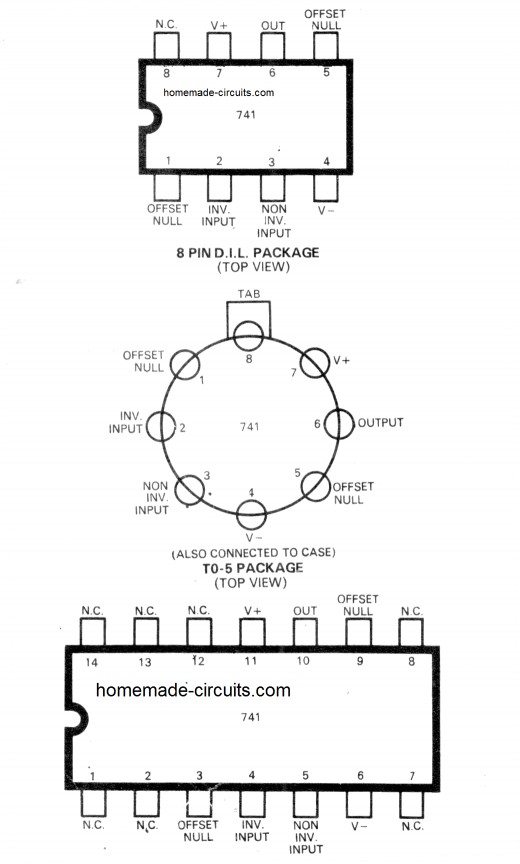
IC 741 Electrical Specifications
Open loop voltage gain
Open loop voltage gain - Ao: This is the basic voltage gain of the internal circuitry as a whole, and may be expressed as a multiple or in decibels. A typical value of A0 for 741 is 100,000 or 100 dB.
Input and Output Impedances
Input impedance - Zm: This is a measure of the impedance, looking into the input terminals of the op-amp, and is expressed in terms of resistance. A typical value of Zm for IC 741 is 1 megohm.
Output impedance - Zo: This 741 electrical specification is a measure of the impedance offered by the output terminals of the op-amp. It is also expressed in terms of resistance. A typical value of Z1 for 741 is 150 ohms. Input bias current - Ib: Op-amps utilizing bipolar transistor input stages draw a small bias current from the input terminals. A typical value of lb for 741 is 200 nA (200 x I0^-9 amperes).
Supply Voltage Range
Supply voltage range— Vs: Op-amps are usually operated from dual supplies that are anywhere between their minimum and maximum limits. If the supply voltages are very high, the op-amp may get damaged. If they are very low, the op-amp may not work satisfactorily. Typical supply limits for 741 are +/- 6V to +/- 18V.
Differential input offset voltage
Differential input offset voltage— Vio: Due to slight imbalances within their input circuitry and due to high gain of the op-amp, it is observed that the output does not register zero voltage even when both inputs are grounded. This small imbalance voltage appearing in the-input, which may even cause the output to swing to saturation, is known as the differential input offset voltage. A typical value of Vio for 741 is 2 mV. It is often required in some particular op-amp applications to nullify this offset voltage by using external offset nullifying circuit, as shown in Fig. (m).
Common mode rejection ratio: CMRR
Common mode rejection ratio - CMRR: In an ideal op- amp, if an identical signal is applied to both the inputs, the resultant output is zero. However, in practical 741 op-amp's circuits common mode signals do not entirely cancel out and produce a small signal at the output terminals. The ability of the op-amp to reject common mode signals is usually expressed in terms of common mode rejection ratio. In CMMR electrical specification is the ratio of the op-amp gain with differential signals to the op-amp gain with common mode signals. CMRR value for 741 is typically 90 dB.
Transition frequency
Transition frequency - fr: This is the frequency at which the gain of the op-amp falls to unity. Though an op-amp has a very high gain at low frequencies. in the interest of stability its open loop frequency response is tailored so that the gain falls off as the frequency rises. The gain falls to unity at a transition frequency known as fr. The value of fr for 741 is 1MHZ.
© 2018 Gladis2011