Home Biogas Production

Is home biogas production a viable solution to reducing home heating costs? It’s a great question. One that people around the world are addressing through on the ground experimentation and technology development. This biofuel could drastically reduce our dependence on natural gas, butane, or propane, for home heating and cooking.
Greenhouse Emissions
What is Biogas
Biogas is methane gas. This methane gas is produced during digestive processes. In fact, cows have been accused of contributing to global warming via their gaseous emissions. Now not all the gas that cows produce is methane. They also emit other gases, but cows do emit 800-1000 liters of gas daily. To put that into perspective Argentina maintains 55 million cows. Doing the math these cows could produce as much as 55 billion liters of methane containing emissions daily!
Biogas is also produced during the anaerobic digestion or decomposition of organic material. This anaerobic environment can be created in a man made structure allowing for the collection and burning of this biofuel.
Anaerobic Digestion
Biogas (methane) is produced through a process of anaerobic digestion. This process requires an anaerobic environment (oxygen free) such as a digestion tract or an anaerobic digester.
Swamp gas is an example of biogas produced in an anearobic environment. When the submerged organic layer in a swamp is depleted of oxygen methane production commences. Anaerobic microbes breakdown the organic material in a complex series of processes. The by-product of these processes is methane, CO2, and other gases.
Biogas digesters duplicate this environment. Seeding the digester with animal waste, typically cow or horse manure, supplies the digester with a source of anaerobic microbes. Once the system is functioning other organic materials such as kitchen scraps, restaurant waste, and rotten produce can be utilized.

The History of Biogas Production
From the collecting of swamp gas by Volta in 1770 to the construction of modern biogas plants, methane production has had a unique history.
China has been promoting the use of biogas digesters for decades and with good reason. Biogas can be produced with little effort in remote locations providing for cooking and heating needs. Rural family farms have a never ending supply of organic waste to feed anaerobic digesters. There is no need to haul or pipe natural gas long distances when you can make it right on site. Today more than 28 million Chinese households utilize biogas.
India, Germany, and China have all developed massive biogas production programs. These programs involve the use of human waste, organic or food waste that would otherwise go to landfills, and in at least one case up to 250,000 cows dedicated to biogas production. These countries not only have developed the biogas industry, but they've done so while promoting home biogas production.
In the United States you will seldom see home biogas digesters employed. Some agricultural facilities have begun to take advantage of this technology, but most do not. The trapping of methane produced by landfills and the utilization of anaerobic digesters in conjunction with sewage treatment facilities is common place in the U.S..

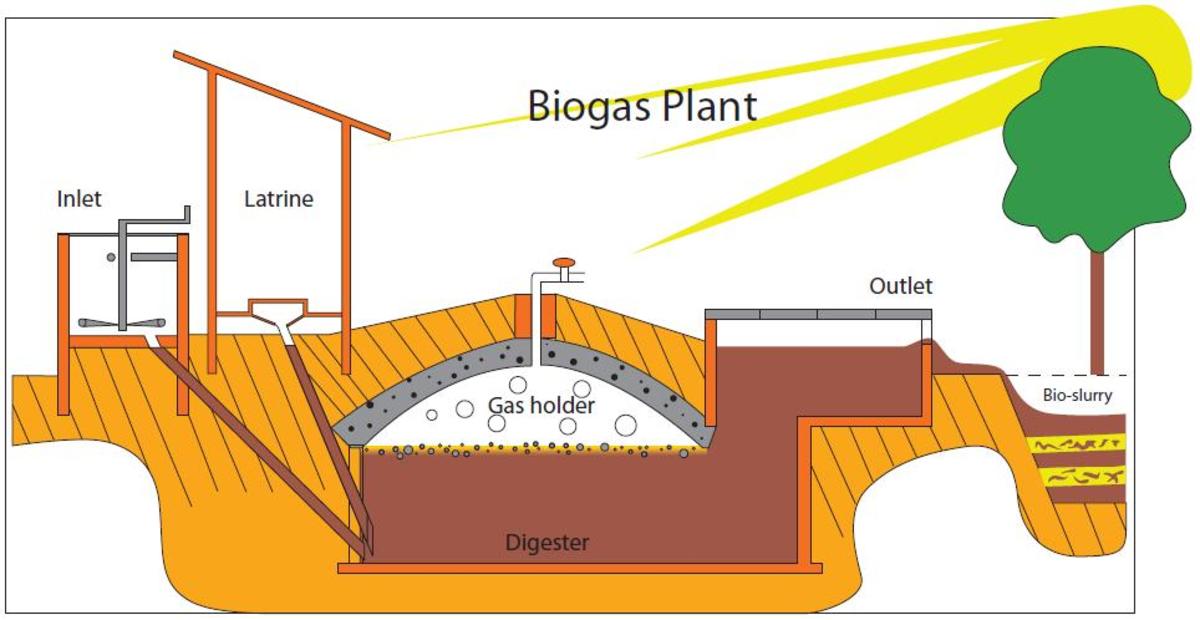
Home Biogas Systems
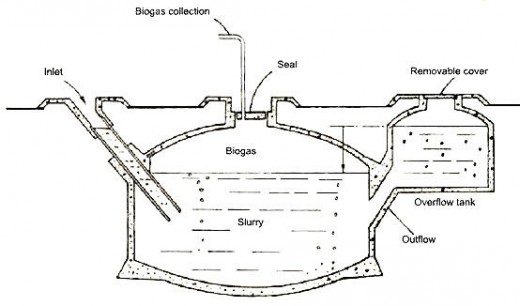
Biogas production systems simply differ in size from commercial production facilities to home biogas systems. Though the dimensions may be vastly different the concepts utilized in most systems are still the same. There are three basic styles of biogas digesters that are typically used for home methane production. Pit systems, bladder systems, and telescoping systems.
Pit systems utilize pits or subterranean tanks to store the decomposing organic material. The waste is poured into the system via a pipe that enters the tank bellow the surface of the slurry. An additional overflow tank is use to both harvest the nutrient rich effluent produced by the digester, but also to pressurize the biogas in the tank.
Bladder style system utilize a storage tank, but differ in that they utilize a rubber bladder to pressurize the methane gas. This bladder allows the owner to visually assess the amount of gas the system produces.
Telescoping digesters are basically two cylindrical container which slide into each other. The top cylinder rises as biogas is produced. This acts both to pressurize the gas and provides the owner with a visual indicator as to the amount of gas the system has produced.
All of these systems can be used for the home production of biogas, but the telescoping types are the most portable. They can be prefabricated and delivered to the installation site adding to their ease of use.
Conclusion
Home biogas digesters are an efficient way to turn otherwise wasted organic material into useable methane gas. Though not seen often in the United States they are gaining popularity in agricultural communities. These systems may never be common place in urban communities in the US, but the most certainly have a place in rural and agricultural developments.
Home Biogas Production Links
- THD & Popular Biodigesters
Statistics and designs of popular home biogas systems. - Biogas as a source of energy - Lesson Plan
This lesson plan designed by Heifer.org is design to teach the principle of biogas production. - History of Biogas - energypedia.info
A brief history of biogas prodcution. - Advanced small-scale anaerobic digester design tailored for household user living in cold climate
An anaerobic digester designed for cold climates. - Anaerobic Digestion in Rural China
China has been promoting biogas digesters on family farms throughout China with great success.