Remembering When Russia Ran Its Own Candidates in American Presidential Elections
Authorities Moscow Used to Select Their Own Candidate for U.S. President & then Fund His Campaign
As Congressional Democrats and their media allies await Special Prosecutor Mueller’s recently submitted, but not yet released, report on the supposed Russian interference in the 2016 election, it is worth looking back on Russia’s extensive activity in America Presidential politics from the 1920s to the 1980s.
The Russian government’s spending some $300,000 on social media activities attempting to disrupt the 2016 Presidential campaign was pocket change compared to the millions of dollars’ worth of political campaign and other propaganda activities in the United States during and before the Cold War.
Russia Began Interfering in Foreign Elections Following the 1917 Communist Takeover
The story begins in the summer of 1917 when a left wing journalist and member of the American Socialist Party named John Reed accepted an assignment to travel to Russia and cover events occurring in that country (Warren Beatty played John Reed in the 1981 film Reds much of which took place during Reed’s sojourn in Russia during and after the 1917 Communist takeover).
World War I was still raging and Russia was still fighting along with Great Britain, France, the United States and other allied nations against Imperial Germany and the other Central Powers in that war. Russia suffered badly in the war and in February of 1917 Czar Nicholas II was forced to abdicate and the monarchy replaced by a weak parliamentary government.
When John Reed arrived in Petrograd (St. Petersburg), which was the capital of Russia at that time, the city and the country were in turmoil. The war was continuing to go badly for Russia, the economy was collapsing and political turmoil was increasing.
The weak Parliamentary government under Prime Minister Alexander Kerensky was under assault by Vladimir Lenin’s Bolsheviks and other far left radical groups.
Reed ended up working closely with radical left wing groups opposing the government and in the process made close contacts with many top Bolsheviks in Lenin’s organization. His reporting reflected far left views that he shared with the Bolsheviks.
John Reed Was in Petrograd When Vladimir Lenin and his Bolsheviks Overthrew the Government
John Reed was present and covered the October 24-25, 1917 Bolshevik uprising which ousted the liberal Kerensky government and replaced it with a Communist dictatorship under Vladimir Lenin.
Reed remained in Russia following what became known as the October Revolution. He continued to report on the events unfolding in Russia while, at the same time, was developing a close working relationship with Lenin and the Bolsheviks.
John Reed - American Journalist and Socialist Activist

Reed Breaks With American Socialists and Founds and American Communist Party
John Reed returned to the United States in 1919 where he became active in the left wing of the American Socialist Party.
In August of that year the radical left wing of the American Socialist Party split off into two parts with the first being the Communist Labor Party of America led by John Reed and Benjamin Gitlow, and the second being the Communist Party of America
It wasn’t long before Reed and Gitlow were ordered by Communist Party leaders in Moscow to merge the two communist parties and purge all those not willing to follow orders from Moscow. This became the Communist Party of the U.S.A. or CPUSA.
Vladimir Lenin forms the Communist International (Comintern) to Spread Communism to Other Nations
Shortly after taking power and while the country was still engulfed in civil war between white (supporters of the monarchy) and various red (communist and other radicals) forces, Lenin formed the Comintern (also known as the Communist International) with the intent of recruiting intellectuals from around the world, like Reed, and providing them with funds to lay the groundwork for communist revolutions in their home countries.
Part of the effort involved public propaganda activities and the formation of communist parties to run candidates in elections in their home nations. A second level of effort involved setting up front organizations that hid the fact they were communist as well as recruiting and funding spies for Russia.
Front organizations were charged with underwriting publishing efforts that secretly supported communist ideals and goals without identifying their communist backing (i.e. fake news), working their way into influential positions in government (ex. U.S. State & Treasury Department Officials Alger Hiss and Harry Dexter White, the infamous Cambridge Five group in the British MI6 Intelligence organization are but a few examples), universities and other organizations.
All of these activities were designed to undermine government and civil institutions in other nations with the objective of fermenting Soviet style revolutions to turn them into communist states like Lenin and his Bolsheviks had done with Russia.
Vladimir Lenin the Russian Communist Leader Who Led the Communist Bolsheviks in their Victory in the October Revolution.

John Reed Returns to Russia Where he is Given $2 Million in Gold to Underwrite Subversion in America
In October of 1919, using a forged passport, John Reed left the United States for Russia to avoid prosecution for violating the Sedition Act of 1918 with some of the articles he had published.
