What is Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load of Foods-Impacts and health applications

Just a brief blog to familiarise ourselves with what the glycemic index is and how it affects our blood sugar levels. There will be more health artices to follow at purplefalcon.hubpages.com!
Glycemic Index
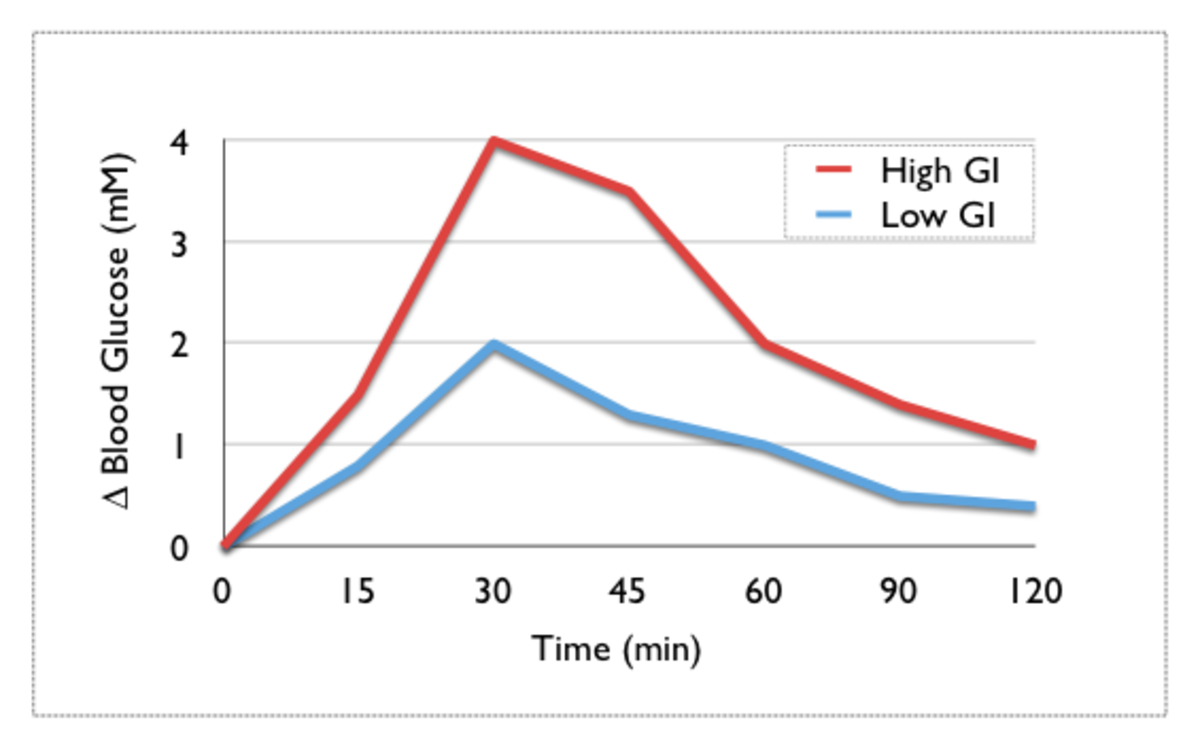
Carbohydrate metabolism plays an important role in treating both types of diabetes. Much research have been focussed on ways to identify the high-risk foods to avoid or limit in diabetics. This led to the development of the concept of ‘glycemic index. The glycemic index (GI) is aimed to compare different foods based on their ability to induce a rise in blood glucose. It is measured as the value of the blood glucose response to food in comparison to a standard food (usually glucose or white bread). Thus the GI of foods help serve as a guideline to modify the foods we eat to better control blood sugar and insulin levels in both healthy and diabetic individuals.
Glycemic Load
Due to the varied amounts of carbohydrates present in a typical serving of food, a new measure known as the glycemic load (GL) was introduced. The dietary GL is defined as the product of a food’s GI and its carbohydrate content [1]. GL takes into account that foods rated solely on the basis of their GI do not quantify common servings that are eaten [1]. For example, although carrots have a high GI of 92, a usual serving of carrots has a low total carbohydrate content of 6 to 8 grams and therefore should produce a low-glycemic response. Recent research strongly suggest than high GI foods and high GL diets cause increased serum glucose levels and increased insulin demand [1]. These have been shown to increase insulin resistance and the risk of type 2 diabetes in predisposed people.