- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Hardware
Mother Board Basic Components
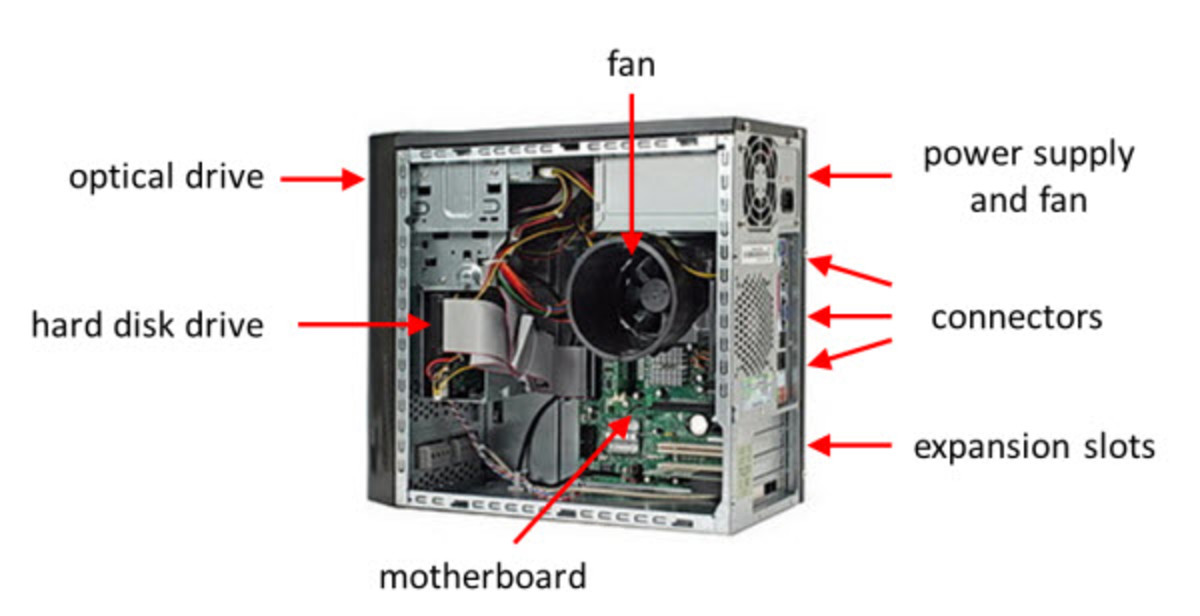
Hardware Components of a Home PC
Every Personal Computer whether it resides in your living room or in a high tech computer firm, is made up of these basic but integral components.
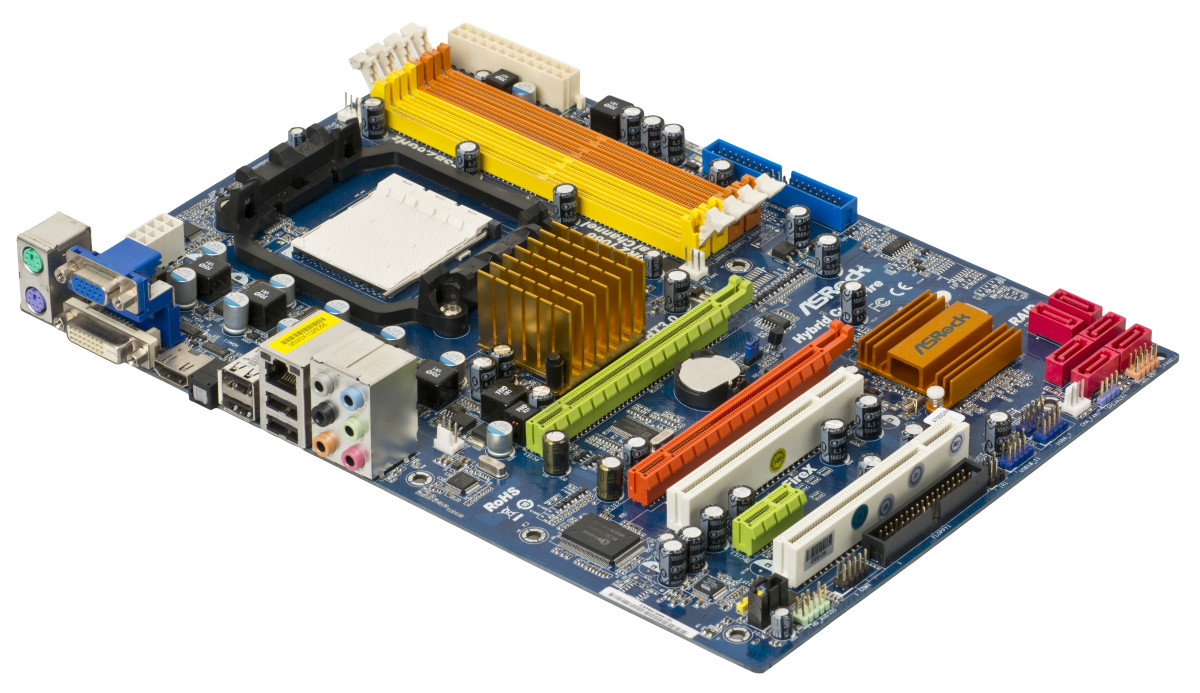
Motherboard
Also known as System board, Main board or Logic board, Motherboard is a printed circuit board (PCB) in which various key components such as Processor, Memory, Peripherals which includes Video card, Sound card, Network card resides.
Before the advent of Motherboards, most of the components were interconnected using electric connectors which join end to end forming a bus structure. However, even though highly stable, these boards also known as back planes did not contain any embedded memory system or processing power which reduced the performance capability. Examples include PICMG 1.3 boards
