ISO Standards 17359 and 13379 and The Role of Thermography In Fault Analysis, and Casual Diagnostics
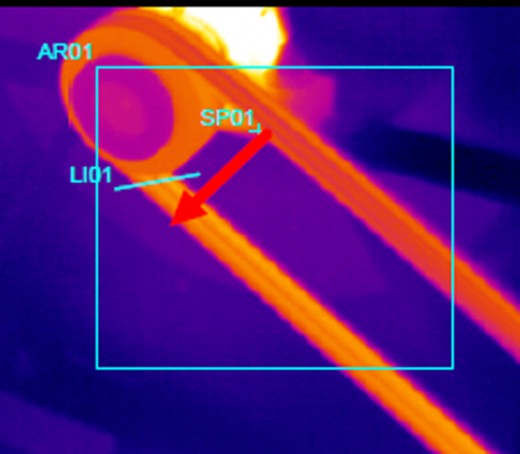
Electrical Connections

ISO 13379
The evolution of maintenance techniques finally reached condition based monitoring about a decade ago and allows us now to incorporate under that title casual diagnostics in fault analysis. Being a thermographer for nearly thirty years allows me to remember that this methodology has been a key factor in that evolution because at its very heart is identification of faults and determining corrective measures. ISO 13379 finally addresses this issue long after many of my colleagues have applied it to their everyday work. Here we examine this in light of Failure Modes Symptom Analysis (FMSA)
Fault analysis in thermographic terms examines various faults and the thermal symptoms resulting from there to determine symptomology of each fault type, that is, what thermal symptoms are present. Causal diagnostics approaches the issue from the opposite direction, seeing thermal patterns will identify the root cause of the problem to enable corrective measures, and an experienced thermographer will consider the root cause of the thermal energy he sees as important in determining and planning proper corrective actions. Causal analysis requires knowledge of the equipment component being inspected, the mechanism of the probable fault, and its potential path to failure.
ISO 13379 notes that the causal approach is used when the objective is to identify the root cause and this dualistic learning approach is imperative for new thermographers in understanding condition monitoring programs.
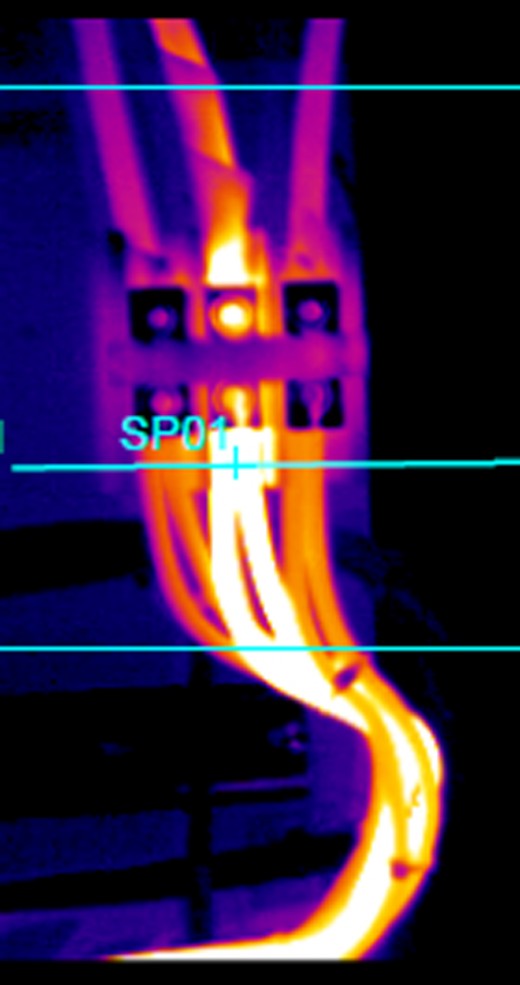
Failure Mode, Power Supply
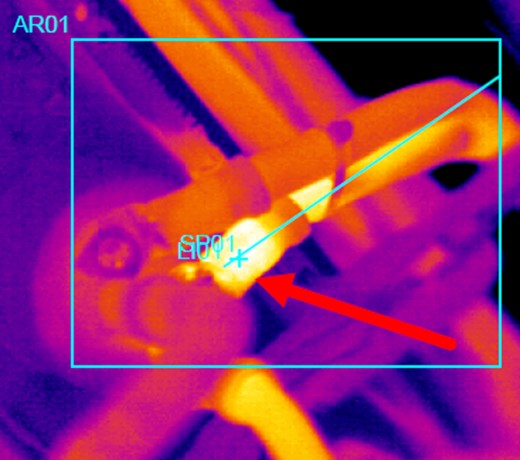

Failure Modes Symptom Analysis
The concept of Failure Modes Symptom Analysis (FMSA) is also introduced in ISO 13379, as a diagnostic and prognosis process and with the selection of the appropriate monitoring techniques. The standard suggests that FMSA should be used in conjunction with existing Failure Mode Criticality Analysis (FMCA) that has already identified and ranked possible failure modes.
For effective FMSA we recommend biannual or quarterly inspections, documenting and tracking every machine to trend the equipment over time and track detected problems, their diagnosis, the root cause, the prognosis of each which is the critical tracking parameter, recommended actions, and then the actual corrective measures that were implemented.
