Why he's just not that into you - 2 quirks of human mating you can't afford to ignore while looking for a partner.


You meet Mr. Right, yet things don't work out?
You meet a guy who really excites you and gives you that "weak in the knees" feeling. You just cant stop thinking about him, call him and seek contact with him. You stalk him on social media. When you have sex, it is HOT - sparks and fireworks, instant chemistry and you rarely have felt anything like that with another man. Could it be a dream come true?
Then his attitude changes, he grows distant and cold. As you attempt to get closer to him, he grows irritated and breaks all contact.
Sounds familiar? If so, this hub is for you, as I will reveal to you the secrets of human mating, as discovered by the science of Evolutionary Psychology.
Meet Evolutionary Psychology
A breakthrough in the understanding of human nature occurred in the early 1990s. A series of experiments revealed that the human mind is not a blank page, as assumed by earlier psychological models. We do not learn everything we know from our parents. Instead, the human mind is a series of exquisite evolutionary adaptations to solve the problems of survival and reproduction of the species.
We are born with built-in knowledge of how to be a human and function in human society. This knowledge and preferences act like an "auto pilot" that guides you through life.
What are some of these preferences? A human mind can intuitively make the following choices:
- Where to live (we prefer prefer lush greenery, sound of running water and elevated dwellings to flat brown desert or concrete jungle)
- What to eat (we prefer high sugar, high fat, high calorie density food like cake to bland tasteless food like oatmeal)
- Who to mate with (we prefer fit, healthy and attractive people to deformed and unattractive people)
- How to communicate emotion (from explosive anger to submissive tears)
Nobody teaches us these preferences, we inherited them from our ancestors and they are active for our entire lives. This article focuses on human mating preferences and how they relate to finding mates.
Attractiveness - Beauty - as proxy for DNA mutation loads
As our cells divide and are bombarded by cosmic radiation, our DNA accumulates mutations. Some of these are beneficial and make us into a different species from apes, while most of the mutations are dangerous mistakes. Our bodies are robust and mitigate the impact of some of these errors, but accumulating them gets more dangerous over time.
Let's take a 15 year old car as an analogy - over its lifetime, an old car has accumulated some defects - rust, scratches, leaks, tears in fabric. If we are to take a sophisticated cloning device to create an exact copy of this car, it would inherit these defects. Because car with defects is less valuable than a brand new one, we can say that one car is more beautiful than the other. If we keep cloning this car and using it, it would degrade and become unusable in just a few generations. If we average this car with another car, the result is much more stable.
It is estimated that an average human has about 300 mutations among our 20000 genes. Because these DNA mutations are at best neutral and at worst harmful, humans have evolved a mechanism to help visually distinguish counts of mutations in each other's DNA. We call this beauty - an inherent, intuitive feeling that we have about people we meet. Replicating mutated DNA passes these mutations to offspring. Mixing mutated DNA with less mutated DNA erases some errors.
How are beauty and mutation loads connected?
Simply put, our genes build our bodies from a single cell through progressive division and ever more fine separation into parts. The less mutations a human has, the more beautiful, symmetrical and proportionate that human's body is. At the same time, errors in this process can produce everything from exaggerated facial features to missing/undeveloped limbs to cognitive deficiencies due to brain abnormalities.
These are dangerous ideas which were misused by some very bad people, and as a result, the entire science was suppressed. We live in the era of ideas like "political correctness" and "blank slate" and "everyone is beautiful". I'm not here to debate the morality of science, I'm simply here to present to you the human mating dynamics as understood by science.
Until we have the technology to permanently erase DNA mutations, our built - in preferences are her to help us.
It is estimated that the person with the least mutations on the earth has about 150 mutations and are thus unbelievably appealing, attractive and beautiful. Mating with this person would erase generations of accumulated genetic defects in your children.
And so our range of DNA mutation loads are:
- 150 mutations for the best human specimen (superior fitness)
- 300 mutations for the average human
- 450+ mutations for the worst (evidenced by birth defects, lack of symmetry and other deformities)
You can find more information in a great evolutionary psychology book called "The Red Queen"
Human attractiveness visualized
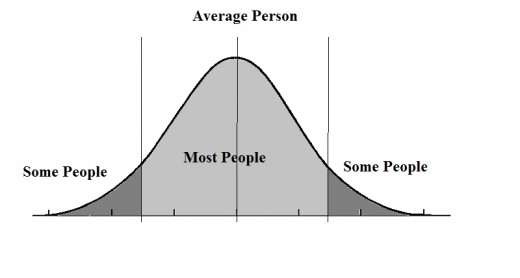
A simpler attractiveness scale uses numbers 3 is Ugly, 5 is Average and 8 is Beautiful
Mutation loads are hard to comprehend - there are easier ways to measure attractiveness
It is difficult to deal in DNA mutation loads - what is the difference between 270 and 240 mutations? To aid with this understanding, we rely on our inherent sense of beauty:
Humans can rank each other according to how beautiful they appear. This is almost universal phenomenon and has been demonstrated to have a very high (90%) correlation between individuals, regardless of age, gender or culture.