Recent motherboards provide a number of advantage compared to back plane which includes
- On Board Bus connection between the main processor and other important components such as memory, graphic cards and Input/Output peripherals.
- Chip sets (North bridge and South Bridge) which connects processor to memory, PCI slots, AGP slots and Input/Output peripherals such as USB 3.0, Keyboard and mouse.
- Provide Firmware/ BIOS located in non volatile Flash Memory
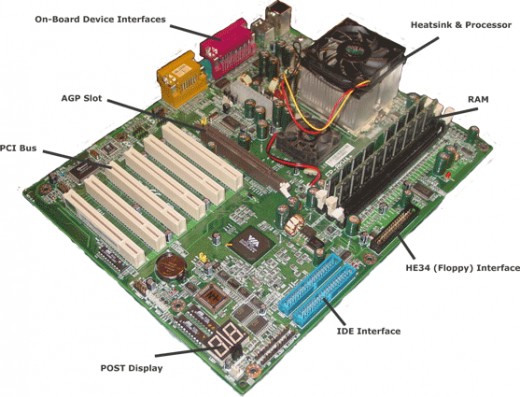
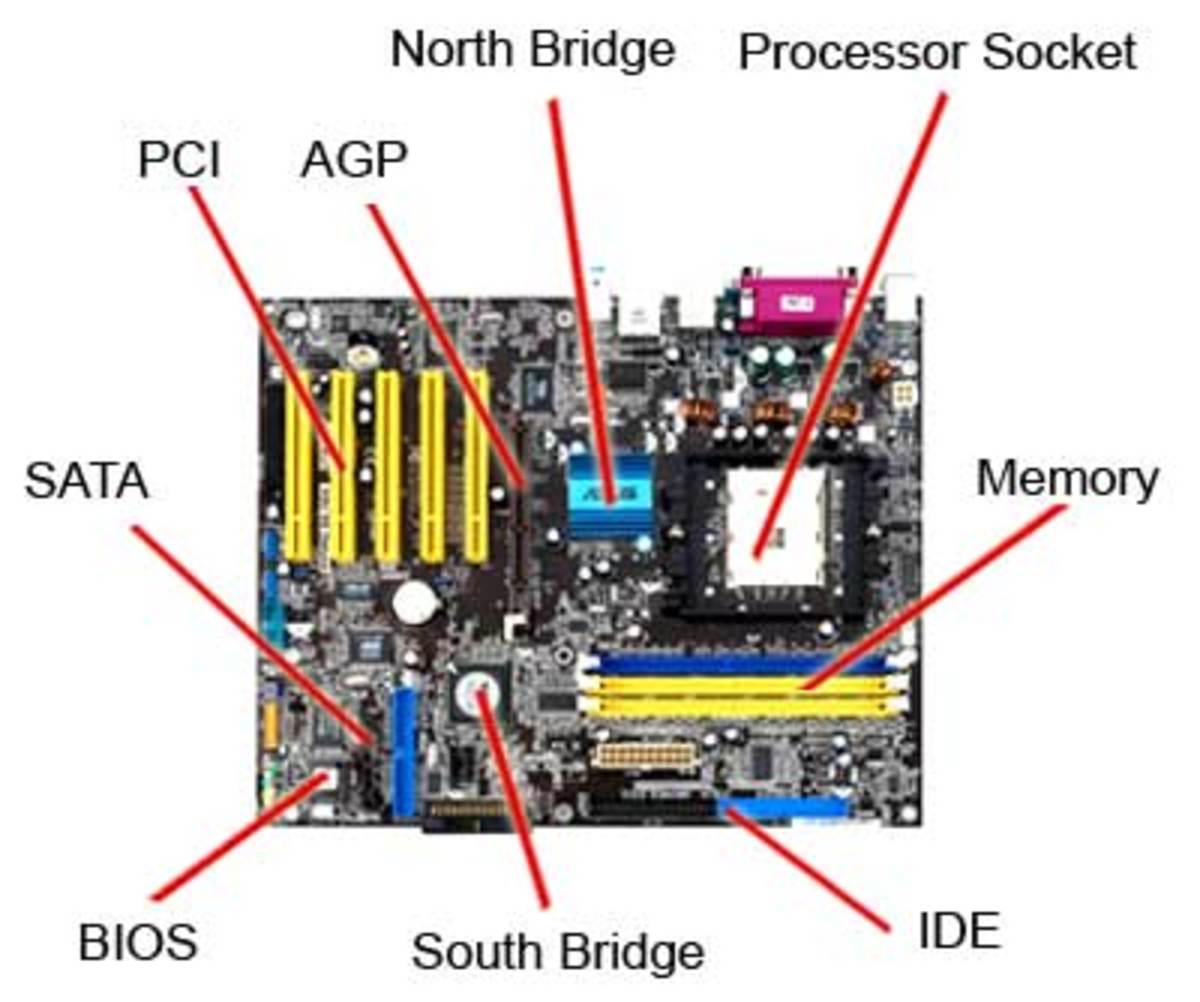
Above given is the basic layout of a modern motherboard. There are number of manufacturers for motherboards such as ASUS, AT&T, IBM, Intel, Daewoo, Macrotek.
Dimensions of a board such as width and length is stated as Form Factor. Form factor for each manufacturer varies, however, most follow ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) standard. Also certain processors are compatible only with specific boards, which should always be kept in mind when assembling a computer.
Now lets go into details regarding the various components present in a motherboard
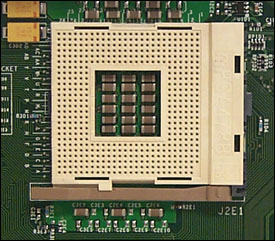
Processor Slot
Also known as CPU socket, It forms the main connection between the processor and the motherboard. Two most commonly used standards are
- ZIF (Zero insertion Force) :- An IC socket, which as the name suggests requires very little force to connect with the Processor. Contains large array of holes which makes contact with the processor pins. Once inserted, the processor is locked into place with a latch system provided at the side of the socket.

