How do Touchscreens Work
Touchscreen Become Ubiquitous
Touchscreens have moved from the banking kiosk to the smartphone, tablet and personal computers. They are everywhere having gotten cheaper over the years.
But one touchscreen may not be like another. In fact there are five basic technologies that are used to make touchscreens work and they are very different from each other.
These five methods are resistive, capacitive, infrared, acoustic wave and optical.
Resistive Touchscreen
If you think of electrical current as a flow of water, resistance is a condition where that flow is reduced. What causes that reduction in flow is called resistance.
In describing electrical current, resistance to that current causes a voltage drop and/or a current drop. A voltage drop can be detected by other circuitry and that can be used to determine where the point of resistance is.
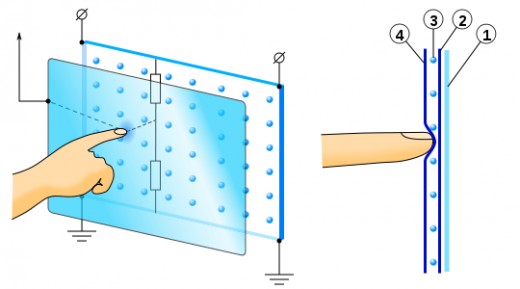
A resistive touchscreen is typically made up of two flexible sheets. These sheets are coated with a resistive material and
separated by an air gap. (see image right) When contact is made to the
surface of the touchscreen, the two sheets are pressed together at a point and resistance is detected. The resistance lasts only as long as that contact is maintained on that point of the screen.
In the image at right is (1) a inflexible backing, (2) is one layer of resistive material, (3) is the structure that keeps a gap between the two layers, and (4) is the outer resistive layer.
On
these two sheets there are horizontal and vertical wires that when
pushed together, register the precise resistive location of the touch. With enough horizontal and vertical wires the point of resistance can be located very precisely.
Resistive touchscreens work well with fingertips, stylus, or any other object that can force the two layers together.
Pros
- Durability - 35 million touches life span
- Can be activated by any object
- Not affected by dust, dirt or liquids
Cons
- Limited accuracy
- Interferes with the underlying display
- High power requirements (reducing the life of the battery)
- Can be damaged by sharp objects
Capacative Touchscreen
Capacitance is the ability of an object to store an electrical charge. Capacitance is measured by an object's ability to hold a charge as well as the amount of charge. Because the human finger can also pass a charge, any touch on a capacitive screen changes the state of charge.
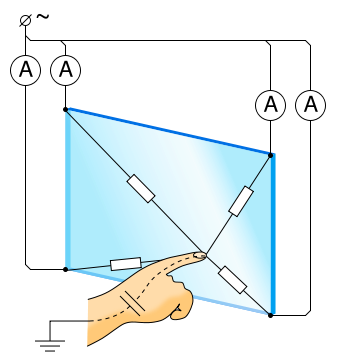
A capacitive touchscreen panel consists of an insulating layer coated with a conductor. Because the human body (including the finger) is also a conductor, any touch on a capacitive screen causes a change in capacitance. With enough sensitivity the capacitive touch screen can be made quite accurate.
In the image at right a small amount of current is sent into the touchscreen at points (A). The human finger represents a ground to that field and a controller connected to the display can detect the change in capacatance at any point on the screen.