Simply put, given a lineup of 10 humans, other humans can rank them in order from the most attractive to the least attractive according to the following rules:
- 100th percentile - number 10 - this person is more attractive than all other
- 90th percentile - number 9 - there's one person more attractive, and 8 people less attractive (overwhelming feeling of attractiveness, "stunning")
- 80th percentile - number 8 - there are 2 people more attractive and 7 people less attractive (strong feeling of attractiveness)
- 70th percentile - number 7 - there are 3 people more attractive and 6 people less attractive (moderate feeling of attractiveness)
- 60th percentile - number 6 - there are 4 people more attractive and 5 people less attractive (slight feeling of attractiveness)
- 50th percentile - number 5 - there are 5 people more attractive and 4 people less attractive (no feeling of attraction or repulsion)
- 40th percentile - number 4 - there are 6 people more attractive and 3 people less attractive (slight feeling of repulsion - "something is wrong")
- 30th percentile - number 3 - there are 7 people more attractive and 3 people less attractive (clear feeling of repulsion - something is wrong with how this person looks)
- 20th percentile - number 2 - there are 8 people more attractive and 3 people less attractive (strong feeling of repulsion)
- 10th percentile - number 1 - there are 9 people more attractive (least attractive human)
In reality, we rarely meet humans in the 1-2 and 9-10 range. Most of our experience is dealing with humans in the 3-8 range. Where we would call a 3 "ugly", 5 "average" and 8 "Beautiful"

Why attractiveness matters - male paternal investment
97% of all mammalian species mate casually. What does this mean? The biggest strongest bull moose will mate with all females who present themselves or who he can find. He has no sense of beauty and mates indiscriminately. Female moose have a sense of beauty, enough to distinguish the biggest, strongest and most fit male. Because a bull moose does not teach, protect or feed his offspring, his "paternal investment" is zero, he provides his sperm and this is it.
The other 3% of mammals developed an adaptation called a "pair bond" - where a couple mates and stays together long enough to raise offspring (sometimes for life). In this situation, both male and female possess the sense of beauty, enough to pick the best genetically fit specimen of the opposite gender. A male in a pair bond situation provides protection, food and potentially teaches his offspring. As he does so, he foregoes other mating opportunities. His paternal investment is large, and he invests resources (time, energy and food) into his offspring.
The pair bond mating dynamic is similar to a marketplace - a merchant does not sell his goods at a loss or at cost. A merchant seeks to make profit on each sale. Just like that, both genders arrive at sexual marketplace with a certain "evolutionary budget" - the number of mutations they inherited from their parents. We can call this attractiveness. Each human seeks to make a "profit" on each mating opportunity. Unfortunately, someone has to lose for another to gain.
What does "the best deal" look like on the "Pair bond" marketplace? Simply put, the offspring inherits half the mutations from the father and half the mutations from the mother.
- 240 mutations male (7M) and 300 mutations female (5F) - the offspring has on average (240 + 300) divide by 2 = 270 mutations (6M/F). The offspring is less attractive than the male (genetic loss for the male), but more attractive than the female (genetic win for the female).
- In this example, a 7Male is unwilling to invest in his 6Offspring with a 5F. He has already invested his superior genes in the offspring. He will leave the female and seek another, more profitable deal.
- If our 240mutation 7M comes across 180 mutation 9F, he will recognize it as a superior deal - the offspring would have on average (240+180) / 2 = 210 mutations (8M/F)
- Because mating with a 7M is a genetic loss for 9F, the 7M makes up for the loss by providing his resources and committment to the deal. He will protect, provide and teach his offspring.
This evolutionary math is buried deep within the human mind, and most people have only a vague idea of the actual dynamics. A single deeply unconscious evolutionary driven feeling may give rise to thousands of surface thoughts directed at the partner.
With this in mind, we are ready to take a look at the human mating strategies:

Humans are a mixed strategy species - we engage in both pair bond and casual mating
Some species are more pair bond oriented and monogamous, for example gorillas. Humans are less so, with the approximate proportion of 1.3 - for each monogamous copulation, a human male hopes to accomplish 0.3 extramarital copulations.
In other words, humans are a mixed strategy species. While we hope to find long term, stable partner, we also engage in "fooling around on the side". Women take lovers, men get mistresses, and casual hookups happen frequently.
Yet another way to look at this is shopping for a house, a significant long term investment. While you are looking for an ideal house, you may be willing to rent a less ideal house short term. Just like this, it is common for people to get into less ideal relationships as they seek more fit mates.