- Land Grid Array :- The Land Grid Array incorporates pins into the CPU socket rather than the processor. The advantage is that, even if one of the pins get damaged, the motherboard can be replaced easily instead of the more expensive processor. However this design is prone to breakages and is not much robust in design.

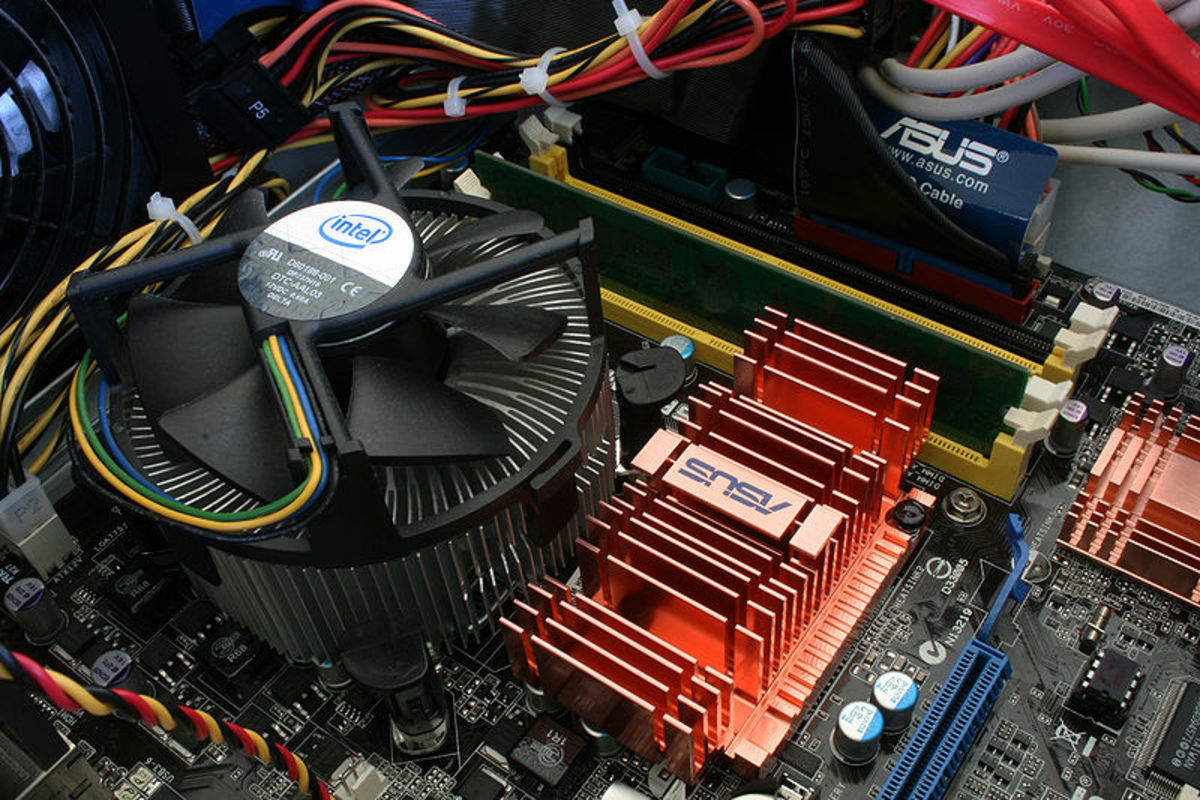
Cooling Fan
Du to extreme heat produced by the processor, a cooling mechanism is provided, which is placed just above the processor slot. The basic structure consist of a heat sink and a miniature fan system. Connection is provided by plastic screws on either side of the processor slot, complete with a latch mechanism.
The cooling fan structure comes in various size and dimensions, which depends on the manufacturer's design
CMOS
Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor or CMOS refers to a chip which stores the start up information used by the BIOS when the computer is turned on.
CMOS battery is button type which on removal resets all the saved passwords in the PC.

