New Treatments for Hepatitis C – Pros & Cons
There is a Cure
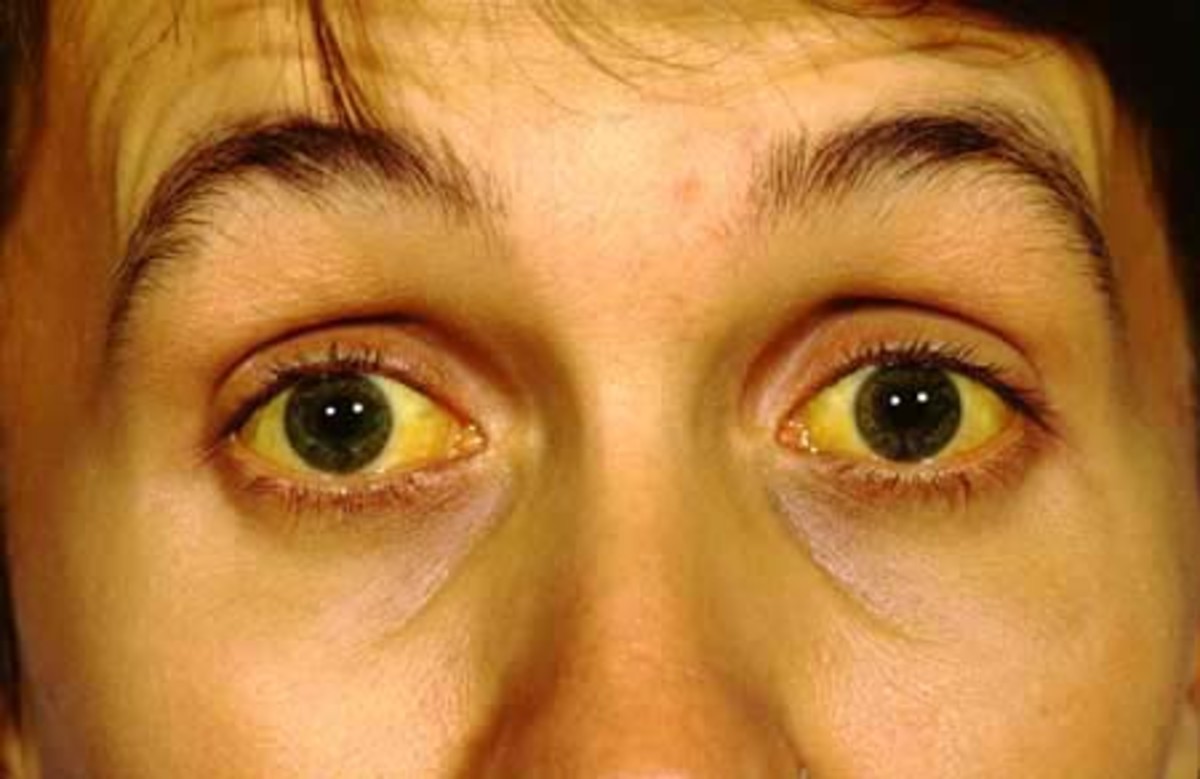
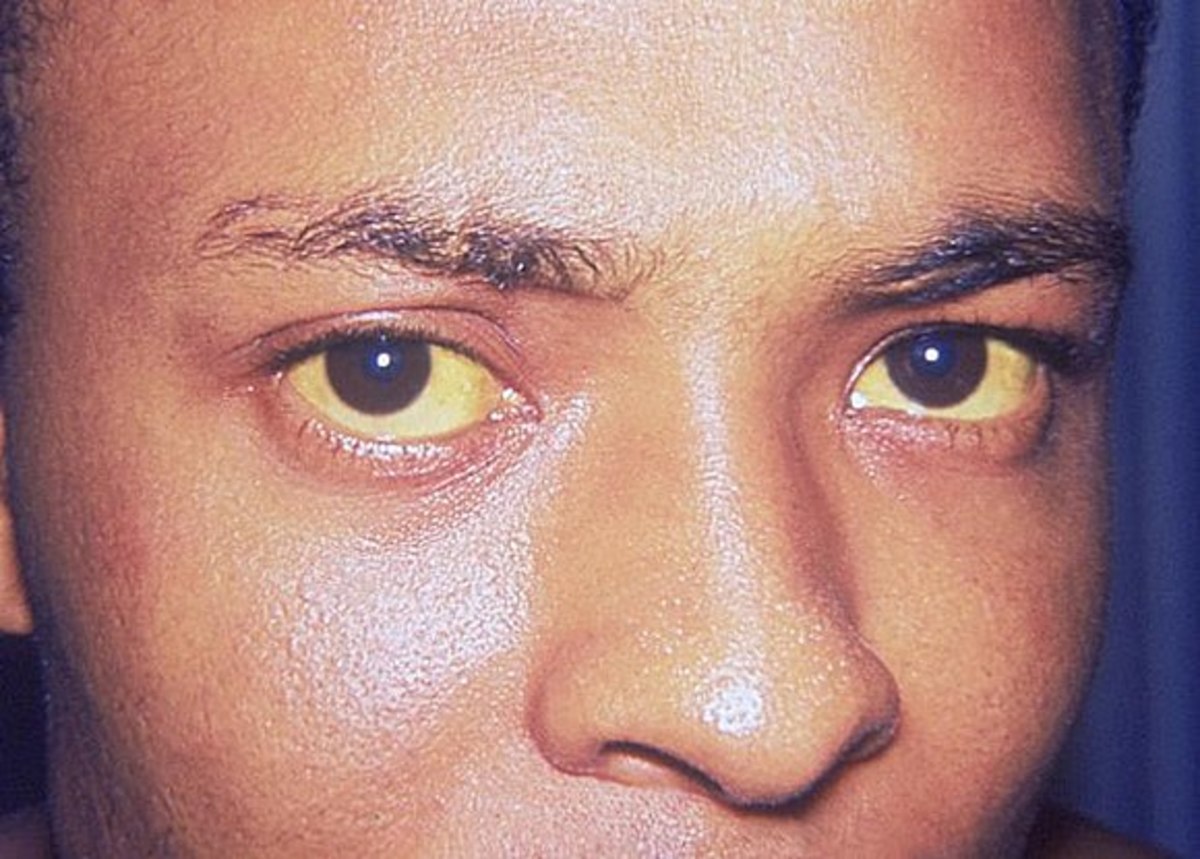
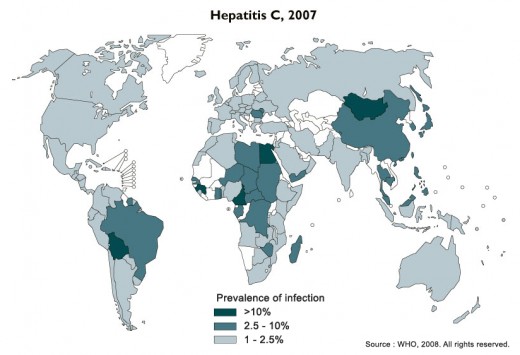
Some three million people in the United States of America are walking around with a serious Hepatitis C infection and haven't a clue that they have it. In the Eastern Mediterranean alone more than 17 million are infected with Hepatitis C. Because hepatitis C's symptoms, jaundice, nausea, stomach pain and fatigue, are easily blamed on something else like a bad burrito, not enough sleep, too much booze or those new fluorescent lights the government made you install at the office, it's easy to go on with your life popping Dramamine and swilling Red Bull and never realize you've developed a Hepatitis C infection. In third world countries, poor health care, poverty and ignorance stoke a growing epidemic of Hep C that may soon overflow into the West.
There is good news on the treatment front, however. In the past 20 years, treatments have changed dramatically. Because the standard treatments just a decade ago, could last a year, be horrifically expensive and have a very low remission rate, doctors used to talk about Hepatitis C treatment in terms of "remission" rather than cure. In recent years, all that has changed.
The Cost of the Cure
Dr. Andrew Aronsohn, assistant professor of medicine at The University of Chicago Medicine points out that a real cure for hepatitis C is within the reach of most hepatitis C patients today. The real barrier Aronsohn sees is "cost and patient access to care.”
