention has to be treated on the usual lines. Infection with herpes virus during pregnancy may lead to affection of the baby during birth. Close follow up is necessary. If the mother develops primary attach of herpes genitalis after the 36th week of pregnancy, caesarian section is advocated before the rupture of the membranes to avoid infection of the baby.
Warts Prevail In Condyloma Acuminata

Molluscum Contagiosum Is A Viral Infection
Genital Warts (Condyloma Acuminata)
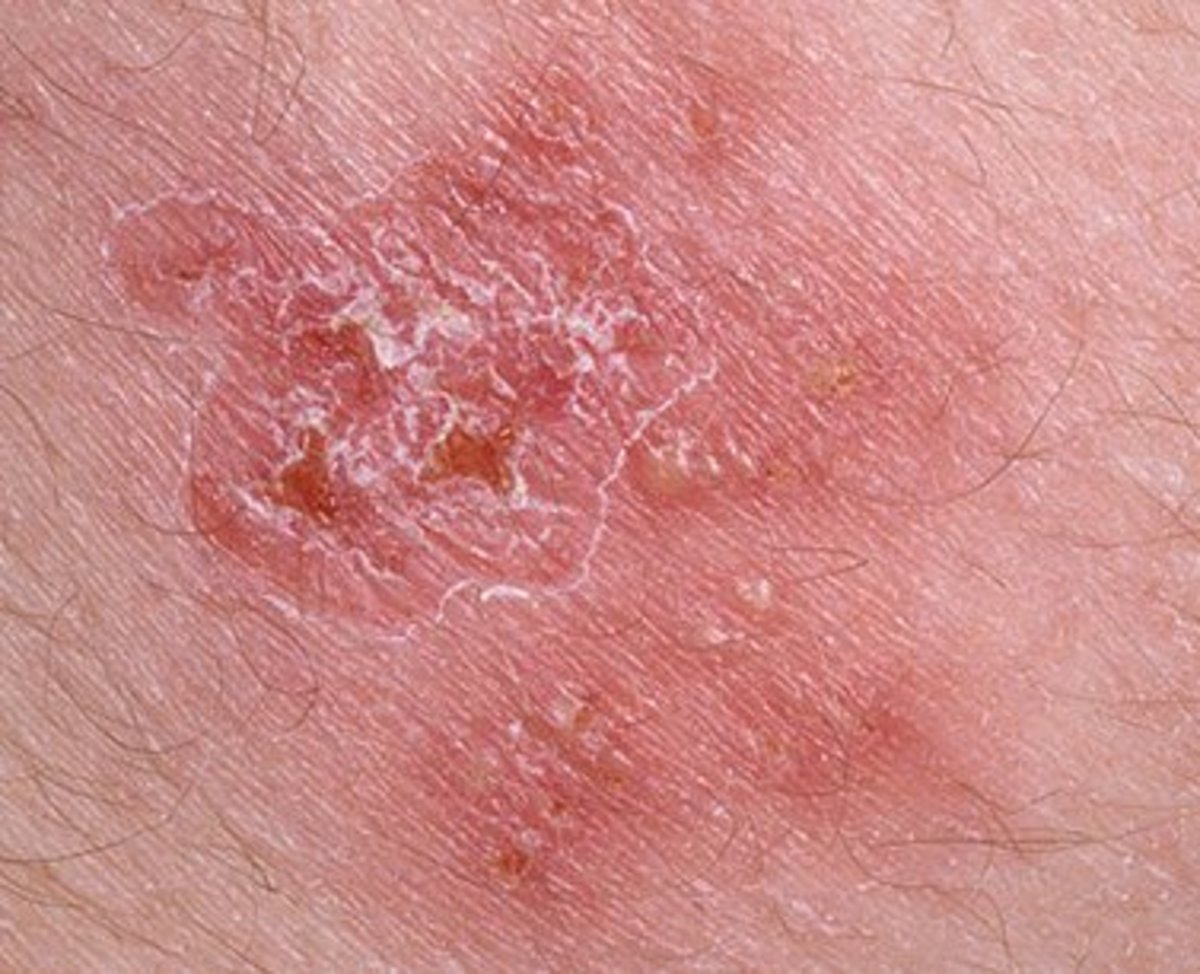
Genital warts are benign growths of the skin and adjacent mucous membrane, caused by the papilloma virus serotype 6. Majority of cases of genital warts are sexually transmitted. Though usually, the incubation period is two to three months. It may be up to a year in some cases.
Clinical features: Warts are commonly seen on the moist surfaces of the male and female genitalia, especially the coronal sulcus, glans penis, frenum and shaft of the penis in the male and posterior part of the introitus, labia majora, labia minora and clitoris in the female. Warts may develop in the urethral meatus and the cervix, even if warts are not seen there. In females, the genital warts enlarge during pregnancy and regress during the puerperium.
