Why Does Social Distancing Matter in Order to Beat Covid-19 for Good?
You're probably tired of hearing the word "social distancing" and seeing the word "Covid-19" everywhere. But we don't have a right to complain until we all practice social distancing and slow down its spread.
To distance ourselves from our friends, family and relatives socially might sound scary. However, it just means we have to distance ourselves from them physically, not emotionally. We can still stay in touch with our loved ones thanks to technology. We can call, text and videocall them. Thus, we can still be with them by staying apart from them. If we accomplish that, we can reunite with them in person sooner than we think. By practicing social distance, we don't only protect ourselves but we also protect our loved ones, since Covid-19 spreads via social contact.
There are still so many unknowns when it comes to Covid-19, also called Novel Coronavirus, since it's a newly identified virus. Therefore, we're all new to it. However, we all know how viruses function. Since Covid-19 is a virus, we can make estimates based on virus' functions.
What is Virus and How Does It Spread?
Virus is an infectious agent with an ability to multiply itself in living cells. Viruses are thought to be inanimate. Humans, animals, plants and so on act as host cells for them. They need these host cells in order to produce, grow and move. Thus, they can't produce, grow and move without a host. In other words, they remain inactive without a host, whereas they become active within a host. That explains why their common aim is to spread. The more host cells they infect, the more they replicate themselves. So basically, they are waiting for host cells they can infect since their existence and activity depend on host cells.
Viruses are too tiny and too lightweight which makes transmission easy for them. They remain in the air and on the surfaces which are either animate or inanimate. If a person infected with virus sneezes, coughes or spawls, droplets spread around. If we touch inanimate surfaces infected by virus such as doorknobs, push buttons, newells, and animate surfaces such as others' skins and/or our skins, viruses find a way to make their entrance into our bodies. Just like other microorganisms, viruses enter our bodies through nose, mouth, eyes, urogenital openings, bites, scratches and wounds in skin. After entering, they hijack our cells, take over some of our cells and make us sick. To cut it short, they are invaders.
Genetic Materials of Virus
Viruses are made up of genetic materials which are either DNA or RNA. Their genetic materials are covered and protected by capsids which are protein molecules. Some viruses' capsids are also covered by envelopes which are fatty molecules also called lipids. The nucleid acids are either single stranded or double stranded.
DNA vs. RNA Viruses
They differ from each other.
DNA Viruses
- They usually contain double stranded nucleid acids.
- Their nucleic acids are less fragile.
- They inject their genetic codes in hosts' DNA for duplicating and decoding. Viral DNA is transcribed into RNA and then mRNA is translated into viral proteins.
- Replication occurs in nucleus.
- If an error occurs during duplication, host cells correct it.
- They have greater genomes since their replication is accurate.
- They can encode a lot of viral proteins.
- Their mutation levels are lower.
- They evolve more slowly.
- They are stable.
- They are less virulent.
- They can barely fool immune system.
- Vaccines work more effectively on them.
RNA Viruses
- They usually contain single stranded nucleid acids.
- Their nucleic acids are more fragile.
- They inject their genetic codes in hosts' RNA which requires to be translated into DNA for duplicating and decoding. But sometimes viral RNA can bypass transcription process since they already contain RNA which means it can skip DNA for duplicating and decoding.
- Replication occurs in cytoplasm after transcription.
- If an error happens during replication, host cells fail to correct it.
- They have smaller genomes since their replication is error-prone.
- They can encode a few of viral proteins.
- Their mutation levels are higher.
- They evolve more rapidly.
- They are unstable.
- They are more virulent.
- They can easily fool immune system.
- Vaccines work less effectively on them.
What is Covid-19 and What Do We Know About It?
Covid-19 aka 2019-nCoV is an infectious disease caused by SARS-CoV-2 which affects human respiratory system. Compared to other recent pandemics such as SARS and MERS, Covid-19's mortality rate is lower for now, whereas its transmission rate is higher. Although at first it resembles flu, it's more contagious than typical flu. Since Covid-19 is a RNA virus, it tricks our immune system more easily and quickly.
Covid-19 Symptoms
- Sore throat (more common)
- Dry and continuous cough (more common)
- Fever (more common)
- Shortness of breath (more common)
- Difficulty in breathing (for severe cases)
- Pain or pressure in chest (for severe cases)
- Pneumonia-like symptoms (for severe cases)
- Fatigue (for some cases)
- Body aches (for some cases)
- Nasal congestion (less common)
- Runny nose (less common)
- Loss of smell and/or taste (less common)
- Diarrhea (less common)
- Nausea (less common)
Who are at higher risk?


