Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria Are Dangerous
Doctor Visit

Role of Antibiotics
Antibiotics are prescribed to fight infections from bacteria and they actually work in two different ways. They help your body fight bacteria by directly killing the bacteria, or they weaken the bacteria enough that your body can eliminate the bacteria by using your immune system.
Antibiotics have been over prescribed to the point that antibiotic resistance to bacteria is a common problem. Quite often a patient will see their doctor and ask for an antibiotic when they actually have a virus. Antibiotics do not treat viruses.
Doctors sometimes give in to the pressure from the patient, or they prescribe an antibiotic to a patient that is ill without really having a culture ordered to know what bacteria is causing the problem. In that case, the antibiotic may not treat the infection and a second antibiotic will be prescribed when a culture is done to treat the bacteria causing the problem.
Bacteria versus Viruses
Bacteria can live independently in our bodies, so they are easier to kill than viruses most of the time. Viruses need a host, which is your body, to live and there are not many medications available to kill viruses. Approximately 2,000,000 get antibiotic resistant infections, and almost 5 million died in 2019.
Antibiotics must be prescribed by a physician. Each year we find more powerful antibiotics on the market because the independent bacteria have the ability to mutate and become antibiotic resistant bacteria. There are literally trillions of types of bacteria on this earth.
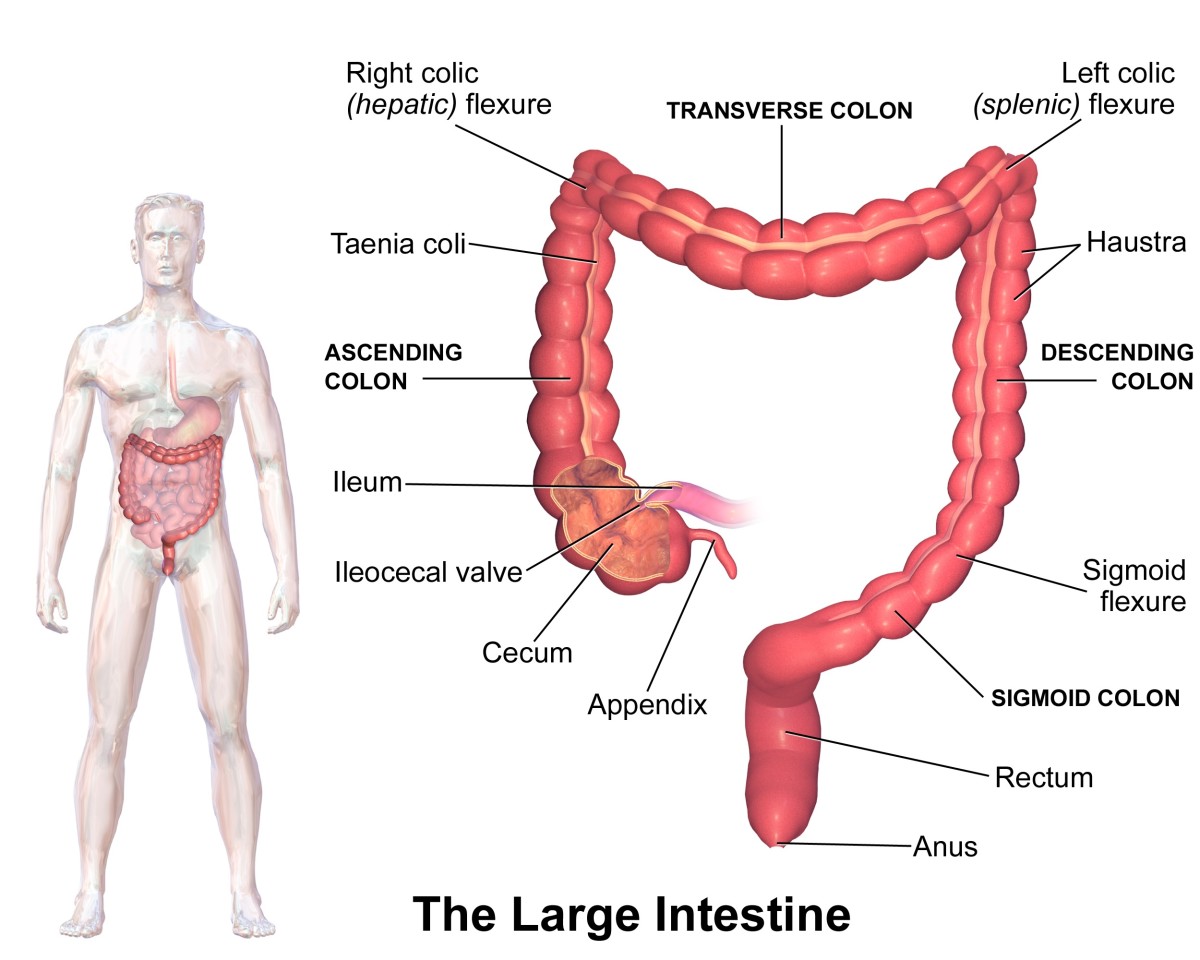
Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria
Scientist found a new bacteria, which is antibiotic resistant. CRE, which stands for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae is the new drug resistant bacteria and MRSA is another difficult bacteria also.
