Can Your Gut Microbiome Handle the Artificial Sweeteners? A Science-Based Analysis
A tug of war between artificial sweeteners and gut health

Disclosure
This article contains affiliate links, which means I may receive a commission if you click a link and purchase something I have recommended. This comes at no additional cost to you and helps support the creation of valuable evidence-based content. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
In today's fast-food world, it's almost impossible to think of sweetness without a sense of regret. This is particularly true when sugar-free yogurts and diet sodas become a regular part of your routine. The sweetness promised by the artificial sweeteners has a hidden cost. It's difficult to believe that this cost is so high that it compromises your immune system. I recently had an opportunity to deep dive into the science behind artificial sweeteners and their influence on gut health. I was stunned to know how these artificial sweeteners interact with the metabolic processes and the microbiome and slowly and gradually compromise the immunity to the extent that the human body finds it highly challenging to deal with any cancer exposure. Let's understand artificial sweeteners from the perspective of the gut microbiome.
Understanding the Significance of Gut Health in the Context of Artificial Sweeteners
The human intestine (or gut) is occupied by countless microorganisms, such as fungi, viruses, and bacteria. They don't sit idle within the gut but have several important roles to play. For example, some of them are engaged in coordinating with the immune system. In contrast, some others optimize hormones or facilitate the production of vitamins. Many of these microbes facilitate the absorption of the food particles. Altogether, this large community of microorganisms inside your gut helps develop a robust defense system against a variety of disease conditions. They also optimize the energy production and transfer mechanisms in the human body. Their actions and inactions are vital to regulating gut physiology, whose proper functioning is essential to maintaining parallel body systems. As soon as this gut coordination of microorganisms gets disturbed by any cause, the risk of debilitating diseases increases manifold.
What science says about artificial sweeteners?
You must have had a chance to check the decks and shelves of several supermarkets many times. Did you realize that the products of your choice contain Ace-K or acesulfame potassium, aspartame, saccharin, or sucralose? These calorie-free artificial sweeteners are lined up one after another, luring you when you fail to resist the temptation for a super-tasting food item. I had a chance to explore the most authentic research studies on these artificial sweeteners. What I found about artificial sweeteners was mind-blowing.
- Research says that the regular or frequent intake of sucralose triggers the activity of highly pathogenic and inflammation-causing microorganisms, such as Staphylococcus, Proteobacteria, and Clostridia (1, 2). The story doesn't end here. Evidence also unravels the silent enmity between Bifidobacteria/Lactobacilli (the gut-friendly microbes) and sucralose (1, 2).
- Scientific evidence indicates that the consumption of Ace-K, aspartame, and saccharin not only disrupts glycemic control (or blood sugar level management) but also deteriorates gut metabolism (2, 4). This occurs because these artificial sweeteners disrupt the overall balance or homeostasis of a variety of beneficial and harmful microorganisms in the gut (1-4).
- Artificial sweeteners not only compromise gut function but also disrupt it (1, 2). Over time, they increase gut permeability, providing a gateway for bacterial toxins to enter the bloodstream and trigger inflammation (1, 4). This persistent leakage in the gut can weaken the immune system, reducing the body's resistance to diseases, including certain types of cancer. This revelation may make you reconsider your sweetener choices and prioritize your gut health.
Artificial sweeteners decisively induce the domino effect.
In a healthy gut, the tiny but mighty short-chain fatty acids, such as propionate, acetate, and butyrate, work in close coordination to empower its inner lining, challenge inflammatory mechanisms, and regulate the immune system balance (1, 4). However, even the slightest imbalance in these fatty acids weakens their action, triggering a domino effect.
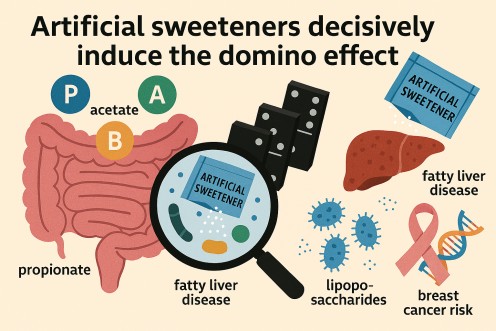
Once that happens, the chain of adverse gut events lowers the gut barriers and increases the risk of toxicity.
- The artificial sweetener-induced shortcomings of the intestine give way to the lipopolysaccharides and other similar bacterial toxins. The moment they gain access to the circulation, the risk of fatty liver disease, dyslipidemia, and hypercholesterolemia increases several-fold (4).
- The long-term inflammation triggered by the artificial sweeteners adds to the risk of breast cancer by downgrading the DNA function (3).
The rivalry between artificial sweeteners and the immune system
The enzymes, such as beta-glucuronidase, and the estrogens are actively recycled with the assistance of a few gut bacteria. They are recognized as the hormonal gatekeepers in the human body. However, the invasion of artificial sweeteners disrupts this delicate balance between hormones and enzymes, which eventually boosts the circulation of estrogen, resulting in fatigue, mood swings, weight gain, breast tenderness, and menstrual disorders (3). Artificial sweeteners do not stop here, but continue to challenge the body's physiology at least until their consumption.
Research has shown that artificial sweeteners play a role in disrupting the immune cell configuration and activity in cancer patients (5). For example, consistent consumption of sucralose reduces T cell activity and triggers the growth of tumors. This is why their intake reduces the beneficial outcomes of cancer immunotherapy (5). This creates a survival crisis in cancer patients, which is too difficult to manage in the absence of adjunctive treatments. Scientific evidence reveals the need for amino acid supplements such as citrulline or arginine in cancer patients with a high intake of artificial sweeteners (5).
The gut theory of artificial sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners are those clever entities that approach each gut with a unique tactic. This is the reason that they trigger different gut responses in various individuals. You may wonder why this happens. Do these sweeteners have their own brain, or is that just a mystery? Scientific evidence suggests that food habits, microbiome composition, and genetic factors interact variably with artificial sweeteners, providing them with multiple opportunities to influence gut function in different patterns (1, 4). That's why some individuals experience a rapid decline in their metabolic health and gut microbial balance as soon as they are exposed to artificial sweeteners, while many others experience a slow but sustained impact (2, 4). The following evidence-based table depicts the underlying mechanisms of artificial sweeteners.
Artificial sweetener
| Microbial cascades
| Underlying mechanisms
|
|---|---|---|
Sucralose
| Lactobacilli (↓)
| Suppression of the immune system
|
Sucralose
| Proteobacteria (↑)
| Alterations in estrogen metabolism
|
Sucralose
| -
| Inflammation cascade
|
Saccharin
| Alterations in the function of Alistipes, Prevotella, and Bacteroides (the human gut microbiomes)
| Inflammation cascade
|
Saccharin
| -
| Impairment of glycemic control (or blood glucose level management)
|
Aspartame
| Clostridia (↑)
| Degradation of the immune system
|
Aspartame
| Short-chain fatty acids (↓)
| Recycling of estrogen
|
Ace-K
| Cascades based on biological sex
| Inflammation cascade
|
Ace-K
| -
| Changes in short-chain fatty acids
|
Artificial sweetener, microbial cascades, and the underlying mechanisms
Simple tips to empower your gut
Now there is no solid reason left with us to back up, support, or advocate the use of artificial sweeteners in our daily routine. Science reveals simple yet powerful ways to enhance gut function and opt for natural sweeteners. I've listed some of them below for your ready reference.
1. A high-fiber diet is a boon to gut health: Your gut microbes thrive when you consume a fiber-rich diet based on whole grains, green leafy vegetables, and fruits.

