What Causes Hyperuricemia?

Introduction
The human body needs to maintain a proper balance of everything, because too much or too low of anything can result to diseases. One of the examples of body imbalance is hyperuricemia. It is a condition wherein the amount of uric acid in the blood becomes abnormally high, exceeding the appropriate range of 2.4-6.0 mg/dL for women, and 3.4-7.0 mg/dL for men.
Uric Acid
Uric Acid is a metabolic waste product created from the breakdown of purines. Purine is a nitrogenous compound produced through cell turnover, or cell death, and is an extremely important component of a nucleoside, which combines with either deoxyribose, or ribose, and becoming a building block of DNA or RNA.
Additionally, purines, which could either be adenosine and guanine, are crucial in energy production and acceleration of many biochemical processes needed by the body. The role of purine-containing molecules in survival meant that the body has to rapidly and efficiently synthesize sufficient amount of purine using materials found in the body such as glucose, as well as a purine-rich diet.
Too Much Purine
Unfortunately, the mass producing of purine results to an excess or a surplus of purine and must be removed from the body. However, humans lack the necessary enzyme to break this down into a completely soluble material, and could only downgrade it as a uric acid.
On the other hand, uric acid is not entirely bad for the body, it just needed to be balanced, as it serves as an anti-oxidant, neutralizing the free-radicals, or pollutants that the body receives from the surrounding.
