- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Science & Programming
How to implement Singleton Design Pattern in Java ?.
Introduction
Design Pattern is nothing but a solution to a common recurring problem in software design. It represent a pattern which solves a complex problem in software design. It is like, someone has already solved your problem and you have to just implement it accordingly. Singleton Design Pattern is one of such pattern which solves recurring problem in software design. Singleton Design Pattern is a pattern which limits instantiation of a of a class to one object. It helps in creating an instance of class only once. Trying to create multiple instance will be restricted and same object will be referenced.
Lets implement Singleton Design Pattern in Java through a video tutorial. Below is the video tutorial which gives walk through step by step in implementing Singleton Design Pattern. There is also complete Java source code provided below which explains it more clearly.
Video tutorial - How to implement Singleton Design Pattern in Java.

Java source code - How to implement Singleton Design Pattern in Java.
// In order to make a class singleton we have to follow two rules :
// 1. That it should have only single instance.
// 2. That this instance should be available through a global access.
// Steps to make a class singleton :
// Step 1 : Create a class which you want to make singleton. Here, we have created
// a class by name Circle which we want to make singleton.
public class Circle {
// Step 2 : Create a private default constructor of class. Below is the Circle constructor
// which has private access specifier. It should be made private so that no other class
// outside Circle class can create instance of Circle.
private Circle() {
}
// Step 3 : Create instance variable of class Circle. This instance variable should be
// private and static. Assign it a instance of Circle class.
private static Circle circleInstance = new Circle();
// Step 4 : Create a static accessor method which could always return back us a instance
// of class created in step 3.
public static Circle getInstance() {
return circleInstance;
}
// Step 5 : There should not be any method or constructor which can create instance of
// Circle class.
// Step 6 : Create a integer variable say radius. Assign it value as 0.
private int radius = 0;
// Step 7 : Create getters and setters method of radius variable.
public int getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(int radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
}
Steps to implement -
In order to make a class singleton we have to follow two rules :
1. That it should have only single instance.
2. That this instance should be available through a global access.
Steps to make a class singleton :
Step 1 : Create a class which you want to make singleton. Here, we have created a class by name Circle which we want to make singleton.
Step 2 : Create a private default constructor of class. Below is the Circle constructor which has private access specifier. It should be made private so that no other class outside Circle class can create instance of Circle.
Step 3 : Create instance variable of class Circle. This instance variable should be private and static. Assign it a instance of Circle class.
Step 4 : Create a static accessor method which could always return back us a instance of class created in step 3.
Step 5 : There should not be any method or constructor which can create instance of Circle class.
Step 6 : Create a integer variable say radius. Assign it value as 0.
Step 7 : Create getters and setters method of radius variable.
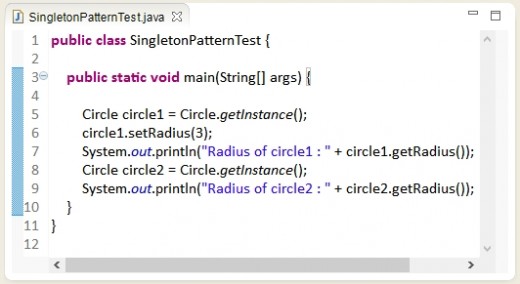
Test class - SingletonPatternTest
// Step 1 : Create a application class to test Singleton Design Pattern.
public class SingletonPatternTest {
// Step 2 : Create a main method which will test Singleton nature of Circle
// class.
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Step 3 : Create instance of Circle say, circle1
Circle circle1 = Circle.getInstance();
// Step 4 : Set the radius of circle1 as 3. Initially it was 0.
circle1.setRadius(3);
// Step 5 : Print radius of circle1.
System.out.println("Radius of circle1 : " + circle1.getRadius());
// Step 6 : Create instance of Circle say, circle2
Circle circle2 = Circle.getInstance();
// Step 7 : Print radius of circle2. Instead of printing value as 0. It prints
// value as 3. It proves no new instance was created. It prints 3 assigned
// to circle1 instance.
System.out.println("Radius of circle2 : " + circle2.getRadius());
}
}
Steps to implement -
Step 1 : Create a application class to test Singleton Design Pattern.
Step 2 : Create a main method which will test Singleton nature of Circle class.
Step 3 : Create instance of Circle say, circle1.
Step 4 : Set the radius of circle1 as 3. Initially it was 0.
Step 5 : Print radius of circle1.
Step 6 : Create instance of Circle say, circle2.
Step 7 : Print radius of circle2. Instead of printing value as 0. It prints value as 3. It proves no new instance was created. It prints 3 assigned to circle1 instance.
Output of the program -
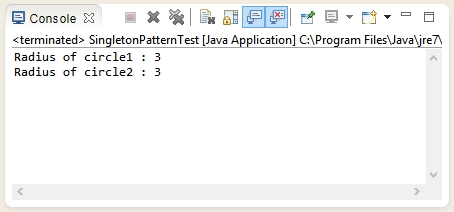
Output of the program - Explanation
In the code of test class "SingletonPatternTest" , there is a main method. This method is the starting point for execution of any Java program. Singleton Design Pattern limits creation or instantiation of a Java object to one. In the test class as soon as we create circle1 instance, that's it , no other instance can be created there after. After creation of circle1 instance, we set the radius to 3. When we create instance circle2 no new instance of class Circle is created. Here, getInstance method returns back the same instance to which circle1 is referring. The proof of Circle being a singleton class is the fact that when we call getRadius method on circle2 it prints 3. It means no new instance was created and it gets back instance which was created once in the memory.
Watch my complete Youtube channel below -
- Java Hubberspot - YouTube
Hello friends, I am Dinesh Varyani. Owner of blog http://www.hubberspot.com . This channel will have Java Programming Tutorials for beginners ... Visit my Ja...