Introduction to Computer Terminology

Everything from sending man to Hubble space station, browsing the internet, uploading and downloading files, sending e-mail, video conferencing, shopping on eBay and Amazon and simply listening to music and playing solitaire, has made computers necessary companions in human life.
Computer per se is a very broad subject, and in order to begin grasping its essence, below are brief explanations of a few related basic terms.
1. Information Age and Computer Technology
Also called Computer technology age, information age is generally viewed as the era when information is accessible and productive. In pioneering computing concepts, the British Mathematician Allan Turing came up with the concept of the Turing Machine early in 1900s, which was programmable to solve infinite number of mathematical calculations.
Since Allan Turing, advancement in information technology has come a long way. Having evolved from enormous machines to pocket size and wearable gadgets, and from use in military and heavy duty industries to offices, schools and big businesses, computers now grace homes, even deep in the African village.
The road towards true information and communications technology was broadly realized when one of the first digital computers was manufactured in 1941. Z3 was designed by Konrad Zuse, and was followed soon after by the mammoth ENIAC in 1945-46.
Turing And Computer Technology
Then came the evolutionary Apple II personal computer in 1977, followed by the IBM-PC in 1981.
In the years that followed, bigger computers like the supercomputer got faster and more complex, while the micro computer got smaller and more personalized.
In the 21st Century, the trend turned towards wearable devices, making computers even more personal.
Popular wearable devices include smartwatches, smart glasses and smart clothes, and their evolutionary trends continue to rotate around mobile and personal human needs.

2. Information and Communications Technology
Information and communications technology (ICT) encompasses the broad sense of computers and communication. ICT or just IT, for Information Technology, explains input\output of data and processing of this data to information.
Data and information can be in analog and digital forms, and is applicable to computer hardware and software and all platforms of telecommunication i.e. computer systems, computer networking, internet, television, radio, telephone networking etc.
3. Computer
A computer is actually a system of many parts; hardware and software, working together via user input to process data and information. Simply put, a computer is a programmable electronic device which is capable of processing data inputs into useful information.

