Skin Lightening Ingredients
What Exactly is Pigmentation?
"Pigmentation" is the color of 'melanin' which is produced by cells called 'melanocytes' in the epidermis, the superficial layer of the skin. Melanin is produced by a chemical reaction via the enzyme tyrosinase. There are two types:
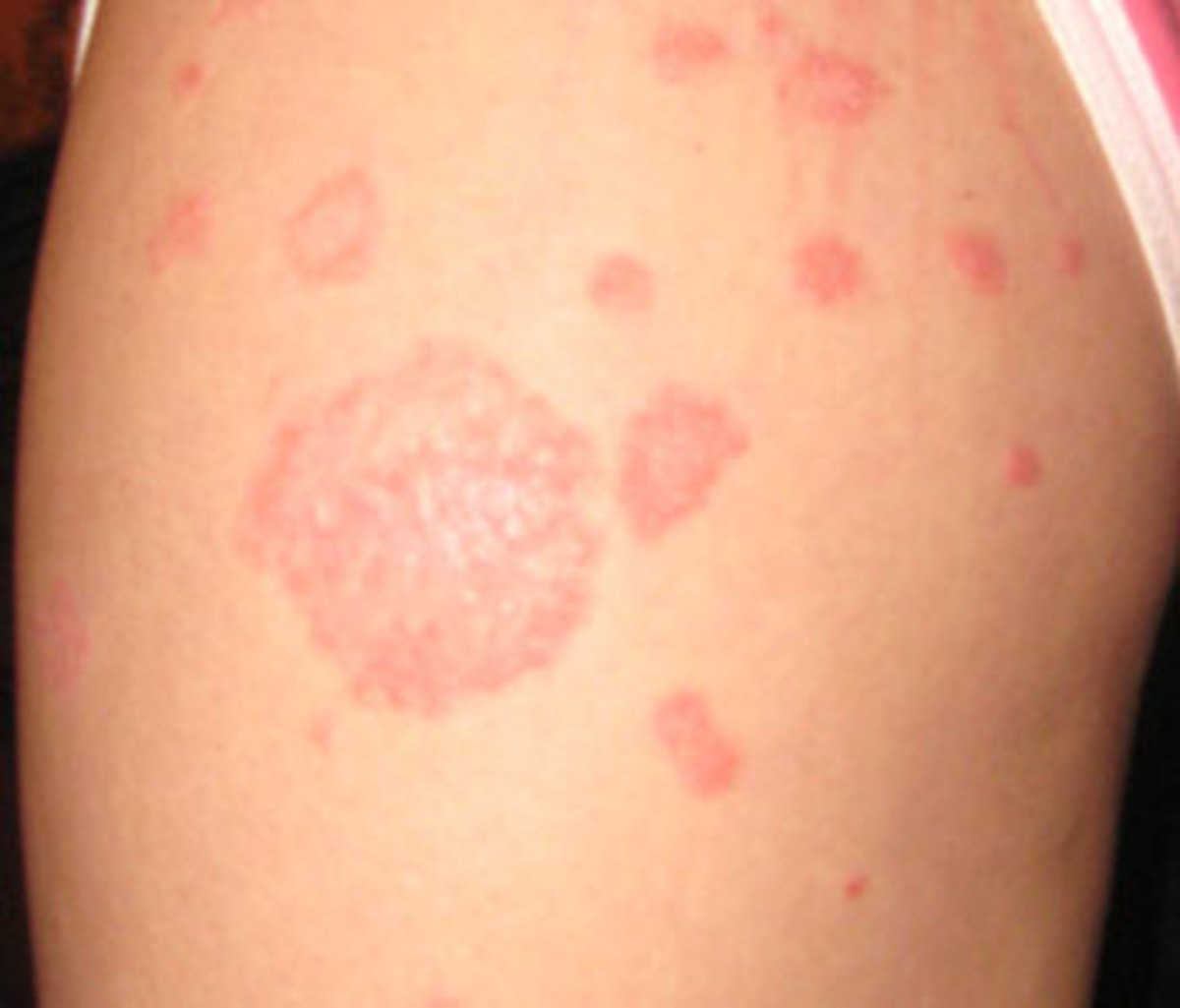
"Hyper" pigmentation - These are 'dark' patches resulting from over production of melanin and abnormal distribution in the skin layer. Also referred to as:
- Melasma / Chloasma from hormones, pregnancy, sun damage, aging process (usually seen on the face)
- Seborrhoeic warts / Keratoses (These are benign warts and can grow in size with age)
- Freckles (small brownish marks, usually on face and arms)
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from irritants, contact dermatitis, chemical peels
- Birthmarks (also known as ‘Cafe au Lait’ and Ota's Naevus (bluish black patches)
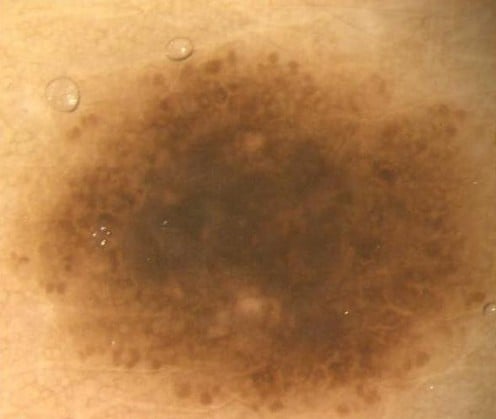
- Solar Lentigenes (also known as age spots which are brown spots from sun damage)
"Hypo" pigmentation - These are 'white' patches from decreased production of melanin. Also referred to as:
- Vitiligo
- Eczema
- Cytotoxcity (destruction of skincells from some chemical ingredients)
- Fungus (eg Tinea Versicolor)
Stay tuned...

