- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Science & Programming»
- Programming Languages
Arithmetic and Logical Instructions 8085
Arithmetic Instructions
Op-code
| Operands
| Description
|
|---|---|---|
ADD
| M / Register
| A<-- A+ M or A<-- A+ Reg
|
ADI
| 8 bit Data
| A<-- A+ 8 bit data
|
ADC
| M / Register
| A<-- A+M+CF or A<--A+Reg+CF
|
ACI
| 8 bit Data
| A<-- A+8 bit Data + CF
|
DAD
| Register Pair
| HL<-- HL+ Register Pair
|
SUB
| M / Register
| A<-- A - M or A<-- A - Reg
|
SBB
| M / Register
| A<-- A - M - CF or A<-- A - Reg - CF
|
SUI
| 8 bit Data
| A<--A- 8 bit Data
|
SBI
| 8 bit Data
| A<--A- 8 bit Data - CF
|
INR
| Reg / M
| Reg ++ / data at [HL] ++
|
DCR
| Reg / M
| Reg-- / data at [HL] --
|
INX
| Register pair
| Increments Register pair by 1
|
DCX
| Register Pair
| Decrements Register pair by 1
|
DAA
| If first digit of 8 bit value is > 9 than add 6h to it and if second digit is >9 than add 60h to the 8 bit value.
|
ADD: The instruction performs the addition of Accumulator with either memory content or the register content. The result generated is stored into Accumulator. One fixed operand and destination register for result is always Accumulator. The result will affect SF, ZF, PF, AF, CF.
For Example: ADD 12h // Acc <-- Acc + 12h
ADI: The instruction add the 8 bit data given immediately into the accumulator and the result is stored back into accumulator. Acc= Acc+ 8 bit Data. The result will affect SF, ZF, PF, AF, CF.
For Example: ADI 05h // Acc <-- Acc + 05h
ADC: The instruction will perform the addition of Accumulator, Register or memory location content and Carry Flag status(0 or 1). The ADC utilizes the Carry Flag status at the time of addition.
For Example: ADC B // Acc<-- Acc + B + CF(0/1)
ACI: The instruction will add the content of accumulator, 8 bit data given into instruction and Carry Flag status and stores the result into Accumulator. The result will affect all the flags.
For Example: ACI 23h // Acc<-- Acc + 23h + CF(0/1)
DAD: The instruction performs the addition of HL pair with the register pair mentioned into the instruction. The operation will be done over 16 bit data(HL pair and Register pair in instruction). All the flags will be affected by the result generated.
For Example: DAD B // L <-- L+ C and H<-- H+B+CF(0/1)
SUB: The instruction performs the subtraction of given register or memory location content from accumulator and stores the result into the accumulator. All the flags are affected by the result generated.
For Example: SUB D // Acc<-- Acc - D
SBB: Subtracts with borrow. The instruction performs the subtraction of given register and the content of carry flag (0 or 1) from the accumulator and stores the result into the accumulator. All the flags are affected by the operation.
For Example: SBB E // Acc<-- Acc - E - CF(0/1)
SUI: Subtract Immediate. The instruction will subtract the 8 bit data given into the instruction form the accumulator and the result will be stored into the accumulator. All the flags are affected by the result generated.
For Example: SUI 25h // Acc <-- Acc - 25h
SBI: Subtract borrow immediate. The instruction will subtract the 8 bit value given into instruction and the status of Carry Flag (CF) from the accumulator and stores the result into the accumulator.
For Example: SBI 95h // Acc <-- Acc - 95h - CF
INC: The content of given register pair is incremented by 1. The instruction is generally useful while looping. The result affects All the flags.
For Example: INC B // B<-- B+1
DCR: The content of given register or memory location specified by HL pair is decremented by 1. The result affects all the flags.
For Example: DCR C // C<-- C-1
INX: The content of given register pair is incremented by 1. The instruction uses the 16 bit data from the register pair.
For Example: INX D // DE<-- DE+1
DCX: The instruction decrements the content of given register pair by 1. The instruction uses the 16 bit data into the register pair.
For Example: DCX B //BC<-- BC-1
DAA: The instruction performs the adjustment of each digits of 8 bit value of accumulator. The instruction converts the hexadecimal digits to valid decimal digits. If any digit is greater than 9 than 6 is added to the digit and adjusted as decimal value.
For Example: DAA // if the Accumulator value is 2Bh than it compares each digit
if B>9 than B+6 = 11h
if 2>9 ? no. so 20 + 11 = 31h
2B+06 =31h
Logical Instruction
Op-code
| Operands
| Description
|
|---|---|---|
ORA
| Reg/Memory
| Acc<-- Acc OR Reg/Memory
|
ANA
| Reg/Memory
| Acc<-- Acc AND Reg/Memory
|
XRA
| Reg/Memory
| Acc<-- Acc X-OR Reg/Memory
|
ORI
| 8 bit Data
| Acc<-- Acc OR 8 bit Data
|
ANI
| 8 bit Data
| Acc<-- Acc AND 8 bit Data
|
XRI
| 8 bit Data
| Acc<-- Acc X-OR 8 bit Data
|
CMA
| Complement Accumulator
| |
CMC
| Complement Carry Flag
| |
STC
| Set Carry Flag
| |
CMP
| Reg/Memory
| Compare Accumulator with Register/Memory
|
CPI
| 8 bit Data
| Compare Accumulator with 8 bit Data
|
ORA: The instruction performs the OR operation of the Accumulator and the given register or memory content. The SF, ZF and PF are affected, CF and AC are reset.
