Cancer - Diagnosis and Treatment
To know what is cancer and what are its causes and prevention, read this
To know what are the different ways of diagnosing cancer, read on......
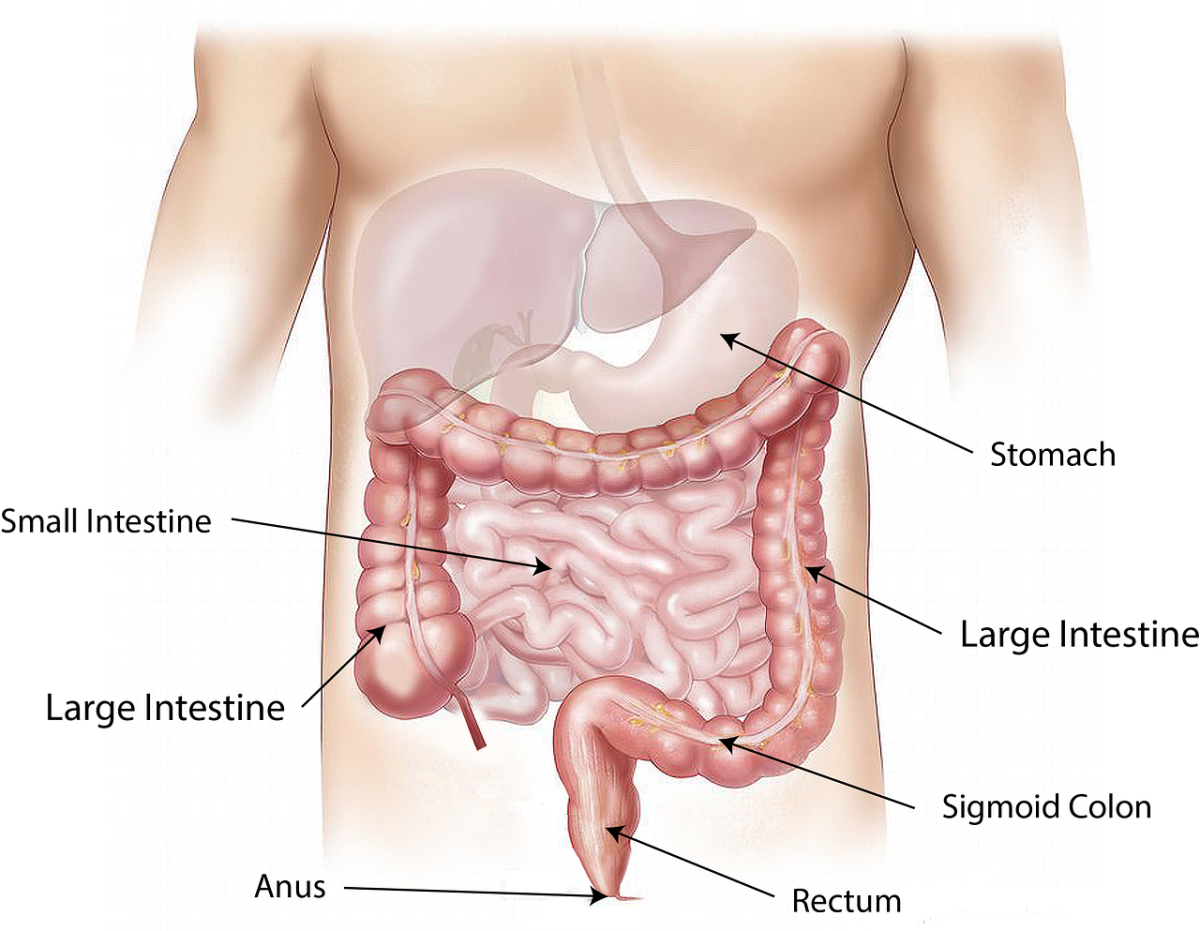
Diagnosing cancer
The tests commonly performed to rule out cancerous tumors are:
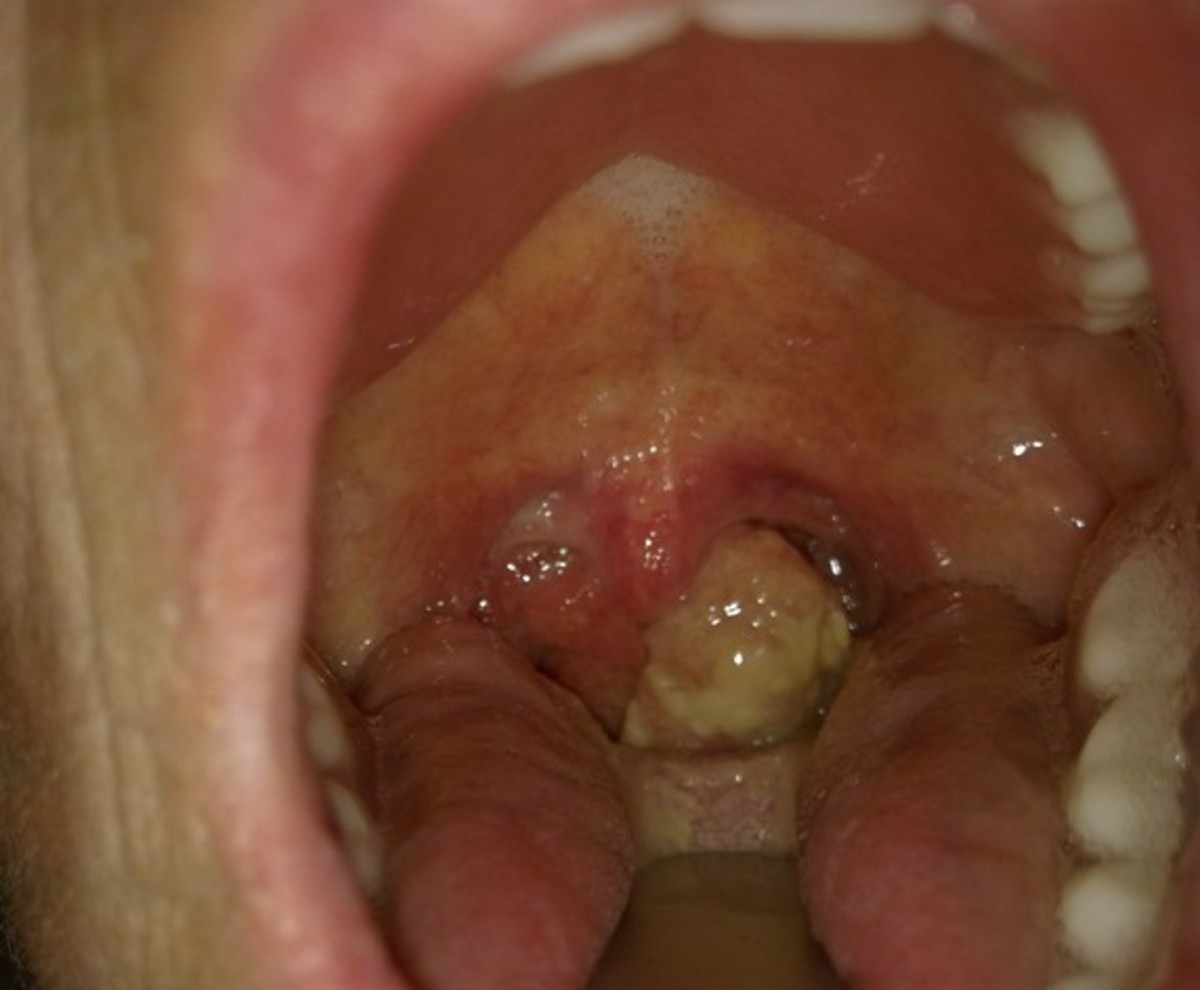
For uterine cancer, the cervical cytology or Pap test is a simple, fast, and painless procedure, which involves taking a sample of cervical secretions for some cells and expanding them in a foil. It is processed in the laboratory techniques of fixation, and then studied under a microscope. This test not only indicates whether there is suspicion of cancer, but the presence of some other infection.
