Types of Computer Networks; Lan, Wan, Man, Wlan
Main Common Types of Computer Networks
The world of computers is made up of computers and other networking devices interconnected together with wires while others are interconnected wirelessly to form what we call a network.
A computer network is an interconnection of two or more computers for the user to share data and peripherals.
There are several different types of computer networks in existence.
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)
- WLAN - Wireless Local Area Network
- SAN - Storage Area Network, System Area Network, Server Area Network, or sometimes Small Area Network
- CAN - Campus Area Network, Controller Area Network, or sometimes Cluster Area Network
- PAN - Personal Area Network
A Local Area Network Setting
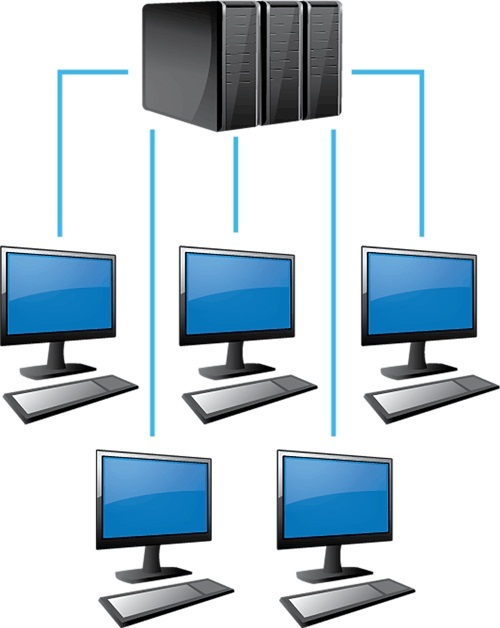
The Local Area Network
A Local Area Network is a network type comprising of a group of computers and other systems located reasonably close to one another within a given area.
Users communicate and share resources for instance within a college, Cyber Cafe' or an office. A LAN connects computers and network devices over a relatively short distance.
A Local Area Network uses TCP/IP network protocol for communication between computers and other connected peripherals.
LANs are the basis of all other types of networks. So if you connect two or more computers in an office, the result will be a Local Area Network.
The smallest LAN may only use two computers, while larger Local Area Networks can accommodate thousands of computers.
A LAN typically relies mostly on wired connections for increased speed and security, but wireless connections can also be part of a LAN.
High speed and relatively low cost are the major defining characteristics of LANs.
Advantages of a Local Area Network
- Easy to troubleshoot - this is because a LAN does not cover a large area and it is not complicated.
- Cheap to install and monitor - the devices involved in coming up with this network are not expensive.
- More secure - because it is usually a small network, it is possible to maintain security.
- Less vulnerable to attenuation - attenuation is the gradual loss of signal strength as the signal tends to travel far from the point of origin. In this type of network, because the computers are situated within a small geographical area, the signals are less prone to attenuation.
- It experiences low error rates.
The Metropolitan Area Network
This is a network that covers an entire city or town. This type of network usually makes use of wireless infrastructure or optical fibre connections to link sites.
It can be created by connecting several LANs. For example, it can be a network covering all the police stations in a big city, local government authorities.
A college with several branches can also interlink their LANs and come up with a Metropolitan Area Network.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Metropolitan Area Network
Advantages of Metropolitan Area Network
- It enhances easier communication
- It offers a faster passage of data.
Disadvantages of Metropolitan Area Network
- It is expensive to install and maintain.
- It is susceptible to tapping.
- It is susceptible to attenuation (gradual loss of signal strength as data flows further from the point of origin).
- It has high error rates.
The Wide Area Network
It’s a type of network design that connects computers across a large geographical area of a city, region and even spans beyond country boundaries.
It consists of several sections of LAN’s and MAN’s connected by devices such as routers.
A WAN transmits information by telephone lines, ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) lines, Radio waves, or satellite Microwave.
A network device called a router connects LANs to a WAN. The Internet is the best example of the largest Wide area network as it covers the whole world.

Wireless Local Area Network
Wireless Local Area Network - This is a LAN based on Wi-Fi wireless network technology.
This type of network can be created within a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, campus, or office building.
It gives users the ability to move around within the area and remain connected to the network. Making use of a gateway, a WLAN can also provide a connection to the wider Internet.
The primary difference between a LAN and a WLAN is how the data is transmitted. In a LAN, data is transmitted over physical cables in a series of data packets. In a WLAN, packets are transmitted over the air.
Storage Area Network
Storage Area Network - Connects servers to data storage devices through a technology like Fibre Channel.
A storage area network (SAN) is a dedicated, independent high-speed network that interconnects and delivers shared pools of storage devices to multiple servers.
Each server accesses the shared storage as if it were a drive directly attached to the server.
A SAN is assembled with cabling, host bus adapters, and SAN switches attached to storage arrays and servers. Each switch and storage system on the SAN must be interconnected.
Campus Area Network
Campus Area Network - A network spanning multiple LANs but smaller than a MAN, such as on a university or local business campus.
By size, a campus area network is larger than a local area network but smaller than a metropolitan area network (MAN) or wide area network (WAN).
Most CANs are made of several LANs connected via switches and routers that combine to create a single network.
CAN (Campus Area Network)

Personal Area Network
A Personal Area Network, or PAN, is a computer network organized around a person within a single building.
This could be inside a small office or residence. A typical PAN will include one or more computers, telephones, peripheral devices, video game consoles, and other personal entertainment devices.
Conclusion
The moment you connect two or more computers located reasonably close to one another, you will be creating a LAN.
Even when you are to create a MAN or a WAN, you will have to start with a Local Area Network.
Types of Computer Network
Do you have interconnected computers in your place
This article is accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge. Content is for informational or entertainment purposes only and does not substitute for personal counsel or professional advice in business, financial, legal, or technical matters.
© 2011 Patrick Kamau