GENERATIONS OF MOBILE TELEPHONY SYSTEMS

INTRODUCTION
Hello dere,
When was the last time you went to buy a SIM card? What you asked for to your retailer?
" Give me a SIM CARD." OR "Bro Give me a 2G/3G/4G SIM card " ??
Until and unless you are damn unconscious or ignorant of your technology standards , you generally mention what generation of SIM Card you want actually. you select your SIM based on facilities you want vs. 'how much you want to spend'.
Interested to know the better deal of what all these technologies say!! lets have it here than...
0G- Zeroth Generation of Mobile telephony technology
Features:
1. Also k/as mobile radio telephone OR pre-cellular standards.
2. Offcourse mobile, and in forms.
- Mounted in moving road locomotives, with transceiver(transmitter+receiver) mounted in the vehicle trunk and attached to "head" (dial, display and handset), mounted near the driver seat.
- briefcase models to be carried handy.
3. Technologies used in 0G system
- PTT(Push to talk also known as Press -To-Transmit).
- MTS(Mobile Telephone System).
- IMTS(Improved Mobile Telephone System) and
- AMTS (Advanced mobile telephone system).
Do you know, the very first invented mobile communications system 0G connections were distributed by selling via WCCs(Wireless Common Carriers, AKA telephone companies), RCCs (Radio common Carriers) and two-way Radio dealers.
Unlike later technologies, they were available as commercial service that was a part of public switched telephone numbers with there own telephone numbers rather than part of a closed network such as a police radio or taxi dispatch system.
1G First generatiom of Mobile telephony system
Features:-
1. First generation is more improved and offcourse faster over 0G.
2. It's an Analog telecommunication system.
3. Speed of 1G varied between 28 Kbps (kilo bit per second) and 56 Kbps
4. This technology comprised of Analog radio signals and instruments for its working, Though it used digital signalling to connect the radio towers(which listen to handsets ) to the rest of telephone system, using a technique called FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access).
5. Hereby, a voice call gets modulated to a higher frequency of about 150MHz and up prior to transmission between radio towers.
6. These services are provided through circuit switching, i.e. a circuit path is setup prior to transmission of message data. and entire message content travels via the same setup path from source to destination.
7. Different 1G standards prevalent were-
- AMPS(Advanced Mobile Phone System)- the prevalent standard in North America and Australia. It was a cellular standard introduced in 1983 using FDMA multiple access technique, working in Frequency band of 824-894 MHz, at a channel bandwidth of 30 KHz using FM modulation technique.
- NMT(Nordiac Mobile Telephone)- adopted by Nordiac countries, Switzerland, Netherlands, Eastern Europe and Russia.
- TACS(Total Access Communication System)- used in United Kingdom.
- Than C-450 in western Germany, Portugal and south Africa., Radiocom 2000 in France, & RTMI in Italy. Japan had several multiple systems introduced by NTT(TZ801, TZ802,TZ803) and DDI(JTACS- Japan Total Access Communication System).
Do you know ??
The first commercially automated cellular network was launched in Japan by NTT(Nippon Telephone and Telegraphy) in 1979, followed by NMT in 1981.
2G - Second Generation of Mobile Telephony
It's now we have that 0G and 1G systems are outdated, and we have nowadays 2G, 3G, and 4G and Intermediate most systems commonly available in market. The all we have to chose from.
Second Generation cellular telecom networks were commercially introduced on the GSM standard in Finland by Radiolinja(now part of Elisa Oly) in 1991.
Main features and benefits of 2G over previous Generations were-
1. Digital Radio transmission giving a possibility of easy Encryption and Decryption thus providing higher on the air privacy, making our data better secure. Digital transmission also improved System Capacity making possible compression and efficient multiplexing of data.
2. More efficient spectrum utilisation over previous standards, improving mobile phone penetration levels.
3. Introduced data facility for mobile, SMS(Short Message Service) was first introduced in GSM systems.
2G technologies can be divided into TDMA(Time Division Multiple Access) and CDMA(Code Division Multiple Access)
The Most popular second generation standards include:
1. TDMA Standards
(a) Global System Mobile(GSM)
- Entire band is divided into 200Khz wide ARFCNs.
- TDMA standard supports eight time slotted users for each 200 KHz radio channel.
- It has been deployed widely by service providers in Europe, Asia, Australia, South America, and some part of US( In PCS i.e. Personal Communication System spectrum band [1800 - 2000 MHz frequency band] only.)