POLL
Do You Have Any Hyperpigmented Areas?
First Step...
The first step is to determine the cause of hyperpigmentation. See a specialist who will have a look at your skin to select the best possible treatment for you. Etiology (cause or origin) of the hyperpigmentation could be from drugs (like the pill), hormonal changes, photosensitising agents (like hydroquinone), the sun, pregnancy or a disease (like Addison’s disease). It’s wise to get these ruled out before you self diagnosing…
Hyperpigmentation can be treated with topical creams and/or with some certain laser treatments (Fraxel is one). This may take up to many months of treatment before significant results are seen by you though and patience is a virtue! During any skin lightening treatments, you should avoid the sun by using sunscreen and a hat to decrease the chance of increasing the discoloured areas.
Common Treatments...
There are topical applications, some available OTC or from your dermatologist - be careful of what you’re putting on your skin. Make sure you do some reading about ingredients before blindly buying skin lightening products. There are some common ingredients that I discuss in this hub, check them out or grab yourself a dictionary of cosmetic ingredients. There are also different vitamins and antioxidants that have a skin lightening effect, like glutathione.
There's also laser treatments, like Fraxel laser. Again, be sure to research this before proceeding as some lasers are effective on certain types of pigmentation and not on others.

Skin Bleaching in Africa...
Hydroquinone...
Hydroquinone is a chemical available in some prescription and cosmetic forms for skin lightening. It acts by inhibiting melanin in your skin and is an ingredient that has been used for years in many preparations and is now being revisited due to its link to cancer. It usually does not have a ‘permanent’ effect and therefore needs to be used regularly to maintain the lightened skin effect.
An very rare side effect is ochronosis - the skin that the compound has been applied to gets darker and darker - in black skinned people who have used high high doses of hydroquinone for many years. If no improvement is seen anywhere up to 6 months, it is advisable that the hydroquinone is stopped. Usual percentages of the active is 2% - 4%, but there has been reports of up to 10% (!). 2% is generally available OTC in some countries, but many have now regulated its use, due to the link to cancer etc.
Similar to hydroquinone is Monobenzyl Ether of Hydroquinone which is a heavy chemical. This compound causes an irreversible lightening effect by almost killing melanocytes. Traces of this have also been found in disinfectants, germicides, condoms and rubber aprons!

Kojic Acid...
Kojic acid is a by-product in the fermentation process of malting rice, for use in the manufacturing of sake, the Japanese rice wine. It is an inhibitor of the formation of melanin, in addition, it scavenges reactive oxygen species released excessively from cells or generated in tissue or blood.
Kojic acid is used in concentrations ranging from 1 % - 4%. Although effective in a skin lightening gel, it has been reported to have high sensitising issues and may cause irritant contact dermatitis.
In a study comparing Glycolic Acid / Kojic Acid combination along with Glycolic Acid / hydroquinone, no (statistical) difference in efficacy was reported between kojic acid and the hydroquinone... however, the kojic acid was reported as more irritating to the skin.

Azelaic Acid...
A naturally occurring acid from Pityrosporum ovale, it is a slight inhibitor of tyrosinase (in vitro). Azelaic Acid is shown to be cytotoxic (destructive to skincells) and its efficacy has been compared with a 4% hydroquinone application. It has been used in the treatment of acne and it has been successfully used in the treatment of lentigines, rosacea, and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. A dermatologist may prescribe this as a 20% cream, combined with glycolic acid (15% -20). This formulation has been reported to be as effective as a 4% hydroquinone cream, but with a higher rate of skin irritation and contact dermatitis.

Beta Arbutin (Uva Ursi)...
A natural form of natural hydroquinone found at high concentrations in plants like the Uva Ursi. Arbutin has been shown to inhibit melanin by inhibition of tyrosinase activity. Because arbutin does not change into hydroquinone (under most circumstances) it is becoming a more popular cosmetic skin lightening ingredient as it is naturally derived.
Arbutin is being widely marketed as a good depigmenting agent, but there is conjecture as to the effective percentage which should be added to a skin lightening formulation – some products say a 1% addition is satisfactory! Studies have shown that arbutin is less effective than kojic acid for the treatment of hyperpigmentation and although arbutin is natural, there are reports of skin irritation.

