- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Software
Explaining Expert Systems (ES) in simple terms
Expert Systems (ES) are computer systems that are best appreciated by first examining what the terms mean. The first term to consider is SYSTEM. A system is an environment entity that is considered to have characteristics that include:
- Purpose or goal of existence
- Composition of several inter-related components that contribute individually to its goal
- Existence of boundaries
In addition a system may be adaptive, closed, open, static or dynamic. Here, the term system is used in the sense of computer systems or computer programs. The term EXPERT is derived from human expert. Expertise is the property of human being described on their abilities to cope with difficulty problem solving situations.

Human experts solve problems in specified area of expertise with appropriate level of expertise. We need experts such as experienced doctors, educators, engineers, analysts, administrators etc.
Human experts have extensive task specific knowledge acquired from training, reading, practicing and experience. The knowledge could include:
- Theories about problem area
- Rules and procedures regarding the general problem area
- Heuristic Rules on what to do in a given problem case
- Global strategies for solving typical problems
- Meter knowledge i.e. knowledge about knowledge
- Facts about problem area
Experts take a long time to develop and when they solve problem they may do so in one or more of the following ways:
- Recognize and formulate the problem
- Provide the solution to the problem fast
- Explain the solution to the problem
- Learn from experience
- Restructure knowledge i.e. understand in parts
- Breaks rules and solve problems in unfamiliar ways
- Recognize their limitations but still offer workable solutions
An EXPERT SYSTEM (ES) is therefore a set of computer programs that act in place of human experts. These programs take and solve problems in a restricted problem domain or areas of expertise.
Expert systems must therefore have knowledge similar to the one held by human experts and use it to solve problems for the type solved by human beings.
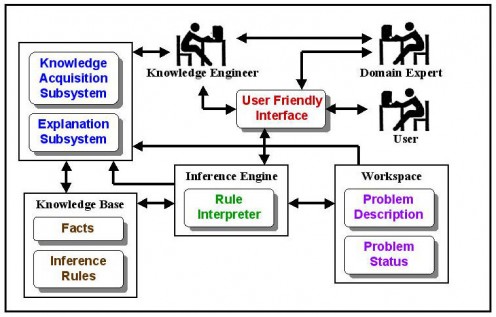

The structure of an Expert System
The internal structure of an Expert system can contain the following parts at minimum:
1. Development environment: This part is used by the expert to build the components and enter the knowledge into an expert system.
2. Consultation environment: This part is used by non-experts to obtain knowledge from the expert system.
3. Knowledge acquisition: This sub-system assists in the accumulation, transfer and transformation of problem solving expertise from the experts or documented knowledge sources to a computer program.
Knowledge can be acquired from knowledge experts, textbooks, multimedia, documents, database, special research, reports and even from internet. The knowledge base of an expert system contains the knowledge needed to understand, formulate and solve problems.
For an expert system to be complete, it must be able to explain itself just like human experts. Thus, an expert system should have an explanation facility to justify conclusions. This sub-system is the part that traces the responsibility for conclusions to their sources. It may explain one or more of the following:
- Why some questions are asked by the expert system
- How some conclusions are reached at
- Why some alternatives are rejected
- The plan used to reach the conclusion
- The required facts to establish the final conclusion

Participants in Expert Systems
1. The expert: This is the person who has special knowledge, judgment, experience of methods used to solve problems or advise on a given class of problems.
2. The knowledge engineer: This is the person who extracts and structures knowledge from sources such as human experts so that it may be put into the computer for use in an expert system.
3. The user: This is the person who is involved with the expert system as a non-expert and the expert system is constantly providing advice of solution to the problems. The user may also be a student who wants to learn from the expert system which acts an instructor. The user may also be an expert system builder who adds knowledge to the knowledge base of the expert system.
Examples of Expert Systems (ES)
- Interpretation systems: They interprets situation description from observation e.g. surveillance, speech recognition, image analysis, signal interpretation etc.
- Prediction systems: Weather forecasting, demographic predictions, economic forecasting, traffic predictions, marketing or financial predictions etc.
- Diagnosis systems: Systems that relates observed behaviors or irregularities to underline the causes e.g. medical, electronic, mechanical and software diagnosis.
- Monitoring systems: Comparing observations and flagging exceptions.
- Control systems: Interpreting, predicting and monitoring system behaviors.
Some benefits of Expert Systems
1. Increased productivity: Expert systems work faster than human being and hence there would be increased capacity to do more tasks in a given amount of time.
2. Decrease decision time: Decision making is faster when using Expert Systems
3. Reduced down-time: Where Expert Systems are used for diagnosis of malfunction and prescription of repairs, down-time is reduced as computer is used.
4. Increased product quality: Since errors are significantly reduced, with computers we can process tasks faster and concisely resulting in consistence in product quality.
5. Capture of scarce resource: Expert Systems can store expertise held in human who may take long to train.
6. Flexibility: Expert Systems can sense changing trends or needs and advise accordingly e.g. in design and production, one can change parameters.
7. Increased capability: Expert Systems can easily integrate with other Decision Support Systems to make applications work faster or produce high quality results.
Some limitations of Expert Systems
1. Knowledge is not always readily available: Human experts are rare and even if you get one, getting that knowledge from the expert is a problem.
2. There is difficulty in extracting expertise from human.
3. There is variation in problem assessment by different experts as experts see things differently.
4. Human experts cannot abstract under pressure.
5. Users may not understand the workings of the system and therefore they may dismiss Expert Systems.
6. Experts Systems work well in narrow domain and may not work if we broaden the problem area.
7. End users may not trust Expert Systems.
Other related hubs...
- What is Decision Support System (DSS) and why every manager needs one
Every manager in an organization is a decision maker and for a long time, managers considered decision making a talent acquired through trials and errors. However, the business environment where business managers operate is changing rapidly and ... - Information Technology tools in today's schools
Different ICT technology tools are available today that can be used to make life of learners in school fun and enjoyable yet productive to their mental growth. School administrators can rely on ICT technologies to manage school activities and ... - What is TelePresence?
Design of a Telepresence system will mostly be limited by installation cost, equipment, cost of bandwidth, expertise, distance, topographical setup, provision of LAN or WAN among other factors. Telepresence systems can be implemented in many areas...