- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Science & Programming»
- Computer Programming Tutorials
How to use Scanner class in Java ?.
Introduction to Scanner class in Java
Scanner class is one of the most frequently used Java class. It comes with Java's in-built API in the package java.util. As the name suggest, it helps in scanning and parsing of string, text and primitive data types such as - int, long, byte, short, float, double and boolean.
- Scanner class provides us the functionality to read numeric values, strings and other types of data from console , keyboards and disk files etc …
- Scanner class was designed to read and scan input from the console, a string, a file, or any source that implements Readable or ReadableByteChannel Interfaces.
- Scanner reads data from above sources in the form of tokens. Here tokens are separated by delimiters such as :- comma(,) whitespace( ) symbols(*, $). The default delimiter is whitespace.
- Example :
String - “Hello World Welcome!!!.”
Delimiter used – “ ”
Tokens would be - “Hello” , “World” , “Welcome!!!.”
How to create a Scanner ?.
Scanner class has many overloaded constructors ( String, File, InputStream, Readable ) through which we can create various types of scanners such as :-
Constructors
| Description
|
|---|---|
Scanner( File file )
| Creates a Scanner that uses the file specified as a source to read from.
|
Scanner( InputStream inputStream )
| Creates a Scanner that uses the input stream specified as a source to read from.
|
Scanner( Readable readable )
| Creates a Scanner that uses the Readable object specified as a source to read from.
|
Scanner( ReadableByteChannel channelSource )
| Creates a Scanner that uses the ReadableByteChannel object specified as a source to read from.
|
Scanner( String string )
| Creates a Scanner that uses the String object specified as a source to read from.
|
Important Methods in Scanner
Scanner class has many methods to read tokens which are of primitive types , String and other data types such as :-
Methods
| Description
|
|---|---|
boolean nextBoolean()
| It returns the next token as a boolean value.
|
byte nextByte()
| It returns the next token as a byte value.
|
short nextShort()
| It returns the next token as a short value.
|
int nextInt()
| It returns the next token as a integer value.
|
long nextLong()
| It returns the next token as a long value.
|
float nextFloat()
| It returns the next token as a float value.
|
double nextDouble()
| It returns the next token as a double value.
|
String nextLine()
| It returns the next token as a string value.
|
BigDecimal nextBigDecimal()
| It returns the next token as a big decimal value.
|
Scanner useDelimiter(String delimiter)
| Change the delimiter of scanner to delimiter provided as an argument.
|
Pattern delimiter()
| It returns the current delimiter used.
|
String findInLine( String pattern )
| It searches for the pattern passed to method as an argument in the next line of text. If the pattern is found it returns it back or else it returns null.
|
void close()
| It closes the scanner.
|
boolean hasNextBoolean()
| Returns true if a boolean value is available to be read.
|
boolean hasNextByte()
| Returns true if a byte value is available to be read.
|
boolean hasNextShort()
| Returns true if a short value is available to be read.
|
boolean hasNextInt()
| Returns true if a integer value is available to be read.
|
boolean hasNextLong()
| Returns true if a long value is available to be read.
|
boolean hasNextFloat()
| Returns true if a float value is available to be read.
|
boolean hasNextDouble()
| Returns true if a double value is available to be read.
|
boolean hasNextLine()
| Returns true if a string value is available to be read.
|
boolean hasNextBigDecimal()
| Returns true if a big decimal value is available to be read.
|
Before using next methods of Scanner, first confirm it with calling hasNext methods so that it not throws NoSuchElementException or InputMismatchException.
Description of few methods -

Complete video tutorial - Scanner class in Java
In this video tutorial, Scanner class has been described with theory as well as through Java code. Scanner class instance creation with the help of String, Input streams etc has been described. After moving further in the video various methods present in the Scanner class such as next, nextLine, close etc has been described.
A simple Scanner class demo -
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ScannerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Scanner object to obtain user
// input from the console.
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// Prompt the user to enter value of name
System.out.print("Enter value of name : ");
// Create a string variable name.
// Using scanner class nextLine method, assign
// value of the name entered by the user to name variable.
String name = input.nextLine();
// print value of name on the java console entered by the user.
System.out.println("The name entered by user is : " + name);
}
}
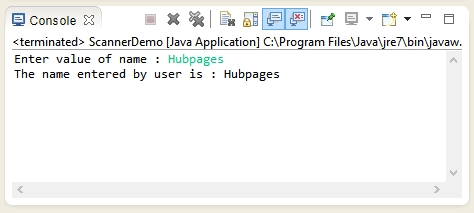
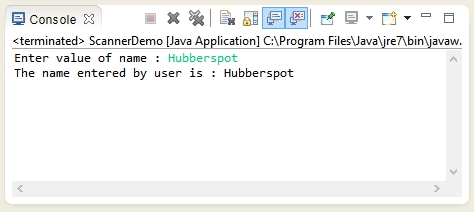
Output of the program -
Output of program - Explanation
Creation of Scanner instance takes in a String, InputStream, Readable, File etc into its constructor. Scanner class in above example takes in a instance of System.in. System.in is a input stream that helps Scanner class to read user inputs from the Java console.
After creation of Scanner object, prompt the user to enter value of a name. Scanner class has nextLine method, it reads user input from the Java console in the form of String.
It reads name entered by the user and assign it to String variable name. In order to check this reading and assignment of String value name to variable name, print the value of name on the Java console through System.out.print method.
In first output user enters "Hubpages" , which is been printed in the next line on Java console.
In second output user enters "Hubberspot" , which is been printed in the next line on Java console.
Watch my complete Youtube channel below -
- Java Hubberspot - YouTube
Hello friends, I am Dinesh Varyani. Owner of blog http://www.hubberspot.com . This channel will have Java Programming Tutorials for beginners ... Visit my Ja...