One of the newest medications for Hepatitis C, Harvoni, is a one-a-day pill that cures most patients of the disease in just eight to twelve weeks and with few side effects. While treatment is far more effective than it was just a few years ago, all of these new medications are relatively expensive. Some are dramatically costly. Harvoni, one of the most effective of the new drugs, will set you back $1,125 per pill. Over 12 weeks, you can expect your medication to cost you $94,500. Most of the other new drugs are almost as expensive and still come with the usual panoply of side effects. To be fair, compared to some earlier treatment regimens for Hep C, the side effects that come with most of the new drugs are rather less dramatic.
There are several new drugs cued up for approval with the FDA and physicians hope that when these hit the market, the increased competition and choice will drive down the cost of treating hepatitis C dramatically in the next few years. In the meantime, let's look at the pros and cons of some of the current crop of new hepatitis C drugs.
Interferon:
The oldest of the "new" drugs, Interferon was approved in 1991 by the FDA. Interferon is an artificially created version of an infection-fighting substance that human immune system cells produce naturally.
- Treatment with Interferon takes 12 to 18 months of weekly injections.
- The side effects are not pleasant and include flu-like symptoms, blood abnormalities, irritability and depression.
- Despite the length of treatment, interferon used alone only cleared the virus twenty percent of the time.
- Cost of treatment can run from $22,000 to more than $30,000 for a 48 week course of treatment.
