- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Science & Programming»
- Programming Languages
Java In Brief
Introduction
Java was introduced by James Gosling, Patrick Naughton, Chris Warth, Ed Frank and Mike Sheridan at Sun Microsystems in 1991. This language was initially called 'Oak' but was renamed 'Java' in 1995. Java is an object oriented language, was initially considered to be simply the 'Internet version of C++'. Java is related to C++, which is a direct descendent of C. Java is most similar to C. Java shares much of C's syntax but you don't need to know C to learn Java.
Difference between C++ and Java
Properties
| C++
| Java
|
|---|---|---|
Data Types
| The type modifiers like auto, extern, register are present.
| Supports all primitive data types.
|
Structures & Unions are not supported.
| ||
Casting is much more controlled (Wrapper Classes).
| ||
Pointers
| They have support for pointers.
| Java does not support pointers.
|
Operators
| Operator overloading is possible
| Operator overloading is not possible
|
Functions
| Have inline functions in contrast to java.
| All the functions are defined within the class & therefore called methods.
|
Functions without arguments may have void mentioned.
| No explicit use of void for empty methods.
| |
Preprocessors
| They use preprocessors and statements like #include & #define.
| No preprocessors hence no #define statements. They use packages instead.
|
Flow of Control
| goto, break, continue
| There are no goto's in java but it has break and continue.
|
Inheritance
| C++ supports multiple inheritance.
| No multiple inheritance but multilevel inheritance is possible.
|
Memory Management
| Static
| Dynamic.
|
It uses automatic garbage collection technique.
|
Features of Java
- Reliability-
It has 3 level of security:- Class Loader
- Bytecode verification
- Security Manager
- Fully supports oops.
- Supports Multithreading.
- Garbage collection
- Platform Independency
- There are 3 types of programs that can be made in java:
- Application programs (Dos based)
- Window based programs (Desktop Application)
- Web based programs (Servlet/Applets)
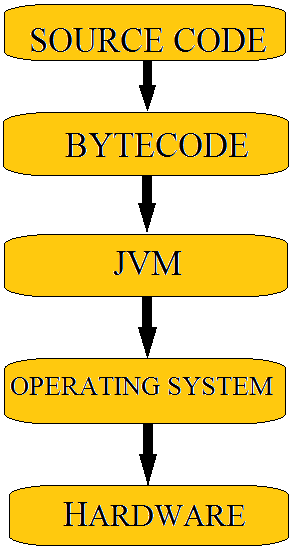
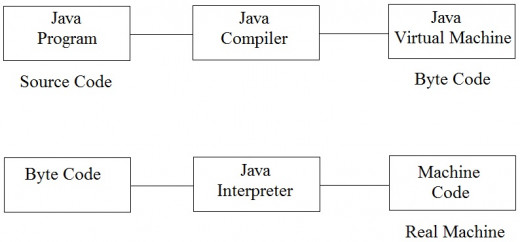
Java Byte Code
Bytecode is computer object code that is processed by a program usually referred to as a virtual machine. The virtual machine converts each generalized machine instruction into a specific machine instruction or instructions that this computer's processor will understand. Java compiler converts the source code into intermediate code is called as bytecode.
Advantages with Java
- Simple
Java system was built as closely to c++ as possible in order to make the system more comprehensible. Java omits many rarely used features of C++. - Secure
Java is intended to be used in networked/distributed environments. So, keeping that view in mind, a lot of focus is given on security. - Portable
Java is compiled to bytecode which is platform independent, this provides portability to Java. - Object Oriented
The object-oriented features are as essential to Java as they are to C++. Object-oriented design is a technique of programming that focuses on the data and on the interfaces to that object. - Robust
Java is intended for writing programs that must be reliable in a variety of ways. Java encourages error-free programming by being strictly types and performing run-time checks. - Multithreaded
Java provides an integrated support for multithreaded programming. Multithreaded programming allow writing programs that can do many things at once. Threads in Java also have the capacity to take the advantage of multiprocessor systems if the base operating system does so. - Architecture-neutral
A central issue for Java designers was 'Write once, run anywhere, any time, forever'. Java is not tied to a specific machine or operating system architecture. - Interpreted
Interpreted means that the computer looks at the language and then turns it into native machine language. The java interpreter can execute Java bytecode directly on any machine to which the interpreter has been ported. - High Performance
The Java bytecode is highly optimized for speed of execution. The bytecode can be converted at run time into machine codes for the particular CPU the application is running on. - Distributed
Java has extensive library routines for copying with TCP/IP protocols like HTTP and FTP. Java handles TCP/IP protocol that is why it is useful for the distributed environment of the internet. - Dynamic
Java was designed to adapt to an evolving environment. Libraries can add freely new methods and instance variables without any effect on their client. This makes it possible to dynamically link code in a safe manner. Java is more dynamic than C++.
Java Code
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("This is my first java program");
}
}The file name of the source code is named the same as the name of the public class itself with the extension 'Java'. So the name of the above file should be Demo.java. The program is compiled on command prompt as follows:
C:\javac Demo.java
After the compilation is done and no error present, it creates class file. It is executed on command prompt as follows:
C:\java Demo
Why do we need public static void main(String args[]) methods in Java?
- public: The method can be accessed outside the class/package.
- static: You need not have an instance of the class to access the method.
- void: Your application need not return a value.
- main(): This is the entry point for the application.
- String args[]: It declares an array of instance of String class.
If the main() was not static, you would require an instance of the class in order to execute the method.
Java Architecture