Multiband Microstrip Antennas in Wireless Communication
Introduction
Multiband Microstrip Antennas or MMA are the literal backbones of wireless communications. Let's review what MMA antennas are and how they are used.
Uses of Multiband Microstrip Antennas
Multiband microstrip antennas are used in vehicle information and communication systems which provide traffic and travel information to drivers. Dedicated Short Range Communications antennas are microstrip antennas that communicate identification information to nearby receivers.
These antennas are used in parking access control systems and electronic toll collection, recording the passage of cars through an unmanned toll both while billing the user's account for each tollgate passed
Microstrip antennas are also used in hand held cell phones.
How Do Multiband Microstrip Antennas Work?
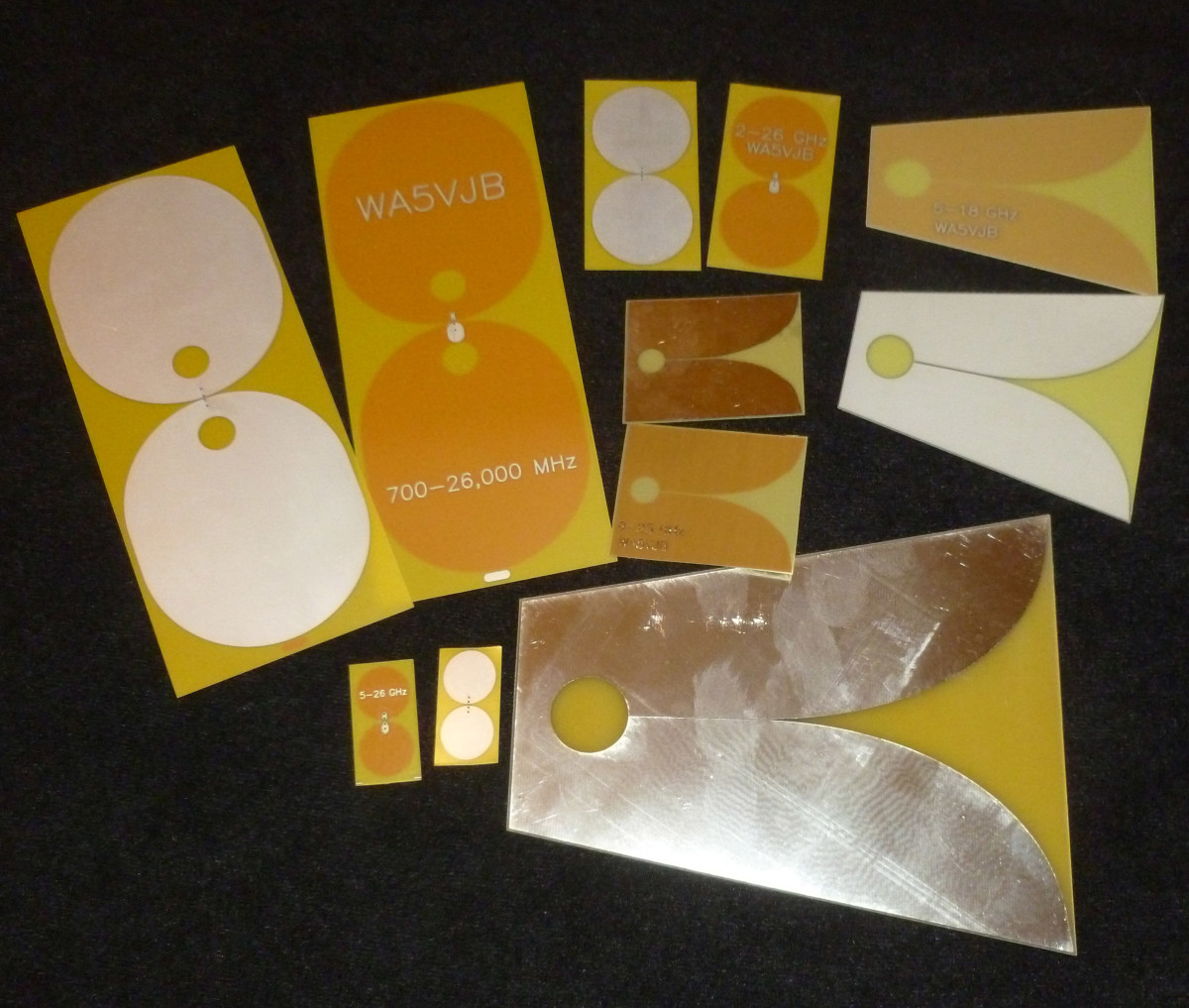
Individual microstrip antennas resemble a resonating cavity with open side walls, vibrating in response to the frequency it is designed to receive. Microstrip or slot-array antennas are one half of a wavelength long.
For cell phones operating at 800 Megahertz and receiving a wavelength of 37.5 centimeters, the microstrip antenna to receive the signal would be 18.75 centimeters long. Stacking microstrip antennas along the central cavity creates multiband microstrip antennas or MMAS which receive signals from several radio frequency bands.
