Type 2 Diabetes - What Is It?
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 Diabetes or T2D used to be called adult onset diabetes. However, it can no longer be called that since our modern sedentary lifestyle and poor diet is resulting in increasing numbers of teens being diagnosed with the condition. However, the odds that someone will develop Type 2 diabetes do go up with age. Our tendency to lose muscle mass and slow down around age 45 is why they say that is the point your risk starts to rise significantly.
But what exactly is T2D? Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder where the body loses its ability to respond to insulin. The body slowly loses its ability to properly respond to insulin, until it stops producing or responding at all. Type 2 diabetes does include cases where the body isn’t producing enough insulin, but because the cells are essentially burned out, not destroyed. It is in stark contrast to the auto-immune condition that defines Type 1 diabetes. In Type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system destroys the pancreas, so the body literally lacks the ability to create insulin because it killed the only cells capable of producing it.
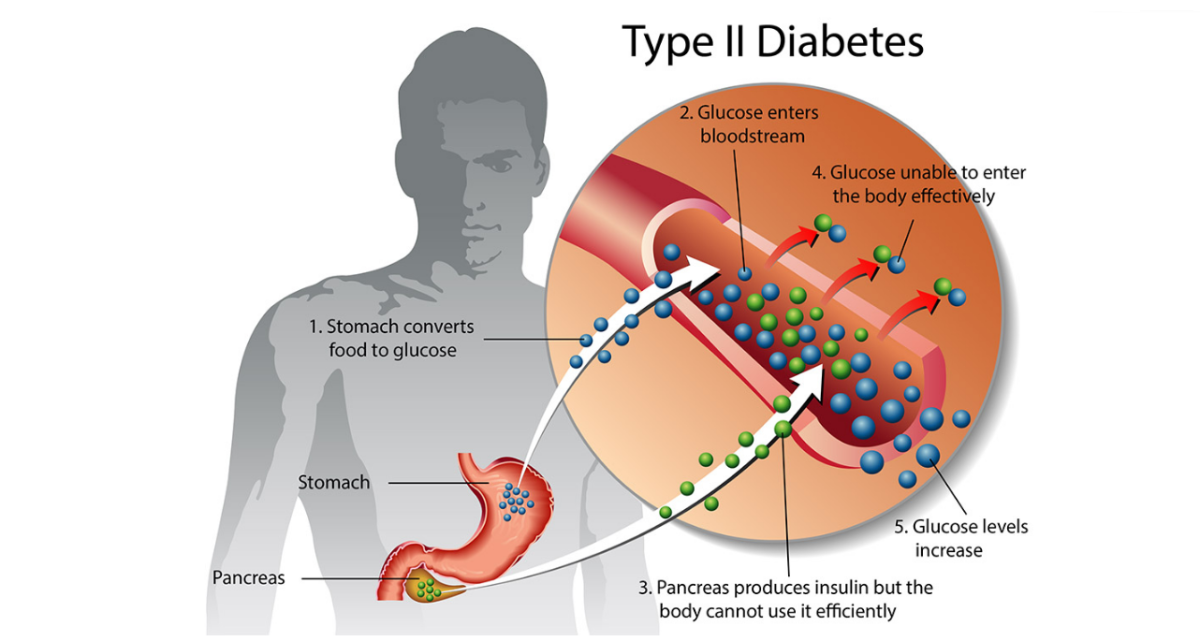
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes. It results in the body being unable to properly move sugar into your cells. The sugar or glucose builds up in your blood instead. This is called hyperglycemia.
The body tries to cope as best it can. The beta cells in the pancreas that make insulin release more insulin in an effort to bring blood sugar levels down, but they eventually can’t make enough to meet the demand.
In some cases, the beta cells are malfunctioning and send out the wrong amount of insulin or do so at the wrong time. In other cases, the liver isn’t storing up the excess glucose or releases stored glucose when it should be mediating blood sugar levels instead. This is why high triglycerides and low HDL cholesterol are correlated with a greater risk of diabetes. Fat stored around the abdomen instead of your hips and thighs is another risk factor for diabetes, since fat stored here interferes with proper liver function. Regardless of why the body can’t control its blood sugar levels, you can end up with Type 2 diabetes when it is bad enough.

What Are Your Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes?
A family history of Type 2 diabetes, being non-white, having had prenatal diabetes or a baby over nine pounds, a diagnosis of PCOS, high blood pressure, and obesity increase one’s odds of becoming diabetic as well. Obesity in children is a major contributor to children developing TD2. However, one doesn’t need to be overweight to develop Type 2 diabetes. Yet losing seven percent of your body weight and getting into the healthy range reduces your risk of developing the condition. Anyone with pre-diabetes is at risk of developing T2D, type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes should only be diagnosed via blood tests. Talk to your doctor if you think you’re at risk of developing diabetes or may already have it.
Why Don’t Some People with Diabetes Know They Have It?
Type 2 diabetes doesn’t happen overnight. More than eighty million people have pre-diabetes, a condition where their blood sugar isn’t normal but it isn’t high enough to be classified as Type 2 diabetes. Left untreated, there is a good chance pre-diabetes will progress to Type 2 diabetes.
The symptoms can worsen over years before someone realizes something is wrong, and there are millions who have Type 2 diabetes who don’t realize it. Some don’t find out that they have Type 2 diabetes until the damage it can cause to their vision, kidneys or heart has already occurred.
© 2018 Tamara Wilhite