Trichinosis: Health Implications, Morphology And Lifecycle, Diagnosis, Treatment And Prevention
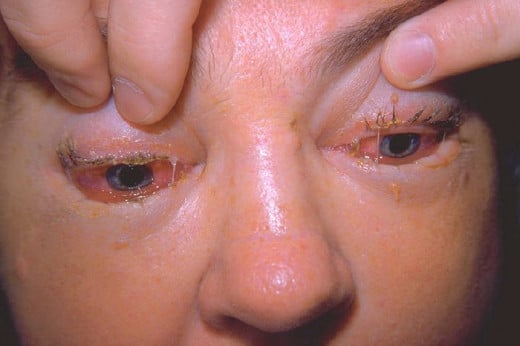
Trichonosis Manifestation On The Eye
Trichinosis (Trichiniasis, Trichinellosis)
This is only rarely seen in India. Trichinellosis is caused by Trichinella spiralis, a nematode parasite of several animals such as the rate, pig, polar bear, etc. Man gets infected when meat containing infective larvae is ingested without proper cooking. The disease has been reported from many parts of Europe, North and West USA, African countries and China. Man usually gets infected by eating partially cooked pork sausages.
The pig acquires infection by eating infected rats or the offal of infected pigs. Both adults and larvae are seen in the same hosts, but two hosts are required to complete the lifecycle.
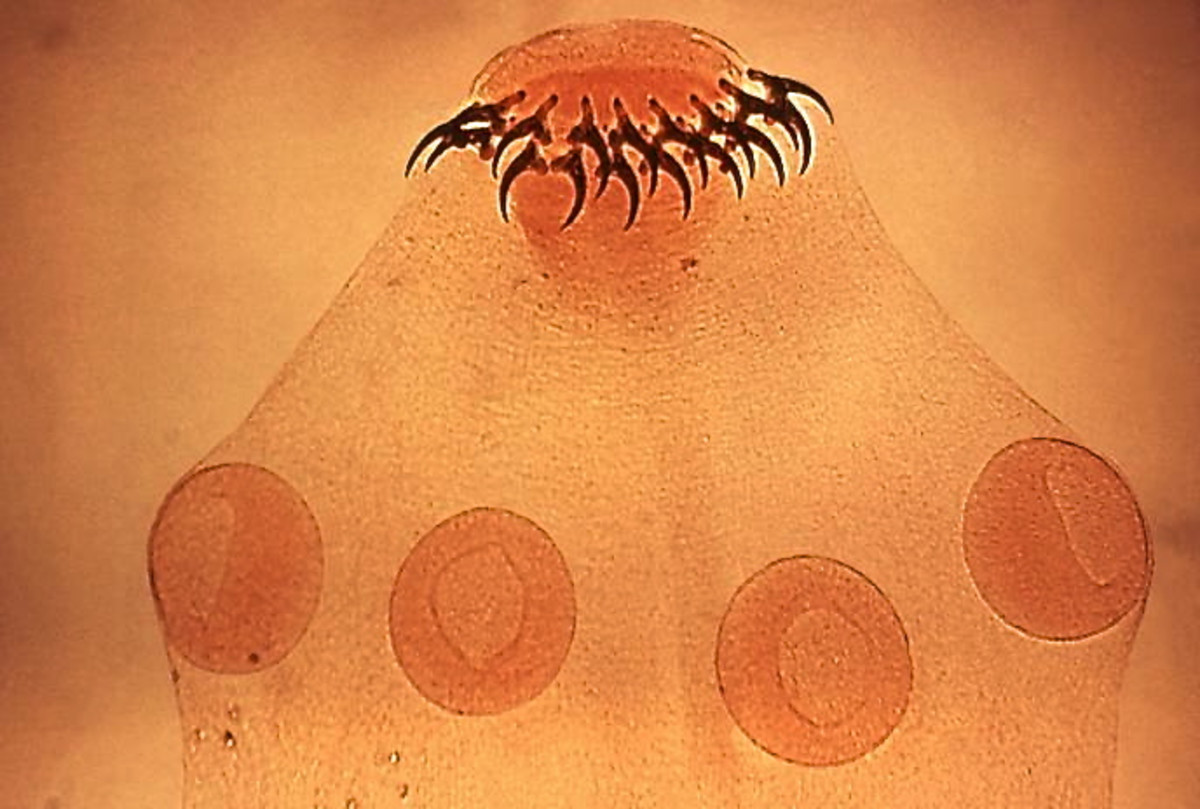
Morphology and lifecycle: It is the smallest nematode affecting man, the adult female varies in size from 3 to 4 mm to 40 to 60 mm. The male is only half this length. When meat containing viable larvae is ingested, the larvae escape in the intestinal lumen, penetrate the mucosal cells of the duodenum and grow into adults in 5 to 7 days. After fertilization, the female discharges larvae into the circulation and the larvae get embolized to many tissues, those reaching the muscles encyst themselves in an oval capsule measuring 0.8mm, grow, mature and become infective after 16 days. They remain viable for 6 months and thereafter die and become calcified. Each female may liberate 1000 to 1500 larvae during its lifespan. The male lives for about a week, while the female lives for 3 to 16 weeks. Intercostal muscles, pectoral muscles, diaphragm and shoulder girdle muscles are heavily affected.
Clinical Manifestations Of Trichinosis
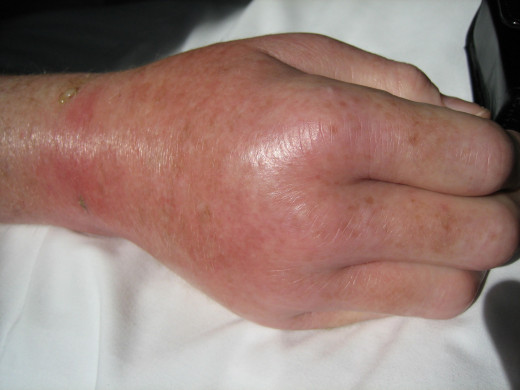