MEM switches turn on and off microstrips within antennas arrays. Microstrip antennas can be made multi-mode using positive-intrinsic-negative diodes, which function as electronic radio frequency switches by changing between positive, negative and neutral states. Turning off antennas causes the multiband microstrip antennas to behave as if it were smaller and receive lower wavelength frequencies.
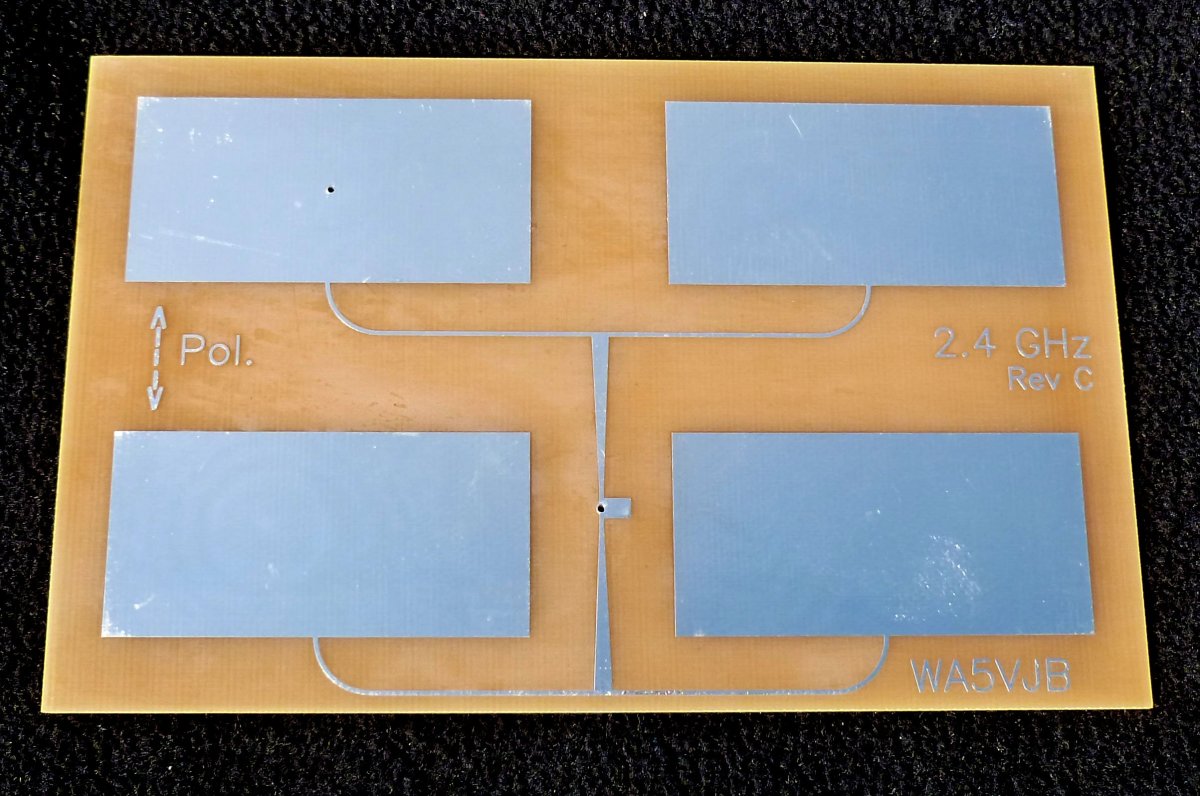
The Advantages of Microstrip Antennas
Microstrip antennas’ low profile allows manufacturers to fold or mold them to curved surfaces, such as the dashboard of a car. Low-cost etching with acidic paste is one method of manufacturing microstrip antennas. Microstrip antennas have low radar visibility, a useful trait for military aircraft.
Microstrip antennas assembled into fractal arrays use less material than a single, large antenna. Microstrip antennas assembled into an array weigh less than a conventional antenna, so they require less support than other antennas.
Microstrip antennas can connect directly to circuit card assemblies using solder instead of using cables. This is especially helpful on cell phone towers or antenna towers already littered with coax cable.
Placing slotted antennas with holes or slots cut out in an antenna array further increases the range of frequency bands it receives at a relatively low cost.
The Disadvantages of Microstrip Antennas
Small microstrip antennas only handle a few watts of power, while larger units can manage a few hundred to a few thousand watts of power. This limits the outgoing signal strength of microstrip antennas. Single microstrip antennas have little ohmic loss, also called resistive heating. Multiband microstrip antennas have greater heat generation from ohmic loss. This can affect the thin printed wiring boards used in most microstrip antennas.
Unless signal filters are used to filter out unwanted signals from nearby frequency ranges, multiband microstrip antennas suffer from interference. Thus microstrip antenna arrays suffer insertion loss with increasing size and at higher frequencies. Microstrip antennas have low bandwidth, as well.