The Causes
Hyperuricemia then happens due to two primary reasons:
- When the level of uric acid in the bloodstream becomes too high because of huge amount of purine synthesized by the body itself or purine coming from the food consumed.
- All of the purine degraded into uric acid is not being excreted fast enough, or perhaps not at all, by the kidney through urine.
The secondary reasons are as follows:
- Medications, especially during chemotherapy, where there is an increase cell death, resulting in mass production of purine.
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Genes – hyperuricemia could be inherited, and the genetic material of the parents might be the reason why the person has high uric acid.
- Too much intake of fructose-rich food, or beverages like soft drinks
- Drugs that suppresses the immune system
- Excessive consumption of niacin, or commonly called as vitamin B-3
- Renal Failure — incapacity of the kidney to filter waste products from the bloodstream.
- Obesity – lack of balanced diet has lots of negative complications, including high uric acid.
- Purine-rich diet — this includes meat, organ meat, sardines, sweetbread, asparagus, and others.
- Starvation – increases the body’s synthesis of purine as it tries to replace the insufficient supply of purine-rich foods, and a low-calorie diet also induces hyperuricemia, while the kidney gets impaired due to lack of support that it could only get from food-intake.
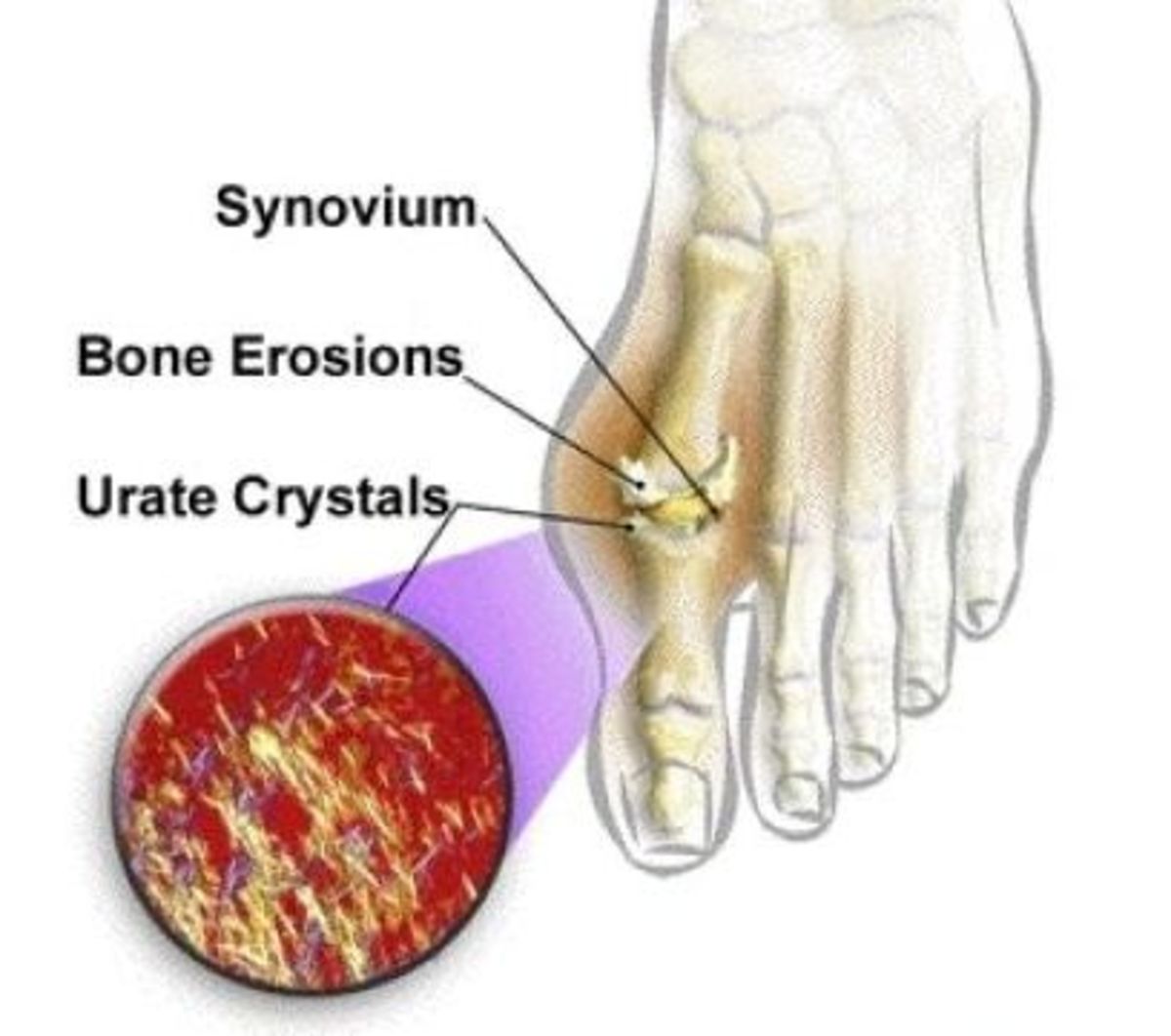
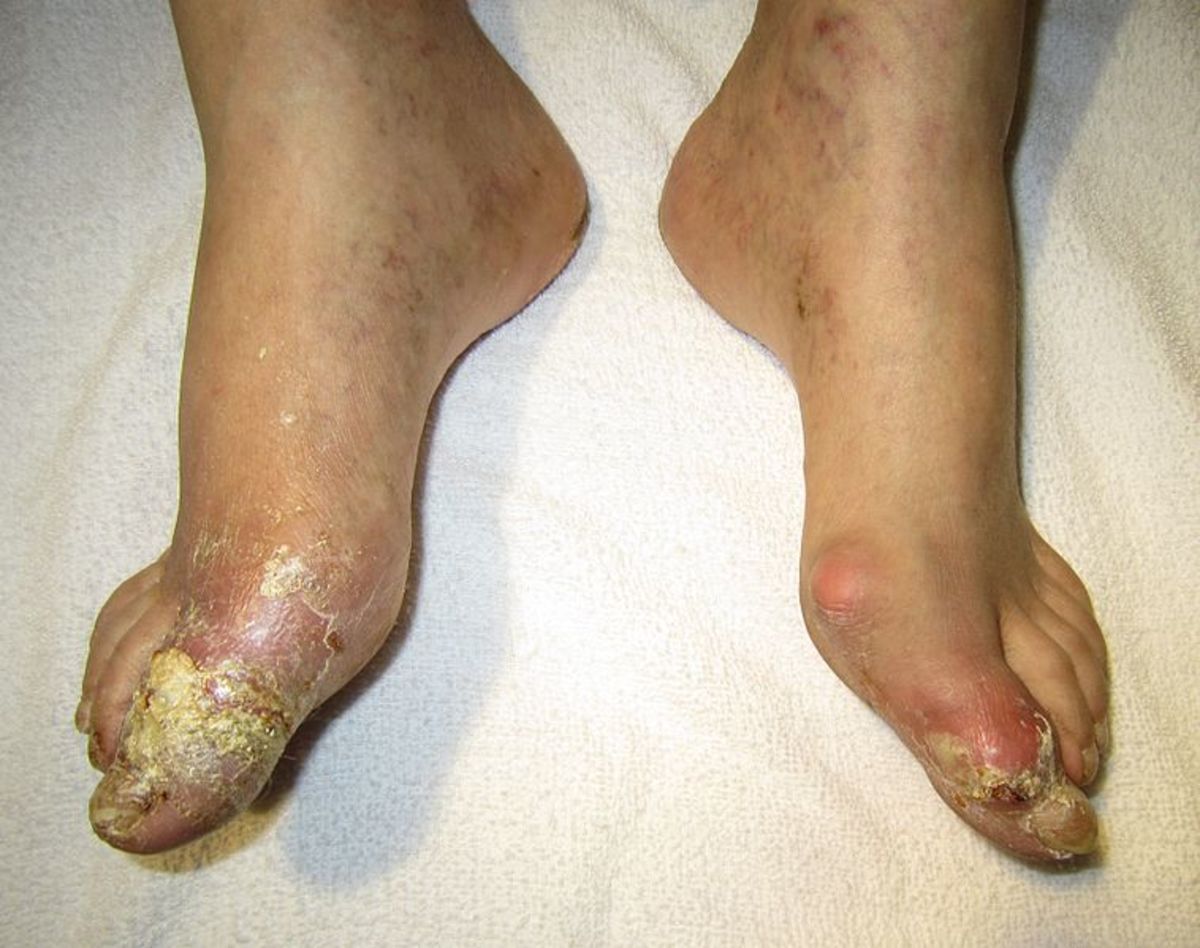
It Is Not Gout!