Who should take the exam? It is recommended that any woman who involves in sex should have a Pap smear review periodically once a year or every 2 years or when the doctor tells you to do it.
There are other tests such as:
1. Identification of malignant cells in blood, urine and cerebrospinal fluid (the latter in case of brain tumors).
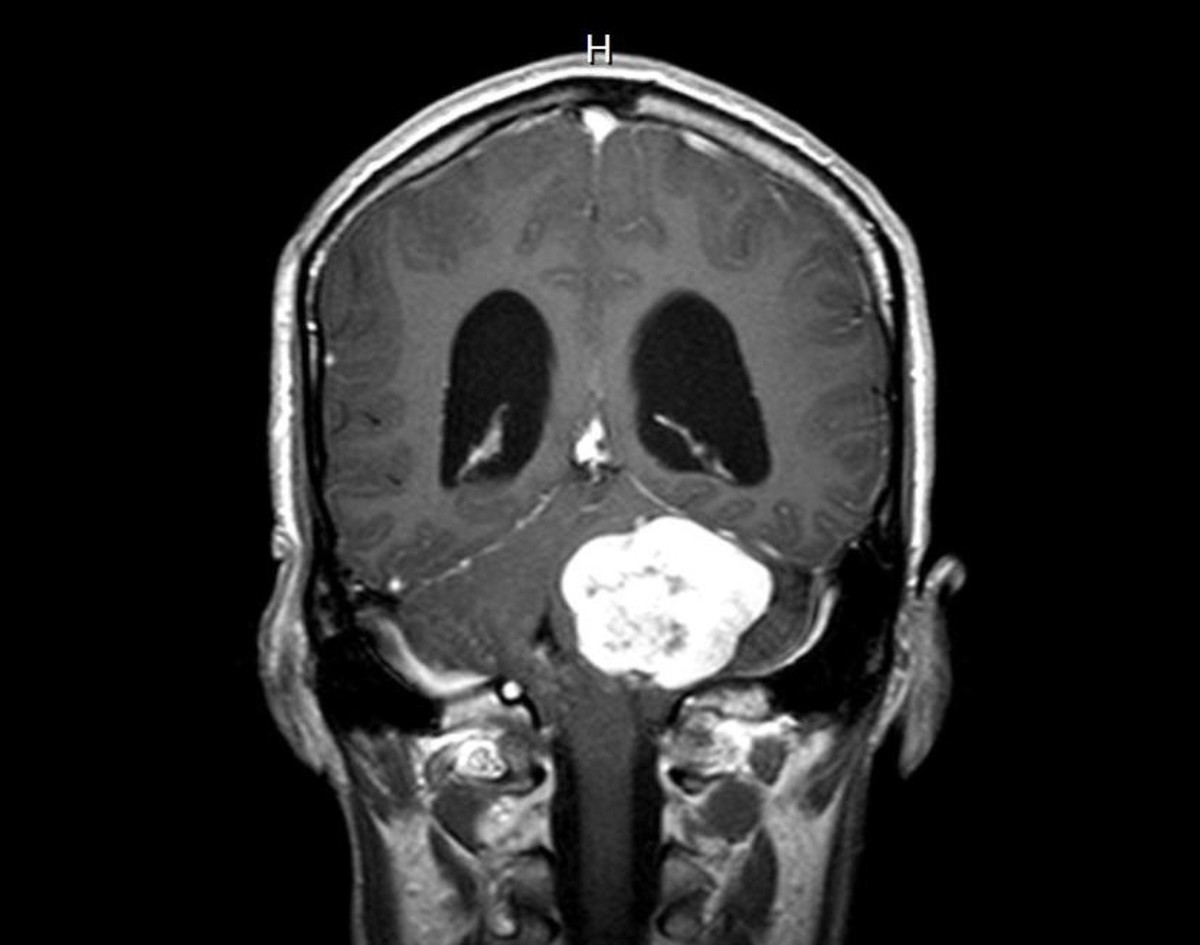
2. Scan using radioactive isotopes.
3. Echosonography.
4. Computed tomography or CT.
5. Magnetic resonance.

How to treat cancer? Part I
Therapeutic measures include traditional surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Many oncologists and cancer researchers worldwide are exploring the usefulness of immunotherapy and the modulation of the biological response.
Surgery: The main strategy for curative treatment of cancer is excision of all malignant cells by surgical intervention. In the past, this involved the excision of all affected tissue and the largest possible amount of tissue potentially affected, including neighboring tissues and lymph nodes. For some tumors, particularly breast cancer, is not precise as ablative surgery (mastectomy) in most cases. Improvements in surgical techniques, knowledge in physiology, and anesthesia in the availability of potent antibiotics and blood products, have led to more limited surgery with fewer sequels and more speedy recovery. However, many cancers are too large at the time of diagnosis. If the extension of local tumor affects neighboring tissues that cannot be resected or if there are distant metastases, surgery is not a curative treatment. However, it may be beneficial for the symptomatic relief of certain conditions such as obstruction, or may have the objective of reducing the tumor mass to allow a better response to chemotherapeutic or radiotherapeutic treatment in the future.
How to treat cancer? Part II
Radiation treatment: Ionizing radiation can be electromagnetic or particulate matter and produce tissue destruction. Electromagnetic radiation includes gamma rays, a form of radioactive emission and x-rays, which occur when an electron beam hits a heavy metal. Radiation beams of particles include electrons, protons, neutrons, and alpha particles (helium nuclei).