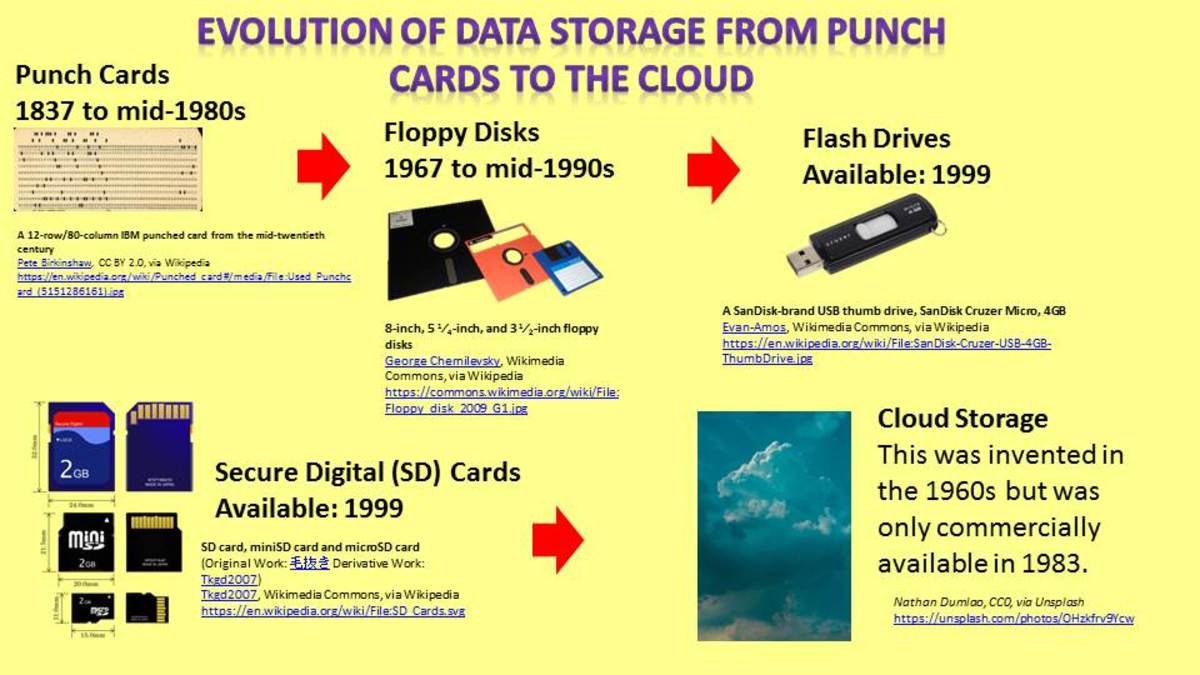
4. Data and Information
Data and information are actually software and the two terms are used interchangeably to mean the same thing. Technically however, data is the raw input that is fed into the computer via the keyboard and other input devices; and information is what is derived out of the raw data for productive use.
Information is viewed/used via visual display devices (VDU) or converted to hard copy printouts. For example in the mathematical task; 1 + 10 = 11, data will be 1 + 10 and the answer 11, is what qualifies as information.
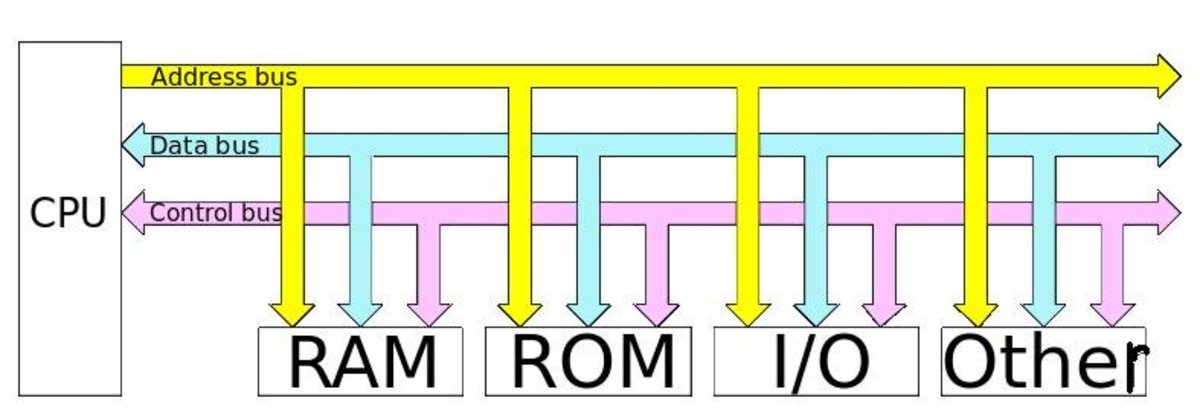
5. Computer Hardware
Computer hardware includes all the physical devices that make computer systems. These devices are tangible and examples are; mouse, keyboard, monitor, expansion card, microprocessor and system unit.

