Making a Simple Temperature Indicator Circuit
Simple Temperature Indicator
The temperature of a heat-sink can be measured with a wet finger: if it sizzles, the temperature is too high.
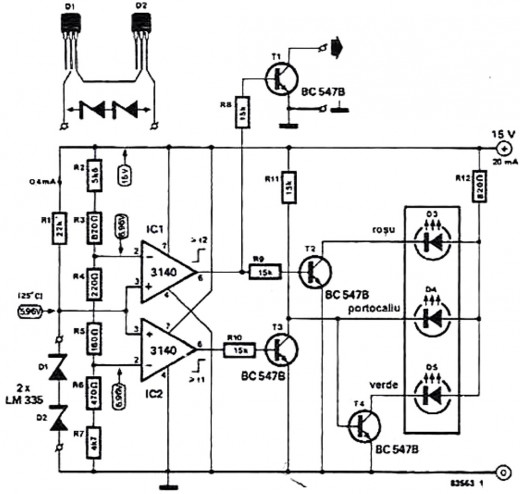
The circuit of a simple temperature indicator in the shown diagram is an alternative method of checking that does not cause blisters: A green ’safe’ LED lights as long as the temperature of the heat-sink does not exceed 500 Centigrade, an orange 'caution' LED for temperatures of 500..750 Centigrade and a red ’danger’ LED for temperatures above 75° Centigrade.
The circuit is simplicity in itself, two special zener diodes, D1 and D2, are connected in series to ensure an accurate zener voltage of 5.96V at 25° Centigrade. The zener voltage will rise by 20 mV for each degree Centigrade rise in temperature. The voltage level corresponding to the temperature of the heat-sink is compared with two reference voltages by IC1 and lC2.
When the temperature reaches 50° Centigrade the output of lC2 goes high so T3 conducts and causes D4 to light and at the same time D5 is extinguished by T4. At or above 75° Centigrade the output of lC1 is high and T2 and T3 then conduct to make D3 light and D4 extinguish. Under normal conditions, that is, considering a heat-sink of sufficient cooling area, a temperature of 75° Centigrade will never be reached.
Parts List for the above Simple Temperature Indicator Circuit
R1 = 22k
R2 = 5k6
R3, R12 = 820E
R4 = 220E
R5 = 180E
R6 = 470E
R7 = 4k7
R8, R9, R10, R11 = 15k
Semiconductors
D1, D2 = LM335 (National Semiconductor)
D3 = LED red 5mm
D4 = LED orange 5mm
D5 = LED green 5mm
T1, T2, T3, T4 = BC547B
IC1, IC2 = 3140
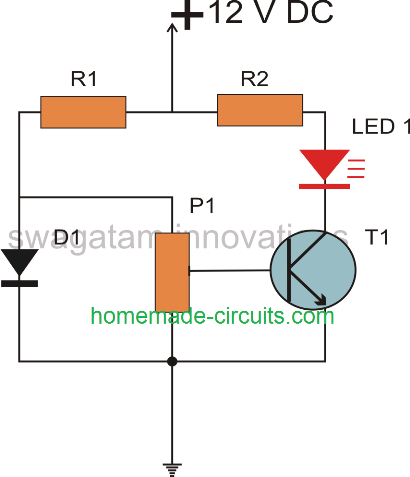
Simple Temperature Indicator using a Single Transistor
So far we learned the procedures for making a temperature indicator circuit using a rather complex circuitry involving many components, and IC.
Now let us study a truly simple circuit which could be built using just a single transistor.
How the Circuit Works
The circuit is based on the fact that any BJT will drop around 2mV across its emitter collector leads when it is subjected to a degree rise in temperature.
This property or characteristic of a BJT has been exploited in this design and is used as a temperature detector as well as an LED driver device.
To compliment the heat sensing operation, a semiconductor diode 1N4148 is also employed as a sensor in this circuit, but this device becomes responsible for sensing the ambient temperature, and provide a reference level for the BJT sensor.
When a heat source is brought near the BJT, it checks the difference in temperature with reference to the potential level across the diode 1N4148, and if the source significantly crosses this reference, the BJT begins conducting heavily, illuminating the connected LED.
The illumination on the LED indicates the rising temperature of the source, and this operation can be effectively implemented on applications such as heatsinks for creating a warning signal if the heat on it exceeds a certain predetermined threshold or level.
The circuit schematic is shown below, for more info such as the parts list and all the calculations you can further refer to this article: simple temperature indicator circuit
Circuit Schematic