How does a basic circuit breaker work?
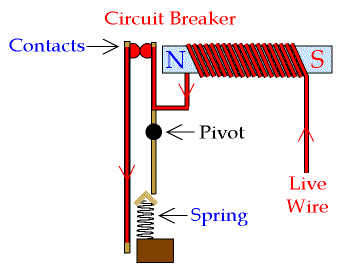
The diagram on the right shows the set of a basic circuit breaker. It is pretty self explanatory, but this article will go through the steps involved when a circuit breaker cuts off the power to prevent damage or injury following a current surge.
First of all, on the diagram we see that the electricity comes from the right hand side, through a live wire. This wire is the wrapped around a magnet, making it into an electromagnet. The wire then continues along the circuit, along a pivot fixed in place by a spring, then there are two contacts at the top left of the diagram. When all is fine and the current is not to strong, the electricity passes along the contacts and then continues to its destination.
However, if there is a surge in the current, the current through the live wire and around the magnet will become so high that the electromagnet manages to pull the right hand contact away from the other and clicks the pivot into the second position (it moves clockwise). This is why you hear a clicking noise. The spring makes sure that the pivot doesn't move back again. When you reset a circuit breaker by flicking a switch, you are manually pushing the pivot back to its original position, allowing electricity to flow through the contacts again.
Thank you for reading, I know that this explanation is rather basic but hopefully it covers all the understanding you need of how a circuit breaker works, feel free to leave a comment below or any suggestions. If you enjoyed this article or found it helpful please like, share or rate.
Want to learn about alpha radiation? Check out 'Alpha Radiation'.
Check out my latest article: Essential books on the British Empire