Treatment: No specific treatment is effective in eliminating the wart virus and therefore recurrences are frequent. At presence, the only treatment is removal of the warts by using podophyllin resin 10 to 25% in spirit or tincture of benzoin. Podophyllin can be toxic and is possible carcinogenic. It should not be used during pregnancy. The warts can be cauterized under local anaesthesia, using electro-coagulation. Cryotherapy with nitrous oxide or dry ice has been used. Large warts are removed surgical.
Infectious Diseases
Molluscum Contagiosum
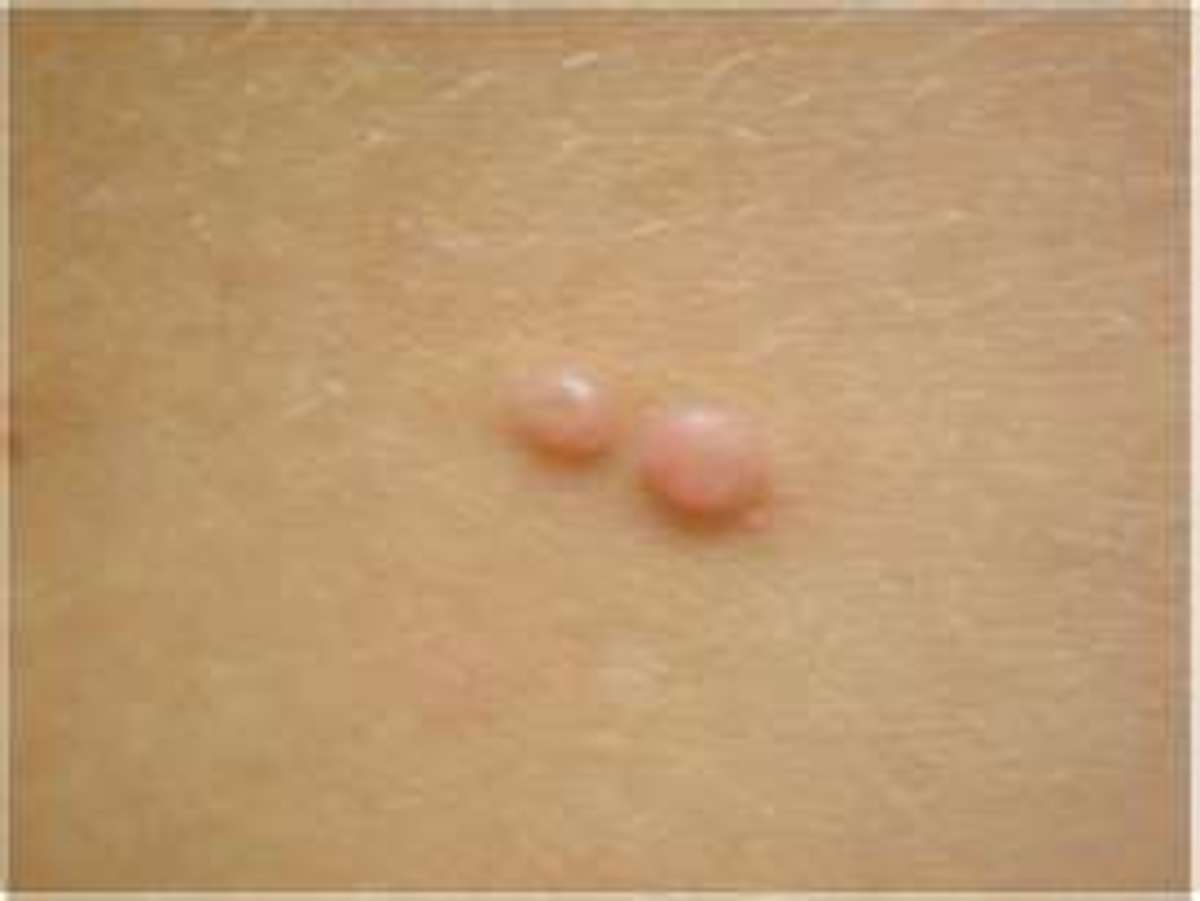
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral disease which can be transmitted from person to person by sexual or nonsexual contact. The latter is more common. Lesions may develop on any part of the skin. The incubation period varies from 3 weeks to several months. The sexually transmitted lesion develops on the genitalis. The lesions are papular, ranging in size from 2 mm to 1 cm. waxy and pale pink with central depression.
Treatment: Local application of pure phenol or concentrated trichloracetic acid by a sharpened matchstick will destroy the virus. Electrocoagulation is also useful.
© 2014 Funom Theophilus Makama