Symptoms depend upon the heaviness of infection. Mild infection may be asymptomatic. Within the first 1 to 2 days after ingestion, fever, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea may develop. Larval dissemination starts around the seventh day and is marked by urticarial rash, remittent fever, edema of the eyelids, conjunctivitis and subungual splinter hemorrhages. Neurological manifestations include polyneuritis, Polio-like paralysis, myasthenia, meningo-encephalitis and psychosis. The CSF does not show any abnormalities. Myocarditis may occur. This is characterized by persistent tachycardia and congestive failure. In 20% of cases ECG shows ST-T wave changes and conduction defects.
Laboratory findings: Eosinophilia is a constant finding in the early stages.
Skin Manifestation Of trichinosis
Infectious Diseases
Diagnosis Of Trichinosis (Trichiniasis, Trichinellosis)
A skin test using the larval antigen is available, which remains positive for even up to 20 years after infection. Precipitin test, complement fixation test, the indirect fluorescent antibody test, bentonite flocculation test and other serological tests are available. Muscle biopsy from the deltoid or gastrocnemius shows encysted or calcified larvae and evidence of myositis.
The acute stage of larval migration has to be differentiated from other conditions characterized by allergic manifestations and muscular pains such as dermatomyositis, other forms of polymyositis, polyarteritis nodosa, serum sickness and food-poisoning.
Treatment, Control And Prevention
Treatment and control: Thiabendazole in a dose of 25 mg/Kg given twice daily for 5 to 7 days gives relief in symptomatic cases. The drug given in a dose of 50 mg/Kg per day in divided doses for two days kills the adult worm. Anti-histamines, corticosteroids and analgesics may be required for obtaining symptomatic relief. The overall mortality is around 2%.
Prevention: The larvae in meat can be destroyed by proper cooking or deep freezing at -180C for 24 hours.
© 2014 Funom Theophilus Makama