Lifestyle: A short history of Astrology
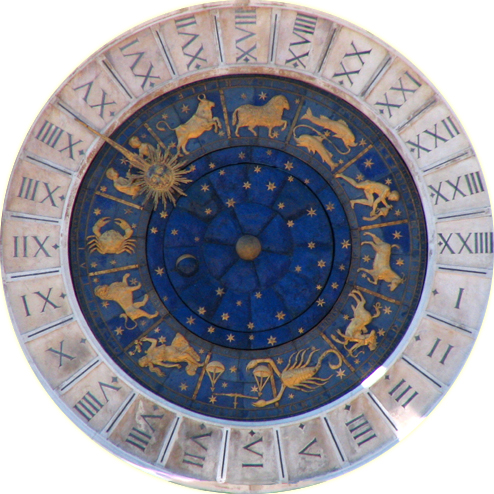

The practice of astrology has a long history and is based on how astronomic phenomena, like the stars, constellations and planets, affect humanity and terrestrial events. Some academics feel the basis of modern astrology goes back over 25,000 years, evidenced by markings depicting lunar cycles found on cave walls and bones, and indicating growing awareness of how these cycles affected the tides and seasons. Certainly though, it is evidenced that astrological studies were one of the ancient sciences of the Babylonians and formed the basis of an integrated knowledge system.
Astrology and Babylon
The Babylonian culture originated in the area now known as Iraq more than 7,000 years’ ago. The Babylonians studied the stars and celestial events for centuries, as they used their studies to predict the onset of the seasons and the likelihood of celestial events. The zodiac was utilized in the astrological practices of the Babylonians, although it’s actually believed that it originated even earlier, in ancient Egypt.
For the Babylonians, the year was split into 12 months of equal length, which were linked to the 12 lunar cycles, and characterized by a celestial coordinate and given a zodiac sign, linked to animals or people. For example, the rainy season was discovered to occur when the sun was in one particular constellation which was named Aquarius, or “Water Bearer”. The Babylonian zodiac system had to be based upon their observational methodology and became a sidereal measurement system as a result, due to use of the fixed star coordinates and failure to take account of particular degrees of movement for celestial bodies within each particular sign of the zodiac.

Astrology in Ancient Greece and Rome
Babylonian astrology was introduced to Greek and Roman civilizations and came to be a highly regarded science. The Greek academic Ptolemy was very influential in developing the basis of the Western tradition of astrology, with its explanation of the meaning and influence of the planets, houses and signs of the zodiac. Ptolemy adopted the use of the tropical coordinate system to adjust for the procession of the equinoxes and movements of the constellations, replacing the ancient fixed constellations method. Ptolemy’s rationalizations and developments of astrology are still in widespread use in modern Western astrology.
Astrology and ancient civilizations
Astrology was recognized as a science by many of the ancient civilizations and astrologers were highly respected and would often belong to priestly or academic groups. Astrological advisors to royalty and emperors were commonplace in the ancient world, and predicted the most auspicious times and dates for significant events. It is also believed that many of the world’s ancient temples were consciously built to align with constellations and heavenly bodies from 3,000BC onwards.

Find out more about Astrology on Amazon
Astrology and the Hindu faith of India
The Hindu faith of India adopted an astrological system at around the same time the Western model was created, based on the Babylonian-influenced 360-day length year. The use of the same Babylon year division was the only resemblance to Babylonian astrology, however, and Hindu astrology developed as a means of predicting the fate or destiny of individuals. The symbols of the zodiac used by Hindu astrologers are very similar to the symbols developed by the Greek astrologers, although they use the sidereal coordinates system, which is based on the fixed stars.
Astrology in Chinese culture
It is not just Western civilizations that have been deeply influenced by astrology, however. Astrology flourished during the Han dynasty in China, from the year 2,000BC onwards, as a development of Chinese culture and philosophy. Chinese astrology does not use separate the constellations into the Western zodiac form though, a system of dividing the heavens into three enclosures is utilized. The practice of Chinese astrology permeated East-Asia and is used in Korea, Vietnam and Japan.
Find out more about Chinese Astrology
© 2014 Dawn Denmar