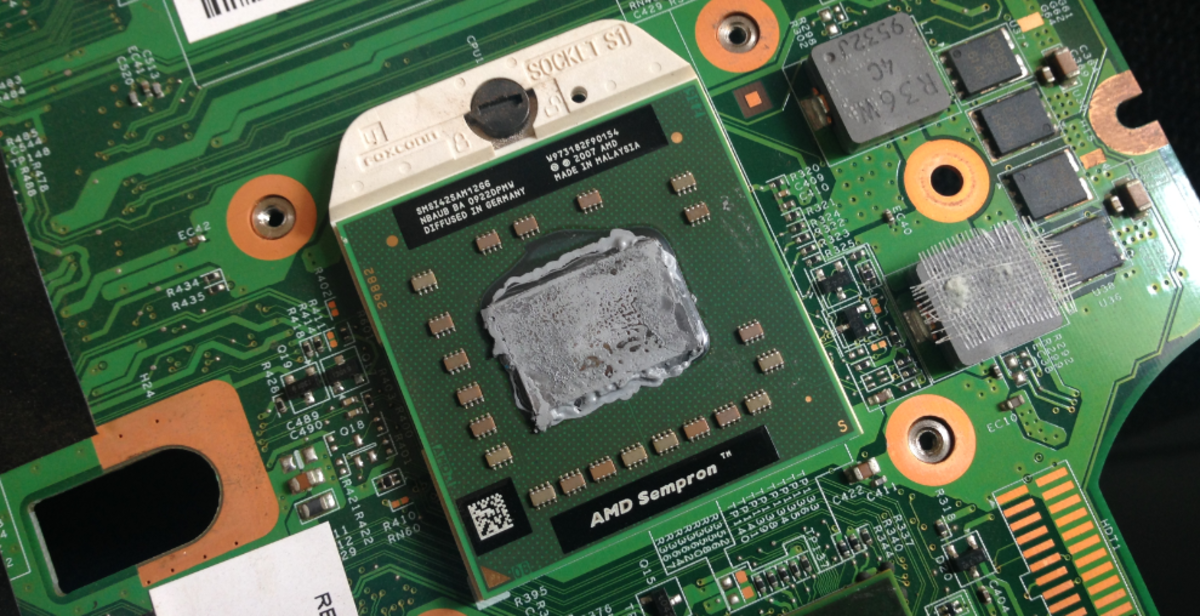
6. The Microprocessor
The microprocessor is a core component in the computer, accomplishing a whole spectrum of processing tasks. The birth of the micro processor in the 1970s probably saw some of the greatest innovations mankind has ever seen. The microprocessor became the cornerstone of present day computer.
Rapid microprocessor advancement is attributed to Gordon Moore, who in 1965, in what became known as Moore’s Law, said that computer processing would double every eighteen to twenty four months.
Starting with the 4004 of 1971, a micro processor that boasted of 2300 transistors, modern processors house millions of transistors, and have gotten smaller. The traditional single core microprocessors have also given way to multi-core processors which have enabled even stronger computers.

7. Computer Software
Computer software include programs, data and protocols which run on hardware parts. Software cannot be touched; it can only be experienced via the various output devices like the monitor and speaker. These basically include programs, graphics, text, video and sound. Examples of computer software: Microsoft Windows 7, Adobe Photoshop, music and video files, pictures and text files. Software is what brings computer hardware to life.
Software development meanwhile, enabled computers evolve from dependence on the keyboard based command line interface to the popular graphical user interface and mouse in about 1984. This made interaction with the computer appealing.
Over the years, user interface has evolved considerably switching from mechanical based input methodology to more natural methodology. Computer input is now possible by a wink of an eye or nodding of the head.
8. Internet
The internet is a massive network of computers from around the world all connected by cable and satellite. When users are connected to the internet, they can send and receive text, images, video and sound on their computer to and from computers around the world.
Just as there is a book or magazine on nearly every subject in local libraries, bookshops, newsagents, so is there information on virtually every subject on the internet. The internet is sometimes called the World Wide Web (WWW) or just the net, and a user is said to be online when using the internet.
The internet became the pillar of information and a platform where this information could be shared easily around the clock. With the proliferation of mobile communication devices in the 21st century, information can only spread wider.
9. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the storage and use of data and information, through the internet. In modern computing, users simply sit back in front of their computers and watch YouTube video or use computer applications on web browsers and actually plug into collective power of thousands of computers that serve these information from far away servers.
We now read the news, listen to music, shop, watch TV shows and store files on the web. Nearly every institution, bank, and government office has a website with loads of data for its users.
Around the time when the cloud was introduced users worried about losing documents, photos and music if a computer malfunctioned. Today, data can be stored safely beyond the boundaries of personal computers.
Cloud print is another big leap in cloud services. A technology championed by Google, cloud printing allows users to add and share their printers online. Consequently one can print a document from anywhere and from any computer and phone running internet and Google apps to the shared printer.
10. Artificial Intelligence – AI
The ability of a computer or machine to simulate human behavior is what is referred to as artificial intelligence. It is the branch of computer science concerned with making computers behave like humans.
Artificial intelligence allows computers to learn from experience, recognize patterns in context and large amounts of data and make informed decisions based on human knowledge.
One particular area where artificial intelligence receives a lot of attention is voice recognition. Not only should a computer understand human vocal communication, it should also be able to respond to questions or challenges in a natural manner.
11. Humanware
The final and most important component in the era of information age is the user. And the user is you, the person that designed and made information technology possible and usable. It is the human that uses technology devices, thus giving them meaning and purpose.
© 2014 Alfred Amuno