What You Need to Know For NCLEX; Respiratory System
NCLEX RN EXAM CRAM
EXAM CRAM PN
All the Important Points for NCLEX
Here is an overview of what you need to know for NCLEX. The key is to have a very broad understanding of the whole system.
You will be asked questions that will ask you what to do, and your response will be something like, "monitor vital signs." This is why studying Assessments with Management is the best way to make these connections.
Weather you are taking the RN or PN, the very best book to practice is EXAM CRAM, because it is well organized, making more sense out of the study time. Sylvesteri is also a good resource. The only complaint from people is that there is so much information that it makes the studying "unfriendly" and boring.
Hay Fever
This is they key to sensitivity to allergic disease of the mucus membranes in the nose and upper air passages induced by external irritation.
ASSESSMENTS:
rhinitis, catarrh, watery discharge from the eyes, coryza, headach, asthmatic symptoms
Management:
epinephrine, antihistamines, nasal sprays, corticosteroids
Nursing Interventions:
remove patient from contact
Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is a streptococci inflammation of the tonsils and adenoids.
ASSESSMENTS:
- fever
- sore throat
Management:
- antibiotics
Epistaxis
bleeding from the nose.
Management: A nasal packing with gauze strips, cauterization of the site with 10% silver nitrate stick.
Nursing Care: Maintain patent airway; have suction available, control bleeding by pinching nose firmly with fingers on soft part. tilt head slightly forward. Monitor vital signs, and avoid hot fluids
Pneumonia
An acute illness caused by inflammation or infection of the lungs and characterized by a productive cough, chest pain, and fever.
Assessment; SOB, dyspnea, painful coughs, elevation of temperature.
Management: Antibiotics, IV fluids, O2 with humidity and analgesics (Codeine-antitussive) expectorants-Robitussin, Phenergan=soft foods &vitamin C- increase protein and carbs
Empyema
Pus collection in the thoracic cavity, S/S-sharp pain upon inspiration, dyspnea
Patient with Chest Tubes
Drainage tubes that are inserted into the pleural cavity to drain secretions, air, and blood from the thoracic cavity. Closed drainage of the thoracic cavity is accomplished by means of a catheter placed in the pleural space. The catheter is securely connected to an underwater seal apparatus.
INDICATIONS: pleurisy, chest surgery, stab wounds of the chest
NURSING CARE: observe underwater seal system q hour, prevent complications of immobility, assessment of respiratory system, provide oral hygiene q 2 hours, anticipate pain; medicate if necessary, spirometer and breathing exercises
Pulmonary Tberculosis
Chronic, progressive infection; alveoli are inflamed, and small nodules are produced called primary tubercles; the tubercle bacillus is at the center of the nodule (these become fibrosed); becoming calcified, identified on X ray film.
Assessments: Malaise; patient is easily fatigued, elevation of temperature and night sweats, anorexia and weight loss chest pain, chronic coughs, and hemoptysis
Management: antituberculin drugs for 18-24 months- Rifampin, Isoniazid, Streptomycin
Nursing Care: provide rest; assist or provide care; plan rest periods between activities; limit conversion. prevent transmission; ensure respiratory isolation. Avoid chills, avoid sharing personal items
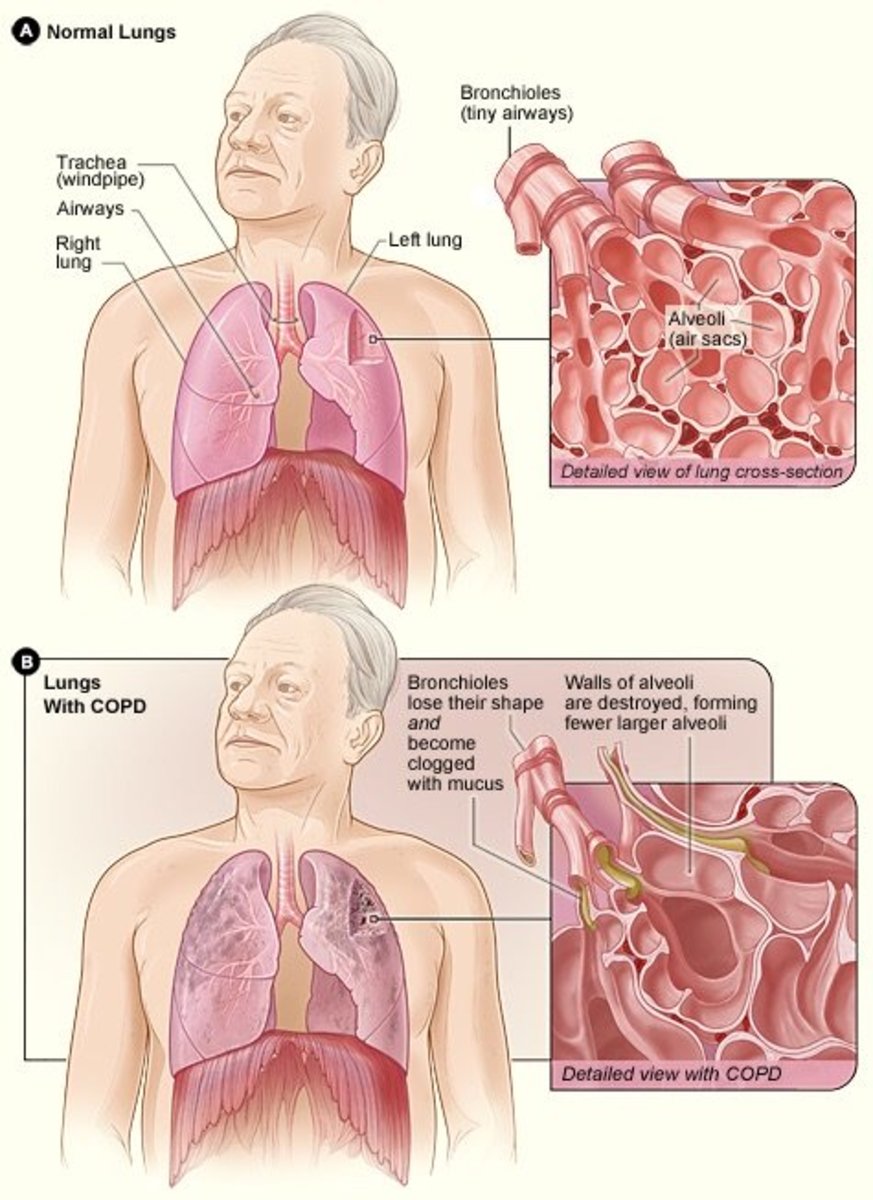
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
COPD- is the obstruction of bronchioles and alveoli caused by A/B/E
ASSESSMENTS: barrel chest, pink skin color due to hypercapnia, hypoxia, SOB dyspnea leading to severe activity intolerance, coughs
Management: Pulmonary function test, ABGs, antibiotics, bronchodilators, 02@2-4L/m
Nursing Care: prevent URI, postural drainage, increase fluid intake, avoid smoking, allergen, and stress