Mumps symptoms in children

Mumps symptoms in children
The classic mumps symptoms in children are:
- Prodroma: the symptoms are preceeded by fever, headache and weakness.
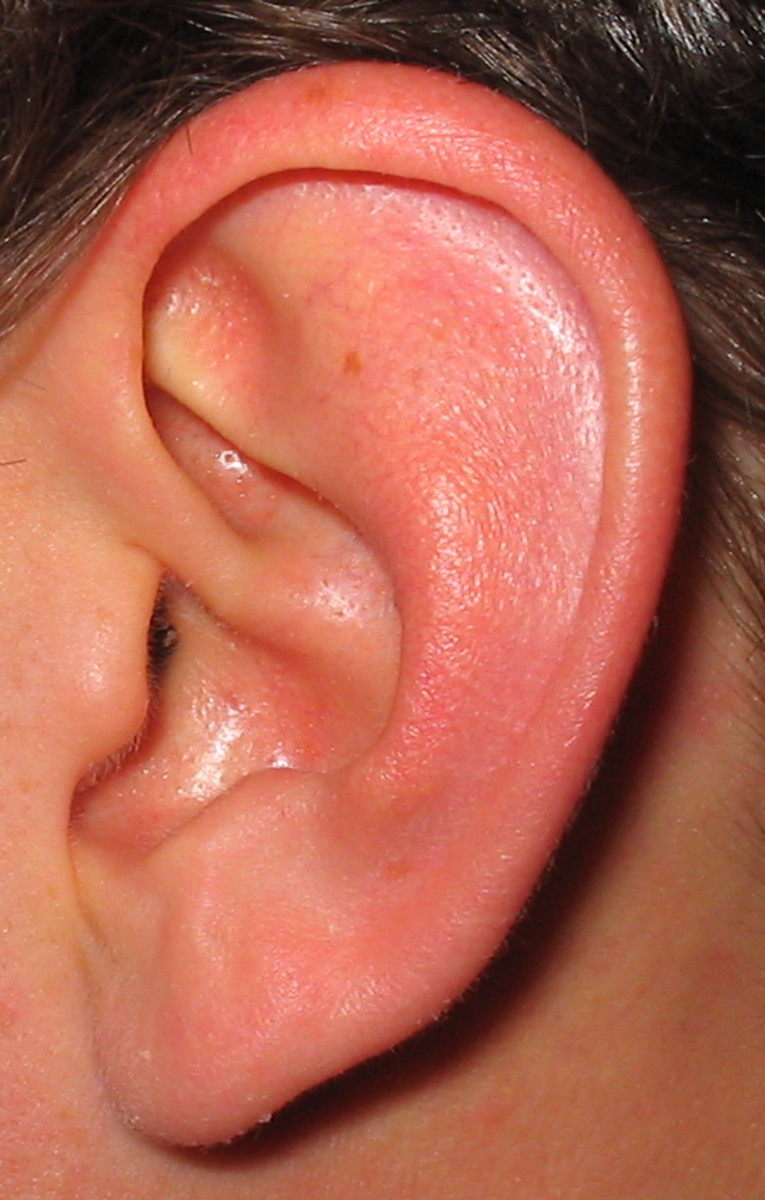
- Enlargment of the parotid gland: it is a salivary gland that lies behind the angle of the mandible and it pushes the ear lobule upwards and forwards. The inflammed gland is painful and tender to touch. The pain increases on chewing or eating sour foods.
The swollen parotid gland is back to normal within 5 days to a week. Other salivary glands may be enlarged such as the sublingual or the submandibular glands.
The disease is caused by a viral infection with the mumps virus. It is transmitted as a droplet infection from cough, sneezing and respiratory secretions of infected persons.
The patient remains infective to others for 10 days from the onset of parotitis (inflammation of the parotid gland).
Diagnosis:
-By detection of the virus itself in salivary secretions
-Increased antibodies titre in the blood.
-High serum amylase.
Prevention and treatment of mumps
Mumps is prevented by active immunization with MMR vaccine which gives life lon immunity.
Treatment of mumps:
Mainly symptomatic treatment:
- Bed rest for a week.
- Diet: By eating soft food. Avoid sour or spicy food.
- Fever reducer and analgesics for pain.
- Cold compresses on the cheeks.
- Treatment of complications:
Some of the serious complications are inflammation of the testis, meningoencephalitis, pancreatitis, arthritis and others.
Orchitis (inflammation of the testes) are more common in adults and can even cause sterility if not treated. In children, Meningio-encephalitis is the most common complication of mumps.