Paper Mulberry...
Paper Mulberry root extract is another naturally derived skin lightening agent, which is from a plant’s roots. A comparison study of the tyrosinase inhibition of paper mulberry with kojic acid and hydroquinone, revealed that the paper mulberry was effective, but not as much as the other combined ingredients. A 1% paper mulberry extract is found to have no significant skin irritation. This is a good ingredient to look for in a skin lightening product, as it does best combined with other actives.
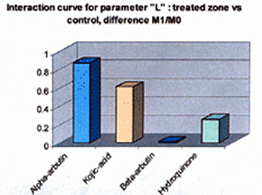
Alpha Arbutin...
Alpha Arbutin is naturally derived extract from plants that are native to the northern Canadian prairie region. The most significant extract is the Rumex variety. Alpha Arbutin inhibits the activity of tyrosinase much more effectively than its beta version, by up to ten times. There are two forms of Arbutin - the ALPHA and the BETA one. Both are tyrosinase inhibitors. Structurally a-ARBUTIN (4-hydroxphenyl-a-D-glucopyranoside) is an A-glucoside and b-ARBUTIN a B-glucoside. The A-glucosidic bond offers higher stability and efficacy than the b-Arbutin.The alpha form offers higher stability and efficacy leading to a skin lightening active that acts faster and more efficiently with significant skin lightening results. Studies show little if any skin irritation. It is also purported to reduce erythema (reddening of the skin).
This is a great ingredient, and preferable over b-Arbutin anyday. The drawback is that a sunscreen must be worn everyday as there is a weakening of skincells while you use it, this ceases once AA is stopped.
Chromabright...
Chromabright is a synthetic ingredient which is relatively new. It has shown no cytotoxicity or sensitisation effects in all its testing and reports a significant skin lightening effect in vitro (test tube) and in vivo (human). It also has an added benefit of having a photoprotective effect which means that it protects somewhat against UV (sorry, you still have to use sunscreen!) - no other ingredient currently boasts this.
This is one I will be keeping my eye on!

Glabridin / Licorice Extract...
Glabridin is the main ingredient in licorice extract. It is a natural extract used in preparations for depigmenting and reducing erythema. Glabridin also exhibits anti-inflammatory properties and a study on glabridin reported that it inhibited tyrosinase activity of melanocytes without cytotoxicity, at a topical application of 0.5%.
Again, glabridin is an active that's best used in conjunction with other natural actives, so it is a good ingredient to keep on the lookout for.

Magnesium L Ascorbyl Phosphate...
Magnesium L Ascorbyl Phosphate (MAP) is a form of Vitamin C and can be an effective skin lightening ingredient when used at about a 10% addition. MAP has been shown to suppress melanin formation AND have a protective effect against sun damage.
This active is a must when choosing a skin lightening product. Yes, you guessed it, it will work better synergistically with other ingredients. You can also use it by itself for a sun protection effect under a sunscreen.
Just ensure you have the right form as there are several found in skincare products, some of which are irritating to the skin. Be careful of the strength of it too, keep under 15%.

Niacinamide - Vitamin B...
Niacinamide (Nicotinamide) is of the Vitamin B family and is beneficial to skin and possess potent antioxidative benefits. Niacinamide does not have the same pharmacologic and toxic effects of Niacin.
Nicotinamide has demonstrated anti-inflammatory actions which may be of benefit in patients with some inflammatory skin conditions like acne vulgaris and is a mild depigmenting agent.
You can purchase niacinamide capsules, masks and creams. A body mask can be used for brightening your underarms, nipples, elbows, knees and external genital areas. You can squeeze a niacinamide capsule and apply to the entire face.
Be careful of the quality that you purchase as it is becoming popular now, low grade stock is being circulated.

Aleosin...
Aleosin is obtained from the aloe vera plant. It is a naturally mild tyrosinase inhibitor, with no cytotoxicity recorded. It has a limited ability to penetrate the skin due to its hydrophilic (has an affinity for water) nature. It is best combined with other ingredients for best effect.
Youtube:
Laser Treatments...
Lasers function by emitting a high-intensity energy source that is absorbed by melanin in your skin. The absorption of this energy destroys certain parts of the skin cells. There are lasers that work better on melasma and some that work better on age spots - consult and research them!
Side effects can include discomfort, redness, swelling and even postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. Please have a spot test before proceeding and ensure the person giving the treatment is qualified…
The Fraxel laser works via thermal damage to small parts of the skin. It has been said that there is less down time with Fraxel, but the pain factor is high...
What is INCI?
Did you know this?
*INCI is an acronym for: International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredient
The INCI name is the accepted full ‘chemical/synthetic/scientific’ name across the world for an ‘ingredient’ and is required to be shown on all packaging. The short name is like a brand name or a shortened version of the INCI, the one which is most likely familiar to you...