How to Protect Ourselves and Our Loved Ones
Covid-19 is covered by lipids so we have to wash our hands with soap frequently. Soaps dissolve viruses' fatty molecules so that's why it's so important to wash our hands. Since viruses enter into our bodies through nose, mouth, eyes and wounds in skin, we should avoid touching them before washing our hands with soap.

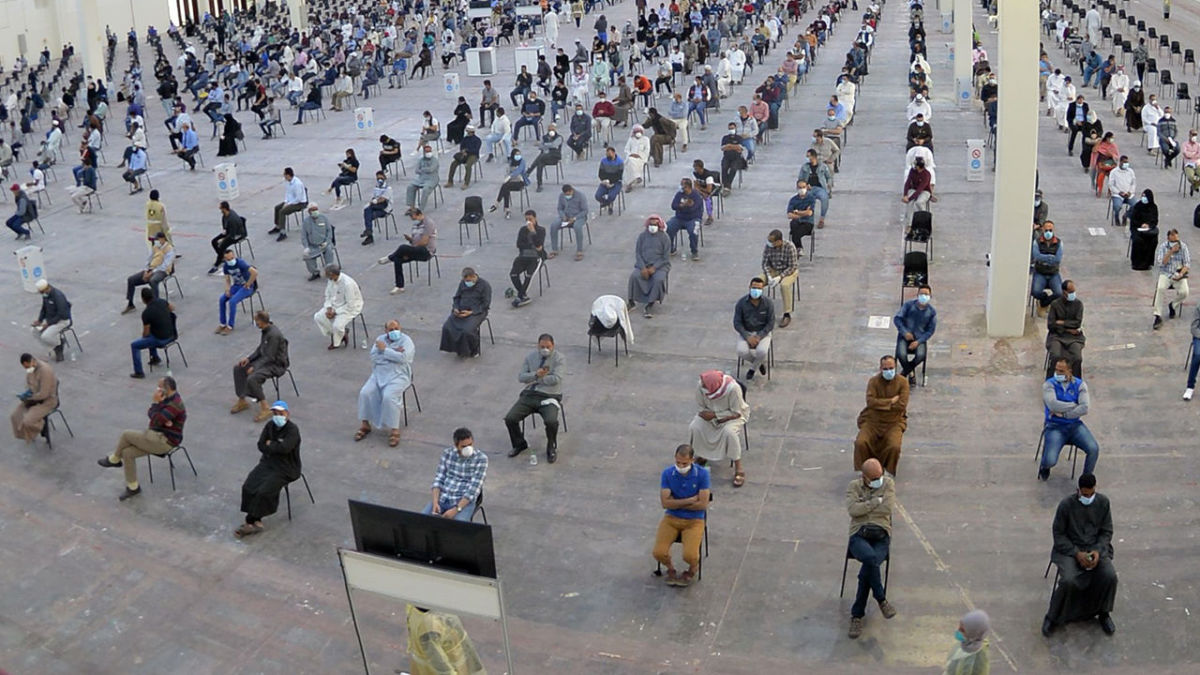
Why Should We Practice Social Distancing?
Covid-19 is the reason why real life pandemic happened. It's highly contagious and infectious. We shouldn't only distance ourselves from people who cough and have fever but also distance ourselves from everyone since some people might be asymptomatic. Others and even us might experience no symptoms but we all might be carriers and infect others around us. It might be easier for us to protect ourselves from those who show symptoms but it's harder for us to protect ourselves from those who show no symptoms. This virus needs more human cells so it can continue to reproduce and replicate. It aims to spread whereas we aim to flatten the curve. That is why social distancing should be compulsory so we can minimize its activity.

Yes, elders are at higher risk. But, it doesn't mean others aren't at risk. Social distancing must apply to everyone no matter how old they are.
Remember what happened to Italy when they didn't think the situation was too serious and social distancing was too crucial? We all should learn from it, do our best to keep our social distance and warn others who violate it. It's our social responsibility.
BONUS: The Coronavirus Explained & What You Should Do
"Stay home. Stay safe. Save lives."
— Governor Whitmer, state of MichiganReferences
- WHO | World Health Organization
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- National Center for Biotechnology Information
- Mayo Clinic - Mayo Clinic
- WebMD - Better information. Better health.
- OU Medicine - Leading Health Care
- ScienceDirect.com | Science, health and medical journals, full text articles and books.
- Healthline: Medical information and health advice you can trust.
- Sciencing: Making Science Fun for All Ages
- Kurzgesagt – In a Nutshell - YouTube
- Business Insider
- News, sport and opinion from the Guardian's global edition | The Guardian
- NBC News - Breaking News & Top Stories
- The Conversation: In-depth analysis, research, news and ideas from leading academics and researchers
© 2020 Sila Ozgoren