A Worldwide Threat

Ribavirin:
Seven years after Interferon came on the market, Ribavarin was approved by the FDA in 1998. Ribavirin is used in combination with interferon.
- In addition to weekly interferon injections, patients take Ribavarin orally twice a day.
- The side effects that come with Ribavarin are also rather unpleasant and include a severe type of anemia that increases the risk of heart attacks and can make existing heart disease worse.
- The treatment takes 48 weeks and cures almost twice as many patients – 40 to 45 percent. Still not a terribly good success rate given the risks associated with the drugs used.
- The cost of ribavirin has come down significantly, costing $1100 to $1700 for a 48 week treatment.
Telaprevir (Incivek/)/Boceprevir (Victrelis):
Approved by the FDA in 2011, telaprevir and boceprevir were the first new drugs that attack the hepatitis C virus directly. They are protease inhibitors, a class of drug that prevents the virus from making copies of itself.
- Taken with ribavirin and interferon, telaprevir and boceprevir treatment lasts just 24 weeks and has a cure rate approaching 80 percent with the telaprevir and 66 percent with boceprevir.
- Telaprevir costs $55,273 for a full course. Boceprevir costs $26,400 for a 24 week course of the drug. Add these costs to the cost of the combined peginterferon ($30,418) and/or ribavirin ($550 to $850).
- Side Effects with telaprevir include nausea/vomiting, a change in ability to taste, rash/blisters, skin or mouth sores, itching, red, swollen, itchy or teary eyes, hemorrhoids, discomfort, burning, or itching around the anus, dizziness/shortness of breath, and tiredness or weakness.
- Side effects with boceprevir include change in taste, decreased appetite, diarrhea, difficulty moving, dizziness, dry mouth, dry skin, hair thinning or loss, irritability, lack or loss of strength, loss of taste, muscle pain or stiffness, nausea, pain in the joints, rash, trouble sleeping, and vomiting
Prevalence of Hepatitis C
Support World Hepatitis Awareness
Olysio (simeprevir):
Olysio, a once-a-day pill was introduced in November 2013 and was approved for use with interferon and ribavirin therapy.
- Approved to treat hepatitis C genotype 1, the triple-combo therapy cured 80 percent of patients in 24 weeks.This cure rate included patients for whom other drug therapies for hepatitis C had failed.
- A full 24 week course of treatment will set you back $66,360, just for the drug.
- Common side effects include skin rash, itching, nausea, muscle pain, and indigestion.
Sovaldi:
Approved just a month after Olysio, Sovaldi is also a combination therapy with ribavirin or interferon.
- Taken once-a-day, a two-drug combo course of Solvadi lasts only 12 weeks.
- Some physicians have gone off label to prescribe a combination of Solvadi and Olysio instead of the usual interferon/ribavarin combination, hoping to avoid the harsh side effects of the older drugs.
- Unfortunately, one of the "side effects" of this two-drug therapy is that it costs close to $150,000 for a course of treatment.
- Solvadi combined with ribavirin also offers a treatment strategy for patients with hepatitis C genotype 2 and genotype 3.
- Patients with the very rare hepatitis C genotype 4 require treatment with both interferon and ribavirin in addition to Sovaldi.
- Most of the common side effects with Solvadi may also be in part due to the combination with ribavirin or interferon and include fatigue, headache, nausea, insomnia, and anemia.
Treatment Price Tag
Harvoni:
In October 2014, the FDA approved Harvoni. The drug combines sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) and ledipasvir.
- A 12 week treatment with Harvoni alone demonstrated a cure rate of better than 90 percent among individuals with hepatitis C type 1.
- In patients who have never taken an antiviral drug like Harvoni, physicians are seeing complete cures in just eight weeks.
- Harvoni is, as we pointed out earlier, very expensive and though designed to cure the most common version of Hepatitis C, the cost ($94,500 for 12 weeks) can be prohibitive for most patients and not all insurance companies will cover treatment with Harvoni.
- The most common side effects with Harvoni include fatigue, headache, nausea, diarrhea, and insomnia.
Viekira Pak:
Just two months after Harvoni, the FDA approved Viekira Pak for treatment of hepatitis C, genotype 1.
- Viekira Pak is interferon-free and can be used with patients with cirrhosis of the liver.
- Taken orally, Viekira Pak combines ombitasvir, paritaprevir, and ritonavir pills, with dasabuvir pills. Ribavirin may also be combined with Viekira Pak as well.
- The treatment takes 12 to 24 weeks, and has a better than 95 percent success rate.
- The cost of treatment is between $83,319 and $166,638.
- Side effects, while not severe, include fatigue, nausea, itching, skin reactions, insomnia, and weakness.
Summary
Like any treatment for particularly difficult to cure diseases like hepatitis C, treatment choice is a balancing act between cost and effectiveness. Always talk to your doctor about both aspects of treatment before deciding which way to go. It's better to know what you're getting into with any course of treatment.