Male mating strategy - Love 'em or Leave 'em
With our understanding of DNA mutation loads, we can use partner attractiveness to describe the human male mating strategy:
- Human male seeks a long term partner more attractive than he is. A 50th percentile (5M) male potentially seeks female up to 20% more attractive than he is - 70th percentile (7F) female.
- Mating with a more attractive female results in more attractive children and erases some genetic errors from the male DNA. As a result, his genes are more likely to survive in the upcoming generations.
- In a long term pair bond with a more attractive female, a human male invests a large amount of resources to support the female and their offspring (think house, car, child care and college costs)
At the same time, a human male is interested in casual mating with less attractive females. This can be casual dating or extramarital affairs:
- An 80th percentile (8M) male will have casual sex with a female up to 20% less attractive than he is - 60th percentile female (6F)
- A male is unlikely have sex with a female 30% less attractive than he is
- In a -20% casual mating situation (8M-6F), a more attractive male is unwilling to commit any resources (only his sperm)
- In a -10% casual mating situation(8M-7F), a more attractive male is willing to invest minimum resources (buy drinks or dinner for the female or take her on a short vacation)
- In an equal trade (8M-8F), a male is hesitant and considers both long term pair bond and casual mating situation. Typically a male is unwilling to commit to an equal attractiveness partner.
An evolutionary arms race between male and female.
Nobody likes being used and dumped, but this is exactly what a male is attempting to do in a casual mating situation - have casual sex with the woman for a few weeks or months, potentially impregnate her and dump her as he seeks more attractive females.
In this arms race, a male is evolving ever more sophisticated deception tactics, while female is evolving sophisticated testing and detection methods to probe for male investment.
- A more attractive male can deceive himself to appear more genuinely interested in a less attractive female. If a male thinks he loves her, he will act like he does.

Female mating strategy - Split the cost
Because both human males and females possess the sense of beauty, human females are also seeking a genetically advantageous deal. In short, they want to mate with a more attractive male who has less mutation loads than they are.
Unfortunately, as described above, more attractive males are unwilling to provide resources and support such children. Some people term this behavior "commitment phobia". There is no such thing, there are simply deeply rooted preferences aimed at erasing survival of our genes.
A female mating strategy is as follows:
- Seek commitment and resources from males less attractive than she is
- Seek best genes from males more attractive than she is
Because it is unlikely that a female will find a more attractive male willing to commit, the human female has the following adaptations:
- Progressively calibrating herself against more attractive males until approximately age 23 - attempting to secure commitment from a series of progressively more attractive males.
- For example, a 7F would approach 6M as first boyfriend, 7M as second boyfriend, 8M as third boyfriend before being dumped by 9M.
- A female would mate casually with the most attractive males in her 20s, potentially getting impregnated by an attractive male.
- A female in her 30s would attempt to pass on support for these children to a less attractive male. A 32 year old 7F with a kid would marry a 5M with money to support this kid.
- A female in her 30s is willing to settle down with a less attractive male.
- A female is potentially willing to have an extramarital affair with a significantly more attractive male. 6F - 8M
These motivations have nothing to do with morals, and are results of deeply rooted evolutionary adaptations, aimed at successful survival and reproduction. These strategies have ensured that humans have survived through 2 million history of our species.
For a more scientific explanation, consult the "Evolution of Desire" by David Buss
Let's revisit our Mr. Right example
Armed with this knowledge, we can analyze the situation at the beginning of this article in a new light. Let's assume we are looking at a 60th percentile (6F) female.
A 6F meets a beautiful 80th percentile - 8 Male. Mating with this male is of great advantage for the 6F. This difference in attractiveness is seen in the "weak in the knees" feeling a female is having. As a result of the attractiveness difference we can see that her sexuality would be maximally open to the 8M, as evidenced by the hot sex they are having.
Yet after a few bouts of casual sex, an 8M has grown cold and does not escalate the courtship to the next level. Instead, he is withdrawing to seek other mating opportunities. Our 8M would be willing to commit to a 9F - a stunningly gorgeous woman. As a result, he drops the casual mating relationship with the 6F.
What did we learn from this example?
- Human attractiveness helps humans keep DNA mutations in check.
- Female "weak in the knees" feeling is typically a sign of her being over-rewarded in the dating market. It is the equivalent of a "get rich quick" scheme which simply does not work out
- Female willing to have hot sex with a hot guy really early on is a sign of trouble - the attraction difference is large enough that the male would be unwilling to commit.
- Male commitment is related to how much the female is more attractive than he is. From zero (sperm) for less attractive females to large (house) for more attractive females to infinite (supporting previous children) for super-attractive females.
- Female sexuality is guarded in proportion to how much more attractive the male is. From cold (for less attractive male) to maximally open (for much more attractive).
- More attractive male is capable of self-deception to appear genuinely interested in a less attractive female. The illusion lasts from a few weeks to a few months.
Love Sex Dating Calculator App
What kind of relationship are you in?
Compare your experiences with other women using the polls below