The sensitivity of tumors to radiation is highly variable. Tumors, which are easily accessible or are tumors in organs like the uterus in which introducing a source of radiation is possible, it can be cured by radiotherapy. The property of radiation to some extent with normal tissue allows treatment of tumors in locations where surgery is not possible because of the proximity of vital tissues or because the tumor has begun to infiltrate adjacent structures that cannot be sacrificed. Radiotherapy is also frequently used as a palliative treatment, especially in metastasis.
Radiation therapy may be useful as an adjunct to surgery. Preoperative radiation may sterilize the tumor cells rapidly, preventing its spread during the surgery. Doctors also reduce the tumor mass to facilitate the surgery or transform an inoperable tumor operable in another. In other cases, radiotherapy is used in the postoperative period.
How to treat cancer? Part III
Chemotherapy for treating cancer: Chemotherapy consists of the use of drugs for cancer treatment. Since the drugs are distributed in the body through the circulatory system, chemotherapy is useful for those whose tumors have spread out and are inaccessible to surgery or radiotherapy. There are many anticancer drugs, most of which act by interfering the synthesis or function of DNA.
The sensitivity of some tumors to chemotherapy is such that it is possible to cure a high percentage: This happens in uterine cancer, acute leukemia (especially children), Hodgkin's disease and diffuse large cell lymphomas; testicular carcinoma, ovarian carcinoma, small cell carcinomas of the lung, and some childhood cancers. Other advanced cancers have a good response to chemotherapy and can be controlled for long periods. It is frequently used as a palliative treatment.
The two main problems that limit the use of chemotherapy are toxicity and resistance.
Techniques that prevent or control the toxicity and decrease the risk of resistance have been refined. It is important to the establishment of early treatment, use of optimal doses of the drug, repeating cycles with short intervals, if possible, to permit patient recovery from toxic effects.
Hormonal therapy: There are many cancers from tissues that are sensitive to hormonal action, such as breast, prostate, endometrial and thyroid hormone responsive to treatment.