- HubPages»
- Health»
- Health Care, Drugs & Insurance»
- Prescription & Over-the-Counter Drugs
list of Biologic drugs and DMARDs ( Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs ) used for Autoimmune disease treatment


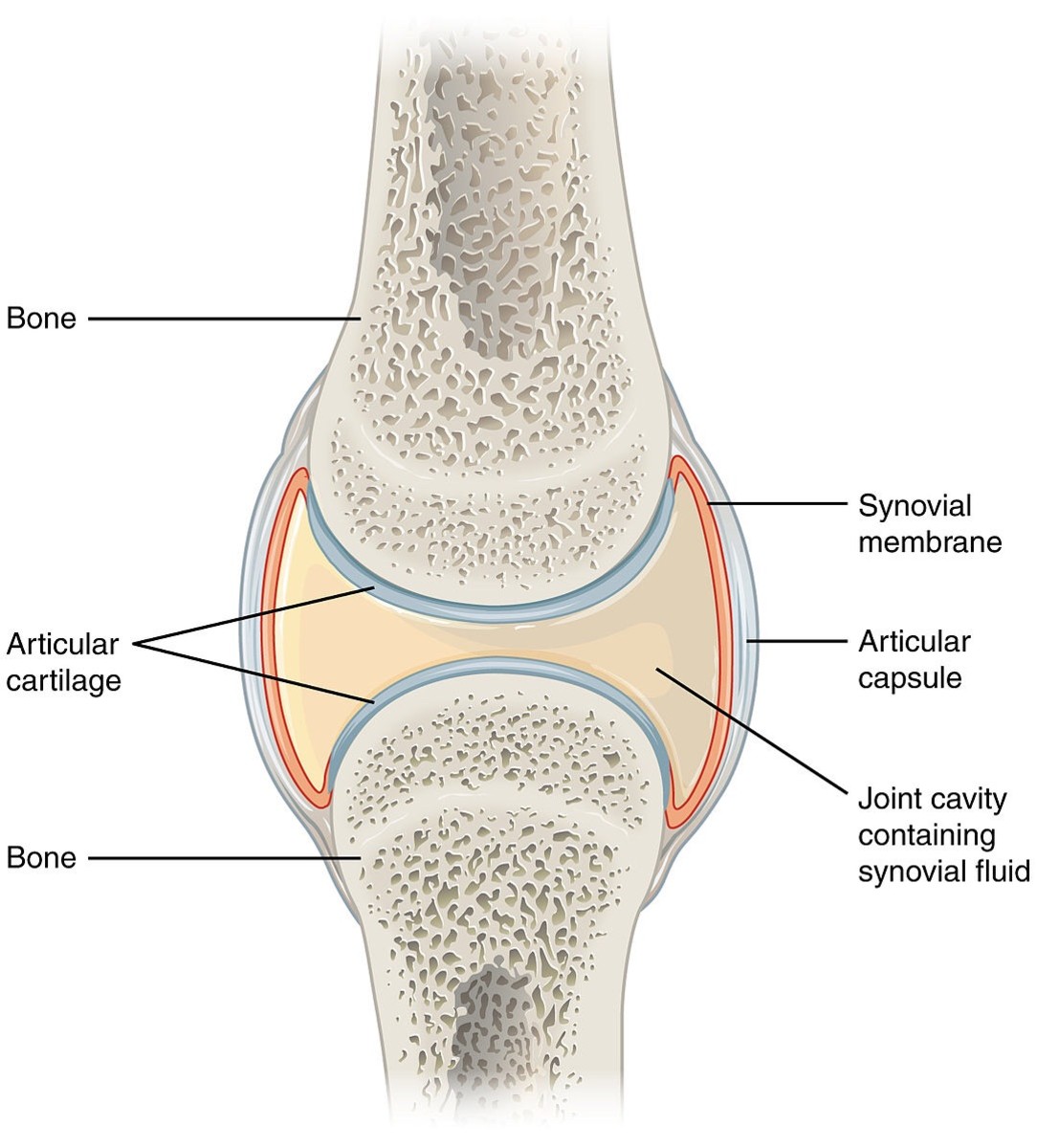
These biologic drugs are specifically engineered molecules designed to block particular immunologic activation steps involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and psoriasis. These conditions involve the actions of various cellular components, including lymphocytes, macrophages and Bcells, and secreted compounds, such as interleukins, tumor necrosis factor, and other cytokines. The agents themselves include monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) and fusion proteins, which are directed against proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and the interleukin (IL) receptor and selected cell surface markers on immune cells, such as cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 immunoglobulin (CTLA-4-Ig) and CD20.
As of May 21, three monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapeutics had been granted their first approval in 2014. Ramucirumab (Cyramza®), siltuximab (Sylvant®) and vedolizumab (EntyvioTM) were approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Rituximab is used in combination with glucocorticoids for treating anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis.
Cyclophosphamide is used to treat lupus, vasculitis and myositis. It's occasionally used for severe rheumatoid arthritis.
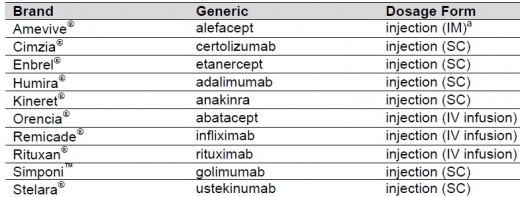
NICE ( The UK's National Institute for Health and Care Excellencerecommends adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab as possible treatments for people with autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, have already tried methotrexate and another disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD), and have 'active' rheumatoid arthritis, as assessed by a rheumatologist on two separate occasions. People who are treated with adalimumab, etanercept or infliximab should normally also be given methotrexate. If methotrexate does not suit them, they may be given adalimumab or etanercept on its own.
certolizumab pegol (Cimzia®): is prescribed for restricted use within NHS Scotland. Indication under review: in combination with methotrexate, for the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis in adults when the response to previous disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) therapy has been inadequate. Certolizumab pegol can be given as monotherapy in case of intolerance to methotrexate or when continued treatment with methotrexate is inappropriate. SMC restriction: Use in patients whose disease has not responded to adequate trials of at least two standard DMARDs either individually or in combination.
There have been several technology appraisals for the use of biologics for active RA. These are:
• TA130 - Rheumatoid arthritis - adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab,
• TA186 - Rheumatoid arthritis - certolizumab pegol
• TA195 - Rheumatoid arthritis - drugs for treatment after failure of a TNF inhibitor
• TA198 - Rheumatoid arthritis – tocilizumab
• TA225 - Rheumatoid arthritis (after the failure of previous anti-rheumatic drugs) – golimumab
• TA234 - Rheumatoid arthritis - abatacept (2nd line)
Note; TA or Technology Appraisal codes are used in England by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence.
For some medicines, the dose is determined by bodyweight, and an average bodyweight of 70 kg for patients was used, as per the NICE assessment “Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure of a TNF inhibitor.
Methotrexate (MTX) { Teva markets Methotrexate} is one of the most popular and safe
antirheumatic drugs under the applied treatment dose. In order to obtain a better curative effect in clinical cases, MTX is also used in combination with other drugs for rheumatoid arthritis and lupus treatment. In addition, MTX is also used as an anticancer drug. Recently, MTX has been widely applied
for the treatment of various cancers, such as hepatoma, osteosarcoma, leukemia, lymphoma, gastric, breast, head and neck cancers.
Tuberculosis (TB) is the most commonly reported opportunistic infection associated with the TNF-á blocking biologic drugs.