Each facility will implement its own response to the thermographic analysis based on their maintenance philosophy and budget, and each corrective measure ought to be tracked to understand the needs and actions taken in the past as failure mode is reached, so management can implement alterations to the maintenance procedures and staff implementing those procedures and standardize procedures.
Fault Analysis
Fault analysis and root cause analysis using thermography allows for a very broad equipment type to be examined and diagnosed before failure mode is reached when applied properly. Implementing the concepts laid out in ISO 13379 allows both the thermographer and the facilities manager to reduce downtime, reduce maintenance costs and creates a large return on the analysis investment made by the company managers and maintenance department.
Pulley Alignment Issues can cause larger issues
Preventative Maintenance
Preventative Maintenance (PM) is an indispensable process for industrial infrastructure as it directly affects the productivity and therefore, the company profit. Predictive Maintenance (PdM) increasingly proves its usefulness as a new maintenance philosophy and methodology as a cost effective and efficient maintenance system. When properly interfaced with production and material management, it will achieve optimum utilization of existing resources improving the reliability of equipment, which is especially important in mission critical equipment. Condition monitoring with a nondestructive and not-interruptive technology such as thermography is the highest form of maintenance in mission critical environments.
Modern business in a worldwide market economy demands the highest and best practices be implemented to reduce costs and maintain profitability, which implies best practices in maintenance to decrease downtime, maintain costly equipment, and increase the safety of personnel.
ISO 17359
ISO Standard 17359 Condition monitoring and diagnostics of machines - General guidelines, which provides guidance for condition monitoring and diagnostics of machines and sets out general procedures to be considered when setting up a condition monitoring program for all machines, here, I present an overview of a generic procedure recommended to be used when implementing a condition monitoring program, and argue that of the three primary diagnostic methodologies, thermography covers the broadest range of applications and equipment types beyond just machines.
Major Issues you can't even see
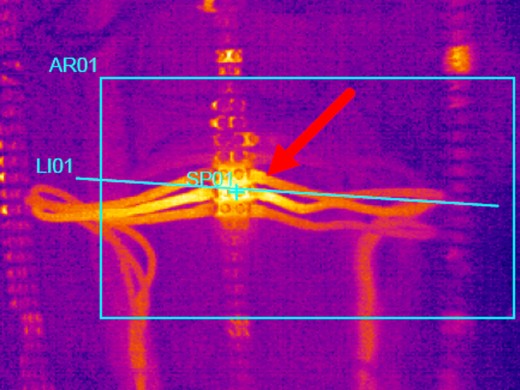
ISO Standard 17359 Condition Monitoring
ISO Standard 17359 links condition monitoring with various diagnostics of machines and indicates various analytical techniques to help define issues arising with the use of these machines. While there is one error (thermography can detect thermal anomalies in some misalignments), the document clearly shows thermography is a chief analytical tool in maintenance operations and reduction of equipment failures.
Condition Based Monitoring invokes the identification of failure modes and strategies that are manageable in the prevention of the impact of failure modes, reducing risk and management of such failure.
Maintenance strategies developed by Condition Based Monitoring are based on scientific evidence gathered during operations and are, therefore, more logical and well documented.
Over the years, thermography has been applied to many applications, ranging from determining energy loss from uninsulated surfaces to fine heat resistance found in microcircuit designs, and proven to be a useful technique to fault identification in many fields and all types of machines and other equipment.
Thermography is perceived by many as a vital and necessary part of a company’s asset management strategy, that when consistently and correctly applied can deliver plant performance that is in line with accounting and maintenance demands for cost efficiency.
Accumulation and formation of data over years of inspections that are correlated into databases provide a knowledge base that can be used to identify design faults or indicate subtle alterations of design or processes that can reduce failures, preserve equipment and operations, and reduce bottom line costs.
The ease of communication using thermograms and simplified analytics help to increase the knowledge and sophistication of the maintenance workforce in day-to-day routines.
Condition monitoring allows maintenance personnel to correct small issues and avoid failure modes which shorten the life of the machine or other equipment such as oxidation of electrical connections, spalling of bearing components, degradation of lubricants, or repeated tripping of breakers reducing productivity and reliability.
Thermography has been used in industry for more than forty years and its applications have continued to broaden as our understanding of thermal energy in equipment continues to grow. While the triad of most useful techniques remains stable, that is, vibration analysis, thermography, and oil analysis, thermography is more useful to a broader array of issues in an extensive list of applications where oil and vibration are simply not applicable.
The evolution of thought, product development and enhancement, and advancements in electronics have allowed the cost of thermographic inspections to largely remain stable over the past three decades while the knowledge base has increased and techniques have been refined making it ever more useful unlike, say, a telephone where the portability increased dramatically along with the average monthly telephone bill.
ISO 17359 suggests a more rigorous approach to the design of a condition monitoring program along a similar course that thermography developed along as thermographers learned to analyze connections of all voltages, faults of nearly all types, and the implications of thermal energy showing in all kinds of equipment operating in all environments.
You can take my word on this, I have corrected conditions on ships that the U.S. Navy considers vital to our national security and found issues that looks small, however, if uncorrected and certain conditions we were monitoring at the time escalated, the damage to the U.S. could have been devastating.
Enough said.