In Russia, Reed again met with Lenin who gave him close to $2 million dollars’ worth of gold, silver and jewels. Communists from other nations also received similar funds with instructions to take the money back home to begin funding both legal political activities as well as secret subversive activities in their home countries.
It is not known what Reed did with the nearly $2 million dollars’ worth of treasure he received from Lenin since he died of typhus in October of 1920. He may have given the money to his wife, Louise Bryant, to take back to the U.S. to use to finance communist party activities.
Bryant, who was also a communist, had joined him in Russia and was with him in Moscow when he died.
Body of John Reed's Body Lying in State in Russia

1924 Communist Party of the U.S.A. (CPUSA) Enters Presidential Politics
From its beginning the Communist Party in the United States had no trouble attracting members - during the first half of the 20th Century it had as many as fifty to sixty thousand dues paying members at any given time.
While recruiting members was not a big problem, retaining them was a continual problem which resulted in membership remaining in the fifty to sixty thousand range due to many members becoming disillusioned and quitting the party after a few years.
It was annual funding from Moscow and not member dues which financed the party’s legal and illegal activities. In exchange for funding, Communist leaders in Moscow rigidly controlled all aspects and activities of the CPUSA and parties in other nations, including the selection of its leaders
In 1922 the party dipped its toe in the political waters by running a candidate for a state or local office in New York State. The candidate finished with 311 votes.
Communists Hijack and use the Farmer-Labor Party to Run their First Presidential Candidate
Two years later in the Presidential election of 1924 the party decided to field a candidate for President. However, instead of running as the Communist Party candidate, William Z. Foster, ran, with Benjamin Gitlow as VP, as the candidates of the newly formed Farmer-Labor Party which the communists had infiltrated.
The communist run Farmer-Labor Party was on the ballot in 13 states concentrated along the northern border of the United States from Massachusetts to Washington State. For their efforts the Foster-Gitlow ticket won a total of 36,136 popular votes and no votes in the Electoral College.
The Farmer-Labor Party eventually rid itself of communists but remained a left of center socialist party. The Minnesota branch of the party eventually merged with the Democratic Party to form the present day Democratic Farmer Labor Party of Minnesota.
Communist Party Selects a Black Member as Their 1932 Vice Presidential Candidate
Foster ran again for President with Benjamin Gitlow as his running mate in the 1928 election. In 1930 he ran for Governor of New York State and lost in both races. He ran again for President in 1932, this time with James W. Ford as his running mate.
The 1932 run is interesting for at least 3 reasons:
-
It was the only race in which the CPUSA’s popular vote total was in the 6 figure range (their total was 102,785). In all the other Presidential races the CPUSA ran candidates for President their popular vote totals were mostly in the 3 to low 5 digit range,
-
James W. Ford, the Vice Presidential candidate was black and, as such, was the first Black to run on an American presidential ticket. Ford, a WW I veteran was a clerk in the Post Office where he became active in the Union of Post Office Workers where he came into contact with communists who had infiltrated this and other unions and was recruited by them.
-
Part way through the campaign, Foster had a heart attack and was unable to continue as leader of the party or with the campaign as he left the U.S. and went to the Soviet Union for treatment. He later recovered and returned to resume leadership of the party
After William Z. Foster was forced to step down as leader of the party following his heart attack, the Russian dictator, Josef Stalin, selected Earl Browder to lead the party. Browder ran for president on the Communist Party ticket in the 1936 and 1940 elections.
However, following a policy disagreement with Stalin shortly after World War II, Browder was expelled from the party by Stalin.
Henry Wallace and the Progressive Party
Henry Wallace served as President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s Secretary of Agriculture during FDR’s first two terms, then as Vice President in Roosevelt’s third term and finally as Secretary of Commerce in Roosevelt’s fourth term.
President Roosevelt died on April 12, 1945 early in his fourth term and was succeeded in office by his then Vice President, Harry S. Truman. Wallace was an outspoken opponent of Truman’s hard line against the Soviet Union. This led to Wallace being fired by President Truman in 1946.
Reaching back to the early 20th century, Wallace resurrected the old left wing Progressive Party as a vehicle to run against President Truman in the 1948 election.
This was the period that saw the start of the Cold War with the Soviet Union (i.e. Russia) and United States opposing each other on the international stage and with increased communist propagandizing and espionage activity within the United States on behalf of the Soviet Union.
The Communist Party of the U.S.A. was still a legal political party. However, many of its members, along with members of socialist and other far left groups, sought refuge in the Progressive Party as this was the start of what became known as the Red Scare, the time when the Cold War between the Soviet Union and the free nations of the West began and when a number of American communists were being exposed as Russian agents working to undermine America and its institutions.