For Example: ORA B // consider A = 05h & B = 93h A<-- A OR B , A= 97h
ANA: The instruction performs the AND operation between Accumulator and register or memory content. The SF, ZF and PF are affected. The CF is reset and AC is set.
For Example ANA B // consider A = 05h & B = 93h A<-- A AND B , A=01h
XRA: The instruction performs the X-OR operation between Accumulator and register or memory content. The SF, ZF and PF are affected with the result AC and CF are reset.
For Example: XRA C // consifer A = 44h & C = 66h A<-- A XOR B, A= 22h
ORI: The instruction performs the OR operation of the Accumulator and the 8 bit content given into the instruction. The SF, ZF and PF are affected, CF and AC are reset.
For Example: ORI 18h // consider A = 09h, A<-- A OR 09h, A=19h
ANI: The instruction performs the AND operation of the Accumulator and the 8 bit content given into the instruction. The SF, ZF, PF are affected by the result and AC is set, CF is reset. For Example: ANI 21h // consider A= 25h, A<-- A AND 21h, A=21h
XRI: The instruction performs the XOR operation of the Accumulator and the 8 bit content given into the instruction. The SF, ZF and PF are affected with the result AC and CF are reset.
For Example: XRI 23h // consider A = 34h, A<- A XOR 23h, A=17h
CMA: The instruction complements the content of the accumulator.
For Example: CMA // consider A = 26h than A<- Complement of A , A = D9h
CMC: The instruction complements the status of carry flag. If the carry flag is set than it will reset it else if the carry flag is reset than it will set the carry flag.
STC: The instruction sets the carry flag status to 1.
CMP: The instruction compares the content of Accumulator with the register or data stored into memory. The instruction sets the status of CF, SF and ZF. The content of second operand is subtracted from the first operand.
For Example: CMP B // consider if A=14h, B = 05h than A>B and CF=0, ZF=0, SF=0
// consider if A=05h, B = 15h than A<B and CF=1, ZF=0, SF=1
// consider if A=14h, B = 14h than A=B and CF=0, ZF=1, SF=0
CPI: The instruction compared the content of accumulator with the 8 bit data given into the instruction. The comparison is done by subtracting the data from the accumulator and flags CF, SF, ZF is set or reset.
For Example: CPI 26h // consider A = 13h, A<26 CF=1, SF=1, Z=0
CPI 26h // consider A = 33h, A>26 CF=0, SF=0, ZF=0
CPI 26h // consider A = 26h, A=26 CF=0, SF=0, ZF=1
OP-CODE
| OPERANDS
| DESCRIPTION
|
|---|---|---|
RLC
| NONE
| Rotate Accumulator Left
|
RRC
| NONE
| Rotate Accumulator Right
|
RAL
| NONE
| Rotate Accumulator Left through CF
|
RAR
| NONE
| Rotate Accumulator Right through CF
|
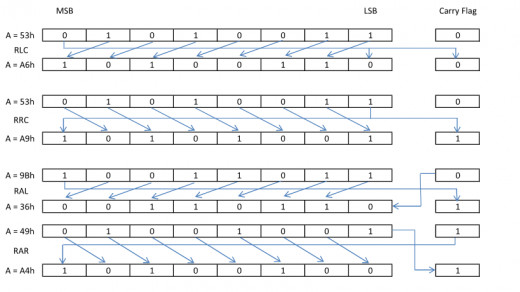
RLC: The content of Accumulator is rotated left side by one bit. The MSB goes to CF and also becomes the LSB of result. Rest of the bits shifts left by 1 bit.
For Example: RLC // Consider A = 53h , CF=0 than the result of instruction is A=A6h, CF=0
RRC: The content of Accumulator is rotated right side by one bit. The LSB goes to CF and also becomes the MSB of the result. Remaining bits shifts right side by one bit position.
For Example: RRC // Consider A = 53h, CF=0 than the result of instruction is A=A9h CF=1.
RAL: The content of accumulator is rotated left side by one bit position. The current CF value becomes the LSB of result. The MSB of the accumulator goes to CF and remaining bits shifts left side by 1 bit position.
For Example: RAL // Consider A=9Bh CF=0 than the result A= 36 CF=1
RAR: The content of accumulator is rotated right side by 1 bit position. The current CF value becomes the MSB of result. The LSB goes to CF and remaining bits are shifted right side by 1 bit position.
For Example: RAR //Consider A=49h, CF=1 than the result is A=A4, CF=1
How do you rate article Logical Instructions of 8085?
Arithmetic Instructions of 8085
- INSTRUCTION SET OF 8085
The 8085 microprocessor is programmed by assembly language programming. The article lists and explains various instructions available in assembly language programming for 8085 microprocessor.