Pros
- Good visibility through layers
- High durability; the outer most layer is typically a hardened glass
- Extremely sensitive to human touch
- Resistant to dust and dirt
- Works with multiple touches
Cons
- More expensive than resistive touchscreens to manufacture
- Must have a relative humidity of 5% and up to work
- Only works with flesh; does not work with a stylus or another inorganic object
- Prone to false readings
- Must be calibrated before installation
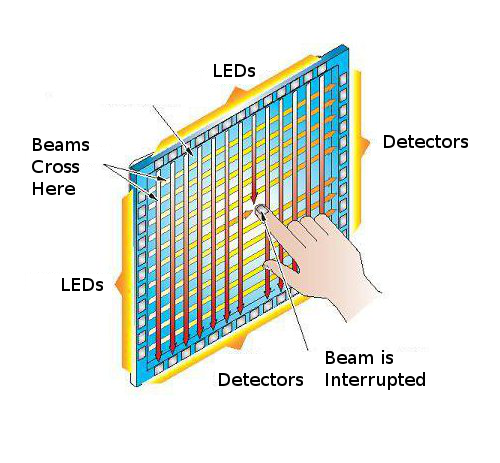
Infrared Touchscreen
An infrared touchscreen uses an array of X-Y infrared LED and photo-detector pairs around the edge of the screen. To imagine this, visualize the screen having hundreds of tiny infrared emitters (light projectors) along the top and right sides of the screen. Also imagine infrared detectors arrayed along the bottom and left side of the screen.
Any object that interrupts the beam of light from the top to the bottom or the right side to the left side is detected.
Because these beams of infrared light are in a tight criss-cross pattern, any interuption of that beam is instantly detected.
Pros
- Works with any object that can interrupt the beam
- Extremely clear displays with nothing interfering with the image
- Highly durable
- Dust and liquid resistant
Cons
- High power requirements
- Touch is detected just above the actual screen surface
- Accuracy is determined by the number of emitters and detectors; therefore they are not as accurate as resistive and capacitive touchscreens
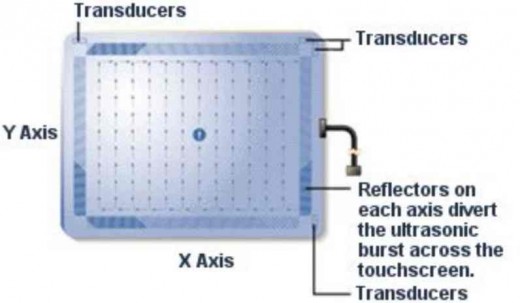
Acoustic Wave Touchscreen
These systems use piezoelectric transducers located at strategic positions around the screen. The transducers produce mechanical energy (sound) and any disruption in the expected energy is interpreted as a touch.
A built-in processor is then utilized to determine where on the screen the touch occurred.
Most acoustic touchscreens are made of common glass, which provides a level of durability. Glass is also a good medium to transmit images through.These systems are good for larger displays. Because a non moving finger does not register these systems are ideal for situations where an object might be expected to rest on the screen.
Applications where the screen also serves as a table-top are ideal for this technology.
Pros
- Provides clear and precise touch location
- Does not interfere with the underlying display
- Ideal for larger screens
- Good for "out-of-door" situations
Cons
- Can be subject to debris entering the field
- More costly than other systems
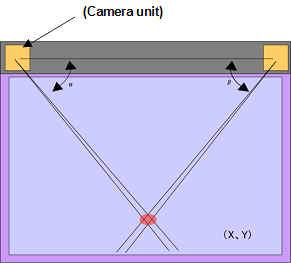
Optical Touchscreen
With this technology true touch is not really required.Two cameras, strategically positioned at the upper left and right corners of the screen, are used to determine if something passes in front of them. With some systems an Infrared back-light is placed within the camera's field of view. A touch is detected when a shadow is detected and pin-pointed via the two cameras.
Because only two sensors are required these systems are scalable, versatile and affordable.
Pros
- Systems are scalable
- Will work in any lighting condition as the light is provided
- Reduces wear on the screen itself
Cons
- Larger than typical items (cameras) are required
- Requires more setup and calibration
- Touch is detected before an object actually touches the screen
Optical Touchscreen
Coda
So, as you can see there is more than one type of touchscreen system. The most common for smartphones and small computer applications are resistive and capacitive. This is why these two were listed first.
Disclaimer
The author was not compensated in any way, monetarily, with discounts, or freebies by any of the companies mentioned.
Though the author does make a small profit for the word count of this article none of that comes directly from the manufacturers mentioned. The author also stands to make a small profit from advertising attached to this article.
The author has no control over either the advertising or the contents of those ads.