Hyperuricemia, however, must not be confused with the inflammatory arthritis called gout, as is the common misconception. A person with hyperuricemia does not necessarily have a gout, but it certainly increases the risk of acquiring the said condition.
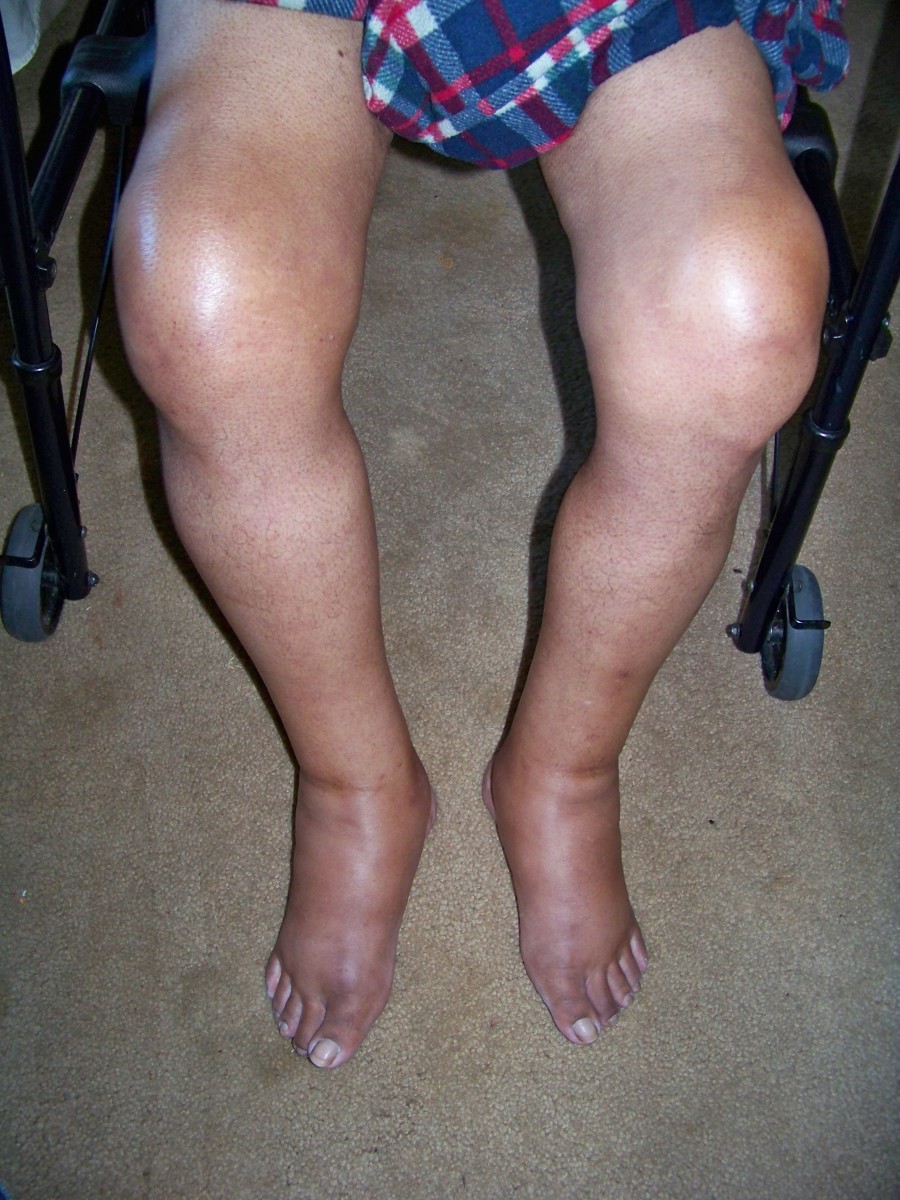
Although it usually does not have a symptom, having a gout is the most visible sign that a person may have hyperuricemia. Other related diseases, as a consequence of a high uric acid, are kidney failures, kidney stones, and cardiovascular diseases.
Conclusion
Without any efficient medicine yet, the best way to avoid, or to lower the level of uric acid in the body is a proper diet, consumption of ionized alkaline drinking water to neutralize the acidity of the body, and a regular trip to the doctor to monitor the body’s immunity and health.