The Genetically Modified Food Debate
What are Genetically Modified Foods?
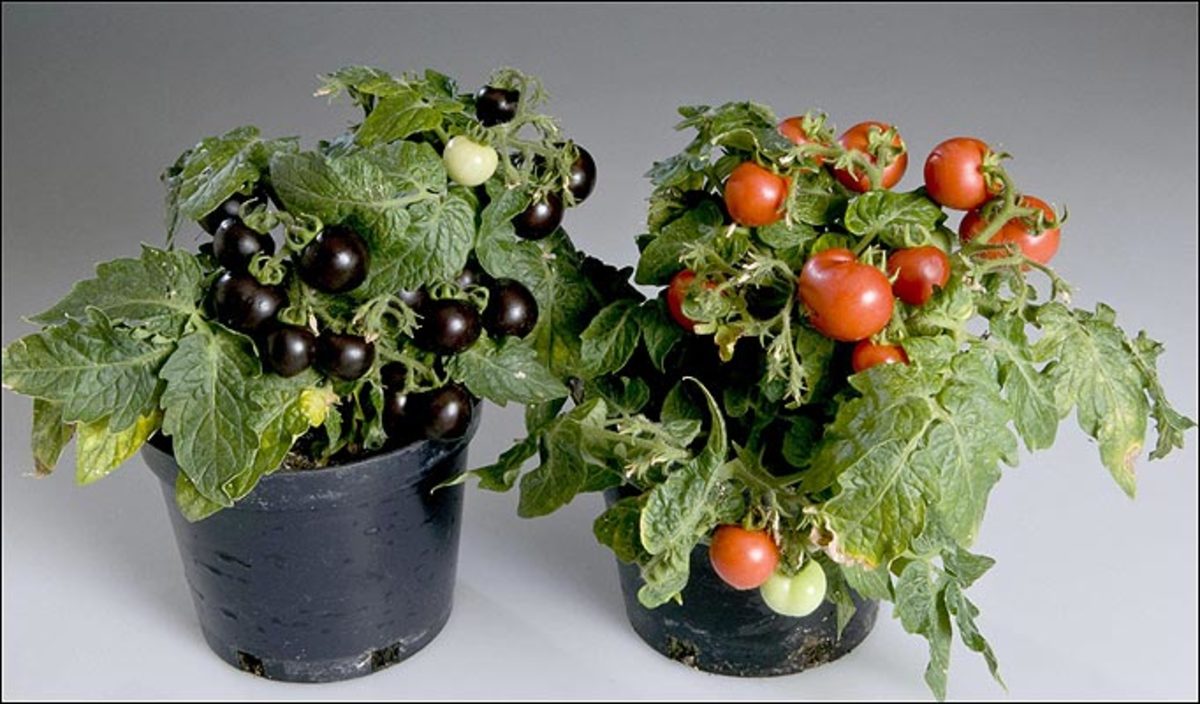
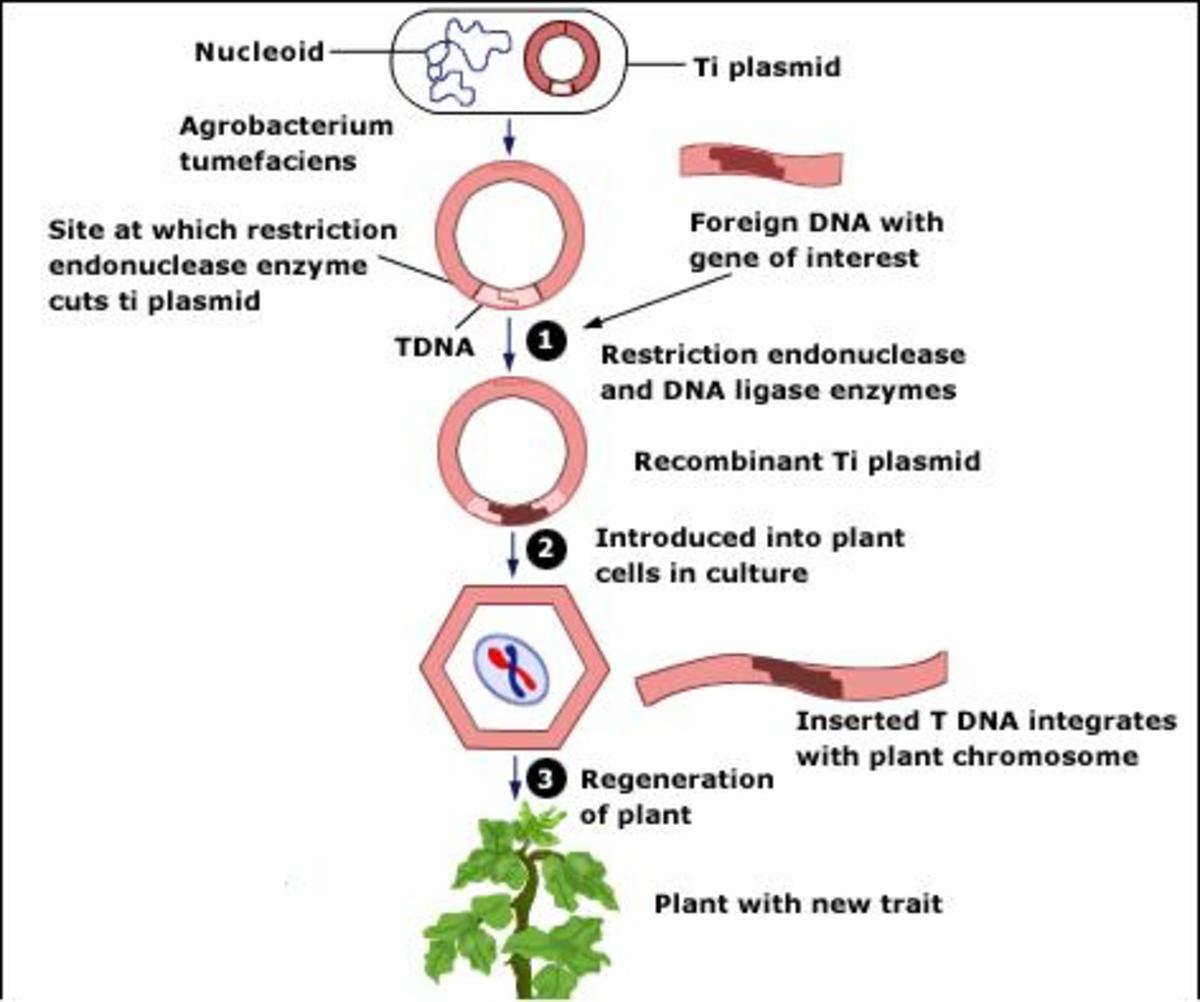
The objective of genetic modification (GM) is to introduce desirable traits in an organism. Genetic modification of food has been practiced for centuries through conventional selective cross breeding. With great advancements in technology, genetic engineering is now used to improve food quality. Genetic engineering involves the transfer and removal of genetic material (DNA), enabling selected genes to be transferred between related and non-related organisms (the transference of genes between non-related species is only possible with genetic engineering).
Using conventional methods of gene modification, the desired traits are formed from naturally occurring variations in genetic composition of organisms, whereas genetic engineering makes it possible to alter genetic material in ways that do not occur naturally. Hence, the advantages of genetic engineering include a greater scope for the development and improvement of food products. However, the alteration of genetic material in ways not found in nature has ignited public debate over the health, safety and environmental implications of GM foods.
Safety, Health, Environmental, Social & Ethical Concerns
The safety assessment process of GM foods generally covers toxicity, risk of allergic reactions, stability of inserted gene, nutrition or toxic properties associated with gene modification, and unintended effects from gene insertion. The testing of GM foods has not been without criticism and has its limitations. There are concerns as to whether basing a safety assessment on substantial equivalence is rigorous enough. Substantial equivalence works under the assumption that if a GM food product has the same composition, functional characteristics, nutrition value, taste and smell to its non-GM counterpart, it is deemed not significantly different. Consequently, only the GM ingredient is tested and not necessarily the GM food. In addition, current toxicity testing is based on known toxins.
The main issues for human health include the transfer of genes from common allergic foods and the transference of genes from GM foods to cells in the body or bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract, potentially resulting in unanticipated changes in cell function.