Memory Slots
Also known as RAM slots, these slots are used to insert the memory sticks. The number of slots vary for different motherboard configuraion.
Memory
Home computers consiust of two types of memory- RAM and ROM.
RAM (Random Access Memory) :- The speed of a computer is largely determined by the amount of RAM it contains. There are two types of RAM. SRAM and DRAM. Static RAM stores data in Flip Flops. SRAM uses less power and is more fast. However they are expensive. DRAM or Dynamic RAM is most commonly used. Data is stored in a cell consisting of a transistor and a capacitor.
Data in RAM is stored in random order, unlike those in Hard disc or CD which are in structured order. This allows for accessing large amount of data within a short period of time. RAM memory are used to store temporary data from Hard Disc, which can be fetched by the processor to perform various tasks.
RAM memory ranges include 256 MB, 512 MB, 1 GB, 2 GB, 4 GB and in some latest computer up to 1 TB (Tera byte). The amount of RAM required depends upon the operationg system used Eg: Win Vista would run better on 2 GB RAM. Also certain high end graphic softwares and games require very good RAM configuration.
PCI Slot
PCI or Peripheral Component Interconnect slot is used to connect various external peripherals such as Network card, Sound card, Video Card, Graphic Cards etc.
They are identifiable by the long white slots parallel to the processor slots.

Network Card
A network card is used to connect the computer or the PC to an existing network such as LAN (Local Area Network).
The card consist of a 48 bit serial MAC address which is provided by the manufacturer itself. A number of LED's states the status of the network connection.
Most of the latest motherboards have network cards inbuilt into it reducing the need for external NIC (Network Interface Card).
.

Audio Card
Audio Card also known as Sound Card is used to provide audio input and output to and from a computer with the help of software. An Audio Card gets connected to the PCI slot of the motherboard.
Most Audio Card uses Digital to Analog converters or DAC. The output is provided to an Amplifier, Headphone or any other Audio Devices via TRS Phone connector or RCA connector.
Some modern audio card has more than one DAC converters.

Video Card
Video card also known as Graphic card or Display Card is used to provide accelerated 3D rendering and 2D Garphics, helps connect to a TV output and also allow connection of multiple monitors.
The mother board itself has a video chip set manufactured into it. However this takes up a lot of RAM memory and can reduce the system performance. Also for higher 3 D applications, an external video card is preferable.
The Video card consist of the following.
1. Graphics Processing Unit
Like the processor in the motherboard, the GPU ia an electronic circuit which accelerates the building of images in a frame buffer for display purpose.
2. Heat Sink
Since the processing power of video card is very high, heat is generated at a high rate. To reduce this, heat sink along with a fan is provided to cool the GPU.
3. Video BIOS
The BIOS consist of minimal programs for setup and starting of the video card. It consist of memory timings, processing speed and voltage ratings for over clocking purpose.
4. Video Ram
Video cards have independent memory and since it is accessed very often uses high speed or multi port memory. Mostly uses DDR technology. Memory size ranges from 128 MB to 8 GB..
Video Cards are connected through
- AGP Port
- USB (Universal Serial Bus)
- PCI Express Slot

Integrated Drive Electronics
Integrated Drive Electronics or IDE was developed jointly by Control Data Corporation and Compaq in 1980, to provide a faster connection link between the hard drive and the on board controller. Controller is a circuit board with number of chips which decide how data must be accessed and processed by the hard drive. Initially mend for data storage, IDE is now used to connect both Floppy as well as CD drive.
It is also known as ATA/ATAPI (Advanced Technology Advancement/ Advanced Technology Advancement Packet Interface) and comes in versions such as ATA-1, ATA-2, ATA-3, ATA-4, ATA-5.
IDE Ribbon Cable
IDE Ribbon Cable is used to connect the motherboard to the external drive. The cable constitute of number of flat wires joined together side by side. The total number of wires numbers from 40 to 80.
To maintain the right connection there is a notch attached to the top of the connector which allows the cable to slide in the correct direction.