I am acutely aware of this problem as I have two drug resistant bacteria living in my lungs. When you have a disease such as lupus, you are typically taking immunesuppression medications. These medications compromise your immune system, so it is unable to kill the bacteria effectively.
After developing lung disease two years ago (I never smoked), I got one bacterial infection, which did respond to antibiotics initially. The bacteria keep returning, as it has the capacity to lie dormant in your body for a period of time, and then flares up again. Gradually when you take antibiotics over a long period of time, the bacteria becomes more resistant. Then, the prescribed antibiotics become stronger and more side effects can develop. This is what has happened to our society as a whole.
People often run to the doctor demanding an antibiotic when they are sick, and the doctors are very conscious of our litigious society. Often they won’t take chances, so they prescribe an antibiotic when some extra Vitamin C, chicken soup and bed rest might have sufficed.
The end result is antibiotic resistance bacteria. Also, we have newer types of bacteria, such as MRSA, which was unheard of until 1960 in the United States. As an RN, the first time I remember MRSA becoming a problem in the hospital was 1987.
Common Side Effects to Antibiotics
A vaginal yeast infection is a common occurrence for women on antibiotics. The reason is antibiotics kill not only the invading bacteria, but also the good bacteria in our bodies, so a yeast infection or constipation is common.
It is possible to ward off some of these problems by taking Probiotics when you are on an antibiotic. Probiotics can be purchased over the counter at drug, grocery or health food stores. Probiotics are live microorganisms that help balance your body’s immune system. Eating yogurt can also be helpful. These two items help replace some of the good bacteria lost when we are taking antibiotics.
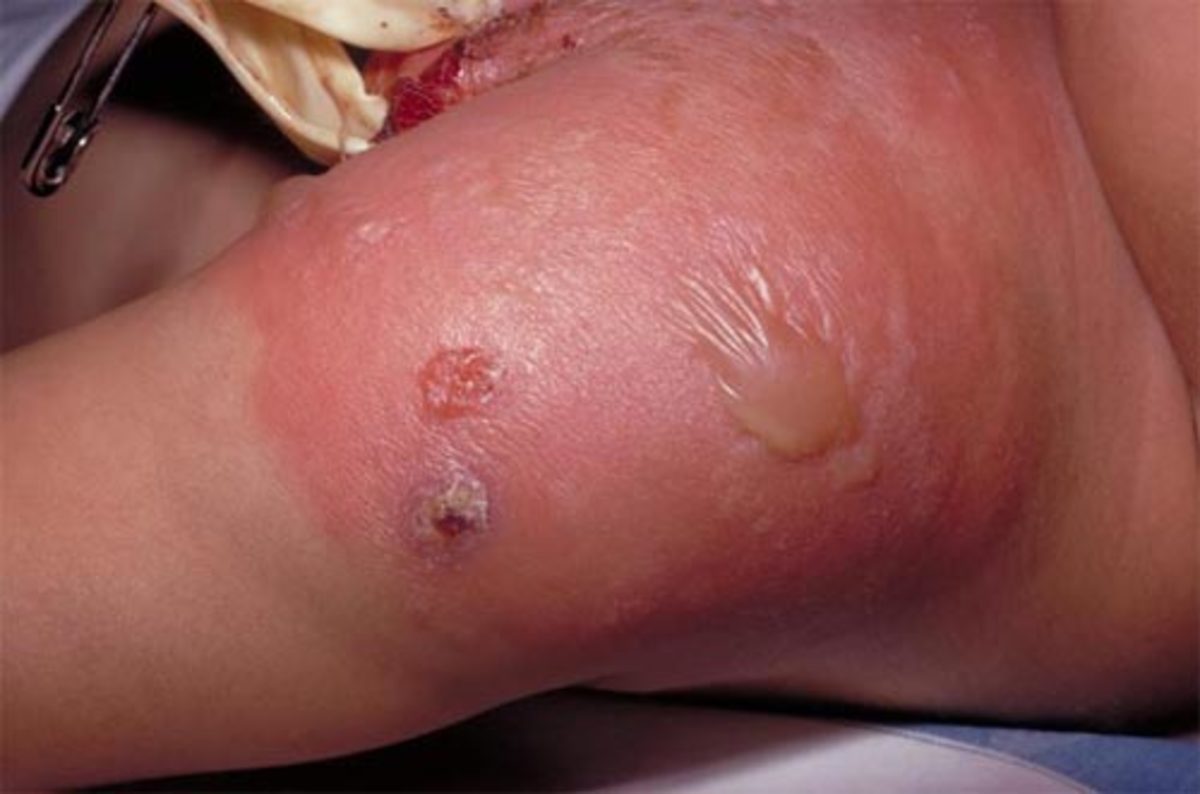
Allergic Reactions to Antibiotics
If you have a severe allergic reaction to any medication a number or symptoms might occur based on the severity of the reaction.