A major environmental concern is the mixing of genes from GM plants into conventional crops or other species in the wild. An example of this occurred in the United States when a maize type intended only for feed appeared in maize products for human consumption. Separation of GM crop fields from conventional crop fields has been implemented to reduce mixing.
Soil damage and harm to insects is another concern. Research suggests that GM plants engineered to produce the Bt pesticide release toxins into the soil through the plants’ roots, thereby posing a threat to insects and other organisms in the ecosystem.
Debate exists as to whether the introduction of pesticide producing GM crops will increase or decrease the use of pesticides; some have argued that the pests’ continue exposure to the toxins from pesticide producing crops will promote their resistance to it, leading to the use of stronger toxic chemicals to combat them and the emergence of superpests.
Social and ethical concerns include the potential domination of large multinational companies involved in the distribution of GM seeds, philosophical and religious disagreements with the use of genes from animals in plant foods, the adverse effect on animal welfare from the use of GM growth hormones, and the patenting of GM organisms which suggests that life is a commercial commodity.
GM foods are relatively new to the market and at this stage only its short term effects have been investigated. Longitudinal studies are required to uncover any long term and unforeseen effects. So far there hasn’t been any health or environmental catastrophes from GM foods or ingredients. Continual surveillance on safety (humans and the environment) and the improvement and development of post-marketing methods will enable a greater understanding of its risks and benefits.
Advantages
With global concerns such as an increasing population and climate change, the use of genetic engineering for food production is becoming an attractive option. Potential benefits of gene modification and the application of genetic engineering include plants that can withstand extreme weather conditions, food with greater longevity and nutritional value, food with medicinal benefits, inexpensive foods, improved crop nutrition and quality, and crops resistant to disease and insects hence requiring less chemical application.
GM Food Labelling
The increasing availability of Genetically Modified (GM) foods is subject to intense scrutiny from the community, who continue to debate over its health, safety, environmental, security, social and ethical aspects. Thus, the labelling of GM foods is an important element in assisting consumers with making informed decisions. Legislation has been mandated in some countries and varies from country to country. For example, in the United States and Australia labelling is compulsory when GM foods have significantly different nutritional properties compared to similar non GM foods, contains an allergen unexpected amongst consumers and toxins beyond acceptable levels. In the United States there are no labelling mandates on food products outside the aforementioned parameters. In Australia, labelling is also compulsory in instances where at least 1% of genetically modified ingredients are present as a result of accidental contamination to conventional foods (this legislation is also mandated in the EU). In response to consumer demand and in protest against GM foods, some food manufacturers are providing GM-free or organic foods.
Consumer Perception & Acceptability
Consumer surveys conducted on the perception of GM foods highlight the skepticism regarding the credibility of GM foods, with consumers more focused on the risks and overlooking the benefits. The lack of consumer confidence can be attributed to the lack of knowledge and understanding about the GM foods in terms of the basic science and biotechnology methods involved, and its advantages and disadvantages.
In 2006 The Pew Initiative on Food and Biotechnology interviewed 1,000 American consumers on their opinions on GM foods, with only 27% of consumers in favour of GM foods. The survey also highlighted the uncertainty surrounding the safety of GM foods with 34% believing it was safe, 29% unsafe and 37% have no opinion; however, with the provision of further information 45% felt that GM foods were safe and 29% unsafe. The survey also indicated that consumers turned to friends and loved ones as trusted sources of information and cited biotechnology companies, food manufacturers, government regulators and news media as least trustworthy. Similar survey results were echoed in the GM foods attitude survey conducted in 2008 by Swinburne University’s National Science and Technology Monitor (interviewed 1,000 Australian residents) and by the Biosciences Department at the University of Nottingham in the UK in 2005 (surveyed 180 people from the general public, bioscience and non-bioscience students). The surveys indicated that the majority of respondents were uncomfortable with the idea of using genetically modifying plants for food and had little trust in institutions responsible for its commercialisation.
An important step forward in the area of consumerism of GM foods is the need for greater transparency and communication from organisations and institutions responsible for its development, production and commericialisation regarding its risks, costs and benefits. The provision of reliable and trustworthy information will be crucial to eliminating the uncertainty attached to GM foods.