(b.) Interim Standard 136 (IS-136)
- Also known as North America Digital cellular(NADC).
- supports 3 time slotted users for each 30 KHz radio channel.
- It's a popular choice for carriers in North America, South America and Australia(in both the cellular and PCS band).
(c.) Pacific Digital Cellular(PDC)
- It's a Japanese TDMA standard that is similar to IS-136 with more than 150 million users
2. CDMA Standards
(d.) Interim Standard -95
- It is also known as cdmaone.
- cdmaone supports up to 64 users that are orthogonally coded and simultaneously transmitted on each 1.25 MHz channel.
- It is widely deployed by carriers in North America (in both cellular and PCS band), as well as in Korea, Japan, China, South America, and Australia
2.5G and 2.75G SYSTEMS
Even before the 3G systems could have come to their proper standards, Certain Intermediate technologies evolved out from 2G systems. 2.5G and 2.75G systems have speed greater than those of 2G systems but not better enough to meet the standards of the 3G systems.
4 major intermediate standards have been found including 3 TDMA upgrade options :
(a.) High Speed Circuit Switched Data (HSCSD) ->>
- This circuit switched technique allows allows a single mobile subscriber to use consecutive user time slots in GSM standard. i.e. instead of limiting each user to only one specific time slot in GSM TDMA standard HSCSD allows individual data users to commandeer consecutive time slots in order to obtain higher speed data access on the GSM network.
- It relaxes error control coding algorithms originally specified in GSM standard.
- Increases available application data rate to 14,400bps, as compared to original 9600 bps in GSM specification.
(b.) General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)
- GPRS is a packet based data network , which is well suited for non real time Internet usage, viz. the retrieval of email, faxes, and asymmetric web browsing etc.
- Implementation of GPRS merely requires the GSM operators to install the new routers and Internet Gateways at the base station, along with new software that redefines the base station air interface for GPRS channels and time slots- no new base station RF hardware is required.
(c.) Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE).
- It is sometimes referred to as Enhanced GPRS or EGPRS.
- It Is a 2.75G standard.
- EDGE introduces a new digital modulation format, 8-PSK (octal phase shift keying) which is used in addition with GSM standard GMSK model.
and the fourth is a CDMA upgrade
(d.) IS-95B,
- Like GPRS, IS-95B is already being deployed worldwide, and provides high speed circuit and packet switched data access on a common CDMA radio channel by dedicating multiple orthogonal user channels for specific users and specific purposes.
- It supports 64 different user channels.
- Here, rate has been improved to 14,400 bps from that of 9600bps in IS-95A.
Upgrade Paths for 2G technologies
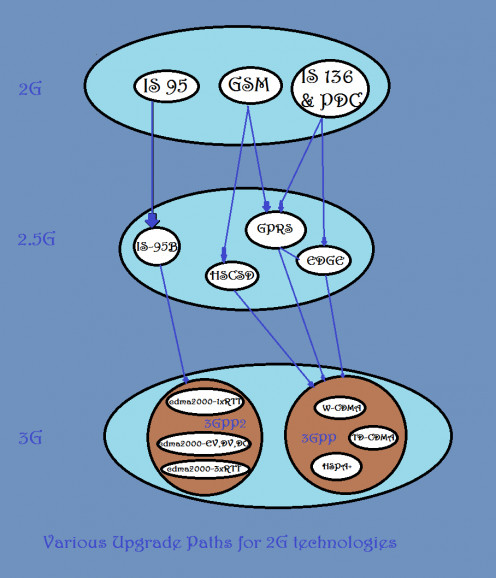
3G Third Generation Mobile Communication System
Third Generation mobile telephony standard was defined by International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in 1995.
It was mainly introduced to formulate the plan of ITU to implement a global frequency band in the 2000MHz range that would support a single, ubiquitous wireless communication standard for all countries throughout the world, and Its technical specifications were made available under the name IMT-2000(International Mobile Telephony).
Features:-
1. 3G standards are defined to have a minimum data rate of 2Mbps for stationary or walking users, and 384 Kbps in a moving vehicle.
2. ITUs 2000 World Radio Conference established the 2500-2690 MHz, 1710-1885 MHz, and 806-960 MHz bands as candidates for 3G.
3. Various 3G standards meeting its criteria are grouped under 3GPP2, one which is downward compatible with CDMA standards and 3GPP, downward compatible with the TDMA standards.