2. Fermented food items: These are the dietary items prepared via enzymatic processes and microbial interventions. They increase the microbial diversity and provide added nutritional benefits that help improve the immune system. Sauerkraut, kimchi, and yogurt are essential dietary staples to consider incorporating into your daily routine.

3. Appropriate sleep and hydration: The communities of gut microbes thrive in individuals who get sufficient rest and maintain a balanced water intake.
4. Regular use of stress busters: Research demonstrates the adverse impact of excessive stress on the gut balance. That's why it's crucial to practice mindfulness and other stress-busting techniques such as steady breathing, aerobic exercises, and intermittent fasting to retain a friendly relationship with your gut. My personal take is to avoid alcohol and drugs as much as possible to kick off the unwanted stress.
Supporting the gut microbiota
Consider using the following supplements to systematically restore and strengthen the beneficial microorganisms in your sensitive gut.
Probiotic supplement

Affiliate Disclosure: I may earn a commission if you purchase via this link. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Prebiotic supplement

Affiliate Disclosure: I may earn a commission if you purchase via this link. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
You can increase the positive influence of the above remedies by adding plant-based food items to your diet. Additionally, a healthy lifestyle will further enhance the effectiveness of these remedies in achieving gut-friendly outcomes. Ensure you consult your physician before taking any of the above-mentioned probiotics or prebiotics, including their duration and dosage.
Caution
Not everyone might be suitable to consume probiotics/prebiotics. Immunocompromised individuals, those with pregnancy/breastfeeding status, children, and people with underlying diseases must not consume probiotics/prebiotics without a medical consultation.
Conclusion
Your alliance with your gut heavily depends on how you take care of the highly diverse microbiome, without which it's practically impossible to think about gut health. When you say no to artificial sweeteners, you show empathy to these little guests in your gut. In return, they will surely help regulate your hormones and enzymes, reducing the risk of inflammation and related diseases. For cancer patients, eliminating artificial sweeteners is the best approach to enhance the effectiveness and outcomes of potential treatments, such as immunotherapy.
My personal anecdote in this regard is to eat a healthy (fiber-rich) diet, avoid the consumption of junk food, follow a strict exercise routine, and opt for intermittent fasting. Don't let your gut be dominated solely by your taste buds. The temptation to eat tasty foods may lead you to bypass a healthy diet and rely on artificial sweeteners for a long time, which will consequently compromise both your gut environment and your immune system.
Stay alert, stay healthy, and look forward to more science-backed health updates.
Have a lovely day!
References
- Feng, J., et al., Non/Low-Caloric Artificial Sweeteners and Gut Microbiome: From Perturbed Species to Mechanisms. Metabolites, 2024. 14(10).
- Crakes, K.R., et al., Impacts of non-nutritive sweeteners on the human microbiome. Immunometabolism, 2025. 7(2).
- Yu, X., et al., Research Progress on the Relationship Between Artificial Sweeteners and Breast Cancer. Biomedicines, 2024. 12(12).
- Harrington, V., et al., Interactions of Non-Nutritive Artificial Sweeteners with the Microbiome in Metabolic Syndrome. Immunometabolism, 2022. 4(2).
- Morder, K.M., et al., Sucralose consumption ablates cancer immunotherapy response through microbiome disruption. Cancer Discovery, 2025.
This content is for informational purposes only and does not substitute for formal and individualized diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, prescription, and/or dietary advice from a licensed medical professional. Do not stop or alter your current course of treatment. If pregnant or nursing, consult with a qualified provider on an individual basis. Seek immediate help if you are experiencing a medical emergency.
© 2025 Dr Khalid Rahman