In this climate the leaders of CPUSA decided it was prudent to endorse Wallace and his running mate (Democratic Senator Glen H. Taylor of Idaho). It also helped that the Progressive Party was supporting many of the same policies CPUSA supported.
Wallace, Upset With Communist’s Activities, Leaves Progressives & Supports Republicans in 1956 & 1960 Races
Following his loss and, upset by the fact that communists ended up manning and running large parts of both the Progressive Party and his own campaign Wallace decided to retire from politics.
Wallace, like many former communist supporters who had seen the reality of communist rule, abandoned both the Progressive and Democratic parties and supported the Republicans in the 1956 and 1960 elections. In his memoirs Wallace expressed regret for having opposed President Truman’s tough stance against Soviet communism.
In 1952 the Progressive party entered the race for President with Vincent Hillinan, a left wing California lawyer and Charlotte Bass a black, female civil rights activist. The CPUSA again endorsed the Progressive party and many of its members were active managing both the party machinery and the campaign.
Political Environment Not Good for CPUSA in 1950s and 1960s
Investigations by the Congressional House Un-American Activities Committee along with increased enforcement of both new and older existing national security laws helped to depress membership in the Communist Party.
Other events such as Russia’s brutal suppression of the 1956 revolt in Hungary and, news reports regarding Russia’s oppression of both its own people as well as those in east European nations it occupied following World War II resulted in many others becoming disillusioned and leave the party.
These and other factors resulted in the CPUSA not fielding a candidate in the 1956, 1960 and 1964 U.S. Presidential elections.
Keeping a lower profile and not running candidates for President was a decision made by the party. Despite rising anti-communist feeling and the threat of the Cold War becoming a hot nuclear war between the U.S. and Russia, the CPUSA was still a legal political organization in many states.
In 1968 the CPUSA re-entered presidential politics with Charlene Mitchell an African-American and feminist activist who now has the distinction of being the first African-American woman to run for President. Her running mate was a 23 year old party member named Michael Zagarell who was the party’s National Youth Director at the time.
Even though Michael Zagarell’s age was 12 years short of the Constitution’s 35 year minimum age requirement for President the couple managed to make it on the ballot of two states (it appears that they ran under the banner of the Communist Party of the USA in two states and in two other states under the banner of different parties – with a total of 1,077 from the 4 states).
Gus Hall (born Arvo Kustaa Halber) – the Last CPUSA Candidate to Run for President
Born in 1910, Arvo Kustaa Halber was the son of Finish immigrant parents who lived in Northern Minnesota. His parents were involved in radical left political activities both before and after immigrating to the U.S. They joined the CPUSA when it was founded in 1919.
One of ten children in the family Arvo went to work at age 15 to help support the family. Two years later in 1927 at age 17 his father recruited him into the Communist Party where he became an organizer in the party’s Young Communist League.
Four years later in 1931 young Arvo accepted an offer by the Party to send him to the International Lenin School in Moscow. This was a school operated by the Russian controlled Communist International (Comintern) from 1926 to 1938 and was used to train foreign communists in the use of both legal public as well as illegal underground activities designed to spread communism around the world.
Upon completion of his studies in Moscow, he returned to the U.S. where he continued his work as a member of the CPUSA.
In addition to legally changing his name from the Finish Arvo Halber to its American equivalent of Gus Hall, he worked full time for the Party (which included going to Prison more than once), serving in the U.S. Navy during World War II and rising to become General Secretary of the CPUSA in 1959.
1954 Photo of Arvo Kustaa Halber aka Gus Hall
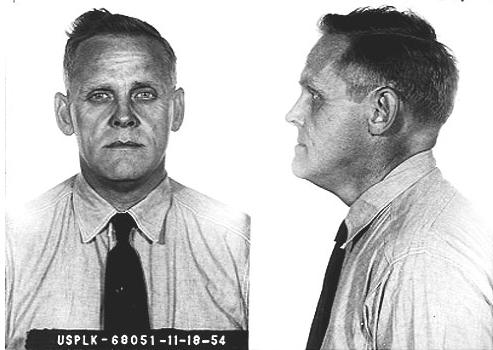
While Communist Parties in Western Europe began to liberalize and started disagreeing with the Party line out of Moscow, Hall remained steadfastly loyal to the party in Moscow supporting and defending their crackdown on dissidents in both Russia and their East European satellite states, the invasion of Afghanistan and other atrocities condemned by the non-Communist world.