4. 3GPP2(Third Generation Partnership project for cdma2000 based on backward compatibility with IS-95) includes:
- cdma2000-1xRTT - The 1st 3G CDMA air interface, cdma2000 1xRTT, implies that a single 1.25 MHz radio channel is used(e.g. 1X simply implies one times the original cdmaone channel bandwidth, or put another way, a multi-carrier mode with only one carrier). Within ITU IMT-2000 body, cdma2000 1xRTT is also known as G3G-MC-CDMA-1X.
- cdma2000-1xEV, DV, DO- It is first commercial 3G network of United State, developed by Monet Mobile Networks, but later faced a shut down down by the Network provider. 2nd was provided by Verizon wireless in July 2002. and also cdma2000-1xEV-DO has been South Korean first 3G technology introduced by SK Telecoms in January 2002. ((Here EV indicates Evolutionary advancement, DV is data and voice, and DO is data only.))
- cdma2000-3xRTT
3GPP(Third Generation Partnership Project for Wideband CDMA standards based on backward compatibility with GSM and IS-136/PDC) standards for third generation includes:
- W-CDMA(UMTS) - Universal Mobile Telecommunication System(UMTS) is a visionary air interface standard that has evolved since late 1996 under the auspices of the European Telecommunications standard institute(ETSI). W-CDMA will support packet data rates up to 2.048 Mbps per user(stationary), thereby allowing high quality data, multimedia, streaming audio, streaming video and broadcast type services to customer.
- HSPA+
- TD-SCDMA The China Academy of Telecommunication Technology (CATT) and Seimens Corporation jointly submitted in IMT-2000 3G standard proposal in 1998, based on Time Division Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access( TD-SCDMA). This proposal was adopted by ITU as one of the 3G options in late 1999.
Note:- The first pre commercial 3G Network was launched by NTT DoCoMo in Japan in 1998. It was first available in may 2001 as a pre-release test of W-CDMA technology, while the first commercial release was on 1st October 2001, also by NTT.
4G Fourth Generation Of Mobile Telephony
Fourth generation is the latest Generation of Mobile Network hitherto.
Features and enhancements :-
- While 3G was basically a mobile telephony system, 4G is an integration of various Wireless technologies.
- It works on a packet switching technology with speed defined in range from 100Mbps to 1Gbps. bandwidth is taken as 100 MHz or more.
- Access technologies are OFDM and MC-CDMA.
- A 4G system provides Mobile Ultra broadband Internet Access, for ex: to smartphones, to laptops with USB Wireless Modems, and to other Mobile Devices
Two standards are available for use in 4G technology system.
(a.) Mobile WiMax, IEEE 802.16e standard- It offers a peak data rates of 128Mbits/s downlink and 56Mbit/sec uplink over 20 MHz voice channel. This standard was first implemented in South Korea in 2006. In United States, Sprint Nextel has deployed Mobile WiMAX networks since 2008. WIMAX Smartphones have been available since 2010.
(b.) Long Term Evolution (LTE) Standard- It was first implemented in Oslo, Norway and Stockholm, Sweden since 2009. MetroPCS was the first operator to offer LTE service in 2010. LTE smartphones have been available since 2011.
In Australia, Telstra launched the country's first 4G network (LTE) in September 2011 claiming 2-40 Mbps speed and announced an "aggressive" expansion of that network in 2012.
In India, Bharti Airtel has launched India's first 4G service using TD-LTE technology in Kolkata on 10th April 2012. Also, Reliance Industries Limited(RIL) is planning to launch its 4G service under the name Reliance Jio Infocomm.
In New Zealand the First 4G standard will be introduced in December 2013.
Note:- Equipments for communication systems made for different continents are not always compatible for use with each other, because of different frequency bands adopted for diff. continents.

Just look 4G already seems a boon for mobile telephony systems with its marvellous speed to provide the mobile web access, gaming, HD mobile TV, Video Conferences, 3D televisions, cloud computing etc. great applications, but we have still more to go.
So here we saw the Generation we passed on, onto our step by step journey to reach............... the destiny which exists somewhere may be still far beyond our imaginations. Don't know exactly till where we may go? May be the mobile telephony may get entirely redefined in some generation, in a way that we may even not need to carry any gadget at all. May be we reach a generation where we move just with a highly technical ring in our finger, to just to create our screen anywhere we want at anytime.
or may be there is something else yet far to be imagined to be done in these technologies. Well world is full of endless possibilities. Lets keep moving..
to be continued when the next generation 5G comes its way.
HAPPY READDING , ENJOY
TZRINZ