These are symptoms of an allergic reaction which you should know:
- Hives
- Rash or blisters, swollen red skin
- Difficulty breathing
- Severe or persistent cough
- Swelling in the area of the mouth, face, lips, tongue
- Stomach cramps, tar colored or bloody stools
- Chest pain
- Unusual hoarseness
- Chills
- Joint or muscle pain
- Confusion, hallucinations, depression
- Decreased urination or dark urine
- Irregular heart beat
- Unusual bruising
- Severe headache
- Weakness
- Unusually pale skin
- Vaginal irritation or discharge
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes
These symptoms warrant immediate medical intervention. The more acute symptoms can lead to anaphylactic shock and death. If you have the more severe allergic reactions listed above, call 911. An allergic reaction is much more serious than a side effect from an antibiotic.
Staphylococus aureus Bacteria
Major Types of Antibiotics
Penicillins and Cephalosporins are very commonly used. Penicillin was discovered by Alexander Fleming in the early 20th century. These antibiotics are usually well tolerated with few side effects. Diarrhea is the most common, but some people do have allergic reactions.
Macrolides include Erythromycin, azithromycin and clarithromycin are also commonly prescribed for bronchitis, Chlamydia and whooping cough. They must be taken with food to prevent stomach ulcers. They seldom produce an allergic reaction but there are some possible side effects, such severe dizziness, stomach upsets, diarrhea, vomiting, hearing problems and skin reactions are the most common. However, they are usually well tolerated.
Other Types of Antibiotics
Sulfa antibiotics more commonly produce an allergic reaction. They are not used as often now, as they don’t treat many types of bacteria. Bactrim is a suflanamide and can have numerous side effects and common allergic reactions.
Nitrofurantoin or Macrodantin is a drug to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs). They may have side effects, like an upset stomach, diarrhea, gas and loss of appetite, but are very effective in treating UTIs.
Aminoglycosides attack bacteria in a different way and are sometimes prescribed along with penicillin or Cephalosporins. They break down easily in the stomach, so they are often given via intravenous. They are, however, used in eye drops to treat pink eye. When they are received IV they can cause ear or liver damage. Therefore, they are usually given for only a short period of time.
Quinolones, better known as Cipro, interferes with the DNA enzyme of the bacteria. They treat several types of infections but can damage cartilage, so they are seldom prescribed for children. They typically have few side effects, unless you are allergic.
Fungal, Yeast or Virus Infection Treatments
Tetracycline treats sexually transmitted diseases for adults. They affect the development of tooth enamel and bones in children, so they are not given to children under 8 years of age. This antibiotic is the most effective treatment of cholera and anthrax.
Antifungals, such as fluconazole, treat Candida. Side effects are rare unless you are allergic.
Acyclovir is an antiviral drug that treats chicken pox, shingles and the herpes virus. They never totally eradicate the virus, but it causes it to go dormant. Possible side effects include low back pain, urinating less, easy bruising and unusual weakness.
In Conclusion
If you have even a small allergic reaction to an antibiotic, make sure your doctor and your pharmacy is aware of this information. If you take the antibiotic a second time it is likely your allergic reaction will be more severe.
Buy a medical ID bracelet to wear if you have a penicillin or sulfa allergy in case you are hurt and cannot give someone your medical information. They make bracelets especially for children as well.
Antibiotics are used to treat bacteria, so viruses are not really in this category. All antibiotics may have some side effects, with some being more serious than others.
A serious disease, like pneumonia, for example, really needs to be treated with an antibiotic as this disease has the potential to kill the patient. The risk of the disease versus the risk of side effects from an antibiotic must be weighed. As a society we should do everything possible to prevent antibiotic resistance.
This content is accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge and does not substitute for diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, prescription, and/or dietary advice from a licensed health professional. Drugs, supplements, and natural remedies may have dangerous side effects. If pregnant or nursing, consult with a qualified provider on an individual basis. Seek immediate help if you are experiencing a medical emergency.