Hall ran, unsuccessfully, for President in the 1972, 1976 (the year former Obama CIA Director John Brennan voted for Hall), 1980 and 1984 elections.
Following the 1984 election the CPUSA ceased fielding candidates in all but occasional local races. The reason was money and not the almost century long string of defeats.
After almost three-quarters of a century of socialist economic mismanagement the Russian economy collapsed. And, without the millions of dollars from Russia that the CPUSA had relied on to fund their electoral and other ventures in the United States the Party was barely able to pay the rent and staff in its New York City Headquarters let alone fund Presidential campaigns.
How Russia Was Able to Run Presidential Campaigns for 6 Decades
The answer to this is twofold. First, until recent decades managing elections was, and to a large extent still is, left to the 50 states and territories. Secondly, there were not as many laws and regulations regarding bringing large sums of cash in suitcases into the country as there are now.
When the Constitution was drafted most of those doing the drafting didn’t envision the rise of political parties at the national level – in fact many actually opposed the idea of national political parties.
While political parties emerged early in the nation’s history, the number of national parties has been limited to two for most of our history.
With fifty separate states setting their rules and regulating elections, the financial, legal and logistical resources needed to field a national Presidential election make it almost impossible for more than two large parties with nationwide membership to undertake the running of a national Presidential election.
In the 2016 Election 35 Parties Ran Candidates for President
According to the WikiPedia article on the 2016 Presidential Election three parties (Republican, Democrat and Libertarian) were officially on the ballot in all 50 states. Three others (Green Party, Independent and Constitution Party) were on the ballot in most, but not all 50 states, and also managed to win 100,000 or more votes.
An additional 29 other parties fielded 27 candidates (a couple of them ran as candidates of different parties in other states). The candidates of the Constitution Party of Idaho received a total of 4 votes in Idaho (probably the votes of themselves and their spouses) along with 71 write-in votes from states where they weren’t on the ballot but were states that allowed write in votes.
U.S. Department of Justice and FBI Closely Monitored CPUSA From Its Founding Until End of Cold War
While creating a political party, even radical extremist ones like CPUSA, is not illegal under Federal law or the laws of many, if not all, states other, non-political, activities such as espionage, sabotage, violation of the Sedition Act of 1918, etc. for which some of the funding from Russia were used, were illegal.
Communist leaders and activists from John Reed to Gus Hall were arrested and imprisoned, often more than once during their careers.
Interestingly the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) was monitoring the activities and leaders of the CPUSA from John Reed to Gus Hall.
Knowing that Federal Agents were waiting to arrest him on return to the U.S. following his 1919 trip to Russia, John Reed delayed his plans to return – while waiting in Russia he contracted Typhus and died in Russia in October 1920.
Following the end of the Cold War many records relating to the FBI’s surveillance of the CPUSA’s illegal activities were declassified revealing the extent of the FBI’s surveillance of the party, its activities and its funding.
Throughout his Long Career J. Edgar Hoover Focused on Monitoring Communists and Other Radical Political Groups
J. Edgar Hoover who joined the Justice Department in 1917, was suspicious of and opposed to radical left groups. During his tenure, first in the Department’s War Emergency Division and later in other divisions dealing with foreign and domestic threats to the nation, he spent much of his time on cases dealing with real or perceived threats from these groups.
He continued this focus after becoming the Director of the Bureau of Investigation in 1924 which became the FBI, with Hoover as Director, in 1935.
From John Reed in 1917 to Gus Hall in the 1980s Hoover and his lieutenants kept a close eye on the party and its members.
However, it wasn’t all just watching and monitoring. The FBI had agents who were infiltrated into both the party itself as well as into underground cells involved in espionage, sabotage and other illegal activity. In addition to its own agents, the Bureau also turned members of the party into double agents whom they relied on to both provide information as well as spread disinformation.
The Bureau and other law enforcement also made arrests. As mentioned above many members, including those who ran for President and other elected offices. It should be noted that a criminal record does not prevent someone from running for President (Eugene V. Debs ran for President 5 times not only despite a previous stint in prison but in his last attempt in the 1920 election he campaigned from a cell in the Atlanta Federal Prison where he was serving time for violating the Sedition Act of 1918).
The goal of the FBI not so much arrest statistics as it was to prevent Russia from undermining our institutions and installing a communist dictatorship via coup or revolution as Vladimir Lenin and his Bolsheviks done in Russia or by making way for a successful military conquest of our country by Russia.
© 2019 Chuck Nugent