Electrc storage commodty
Electric storage as a commodity
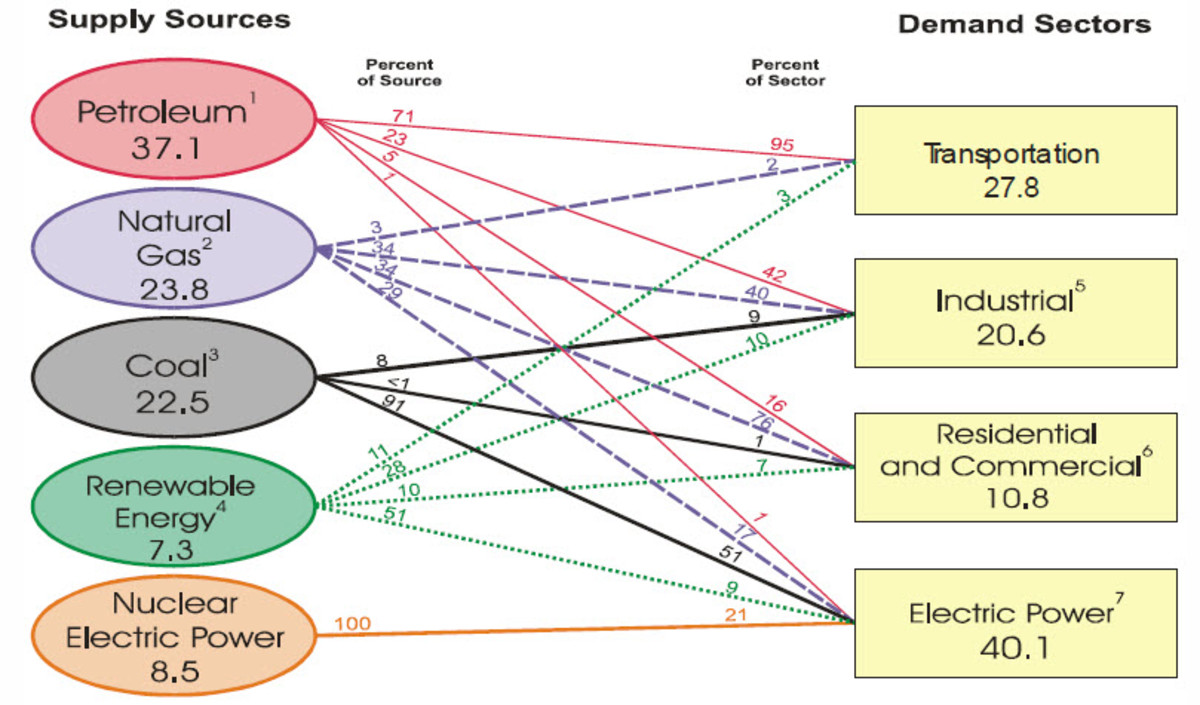
storage facilities and natural gas underground storages have been used to store other commodities to take advantage of price differentials. Large investments in renewable energy have caused volatile power prices. During windy and sunny weather conditions power prices may be low and therefore it would be advantageous to purchase power at these low prices, store it and then sell it at higher prices. This process would make sense as long as the storage cost is lower than the price differential. Many jurisdictions support energy policies that promote renewables. A large renewables rato of the total energy mix presents challenges in terms of price volatility and power plant operation. Electric storage could help smooth volatility and provide back up power.
There are various forms of electric storage. Batteries have been used since the early days in direct current electrical networks. They have been used to stabilize power distribution networks. However batteries are currently unable to store large amounts of electricity. Batteries are generally expensive to manufacture and maintain and have limited lifetimes due to crystallization within the cells.
Possible technologies for large scale storage are flow batteries, liquid metal batteries, and sodium-sulfur batteries. Battery storage has an efficiency of 90% or higher.
Electric vehicles could be connected to the grid and supply electricity at peak demand. They could be charged at night or at offpeak periods. However a challenge with this approach is that each storage cycle causes wear and tear on the batteries.
Compressed air generated during offpeak periods could be stored in a mine or other geological features. In peak load periods, compressed air can be generated with a small amount of natural gas and fed into turboexpanders for electricity generation.
Hydrogen may be used as an electrical energy storage. Hydrogen can be produced using electricity and then compressed or liquefied and converted back to electrical energy and/or heat. Hydrogen can be used as fuel for vehicles or energy generation. Hydrogen production can be produced by reforming natural gas with the steam or by the electrolysis of water into hydrogen and oxygen. Carbon dioxide is a by-product of reformed natural gas. Hydrogen is then converted back into electricity in an internal combustion engine or a fuel cell which converts chemical energy into electricity without combustion. Hydrogen storage typically achieves an efficiency of around 50-60%.