Personal Communication System
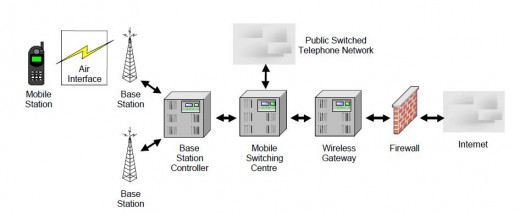
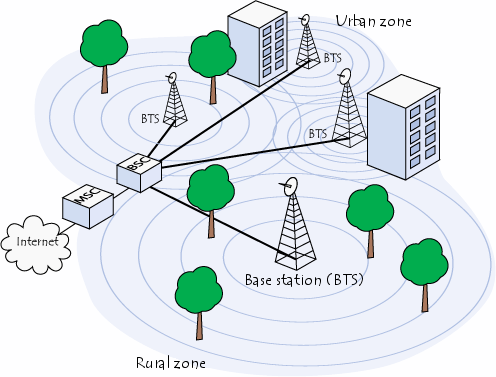
A personal communication system (PCS) is a cellular system operating in a band of frequencies at 1.9 GHz. The original concept for PCS included multiple, new features and services beyond those offered by a basic cellular system. Some of the envisioned features were single telephone number for multiple services (Voice, Data, Fax) and user mobility for home or office use and location determination. Although some commercial PCS offerings provide some new user feature, initial North American PCS systems are basically cellular systems utilizing a new band of frequencies.
When the FCC allocated the PCS frequencies for the United States, they did so without stipulating which type of system should be deployed. Thus, any organization that bids for and receives a franchise for PCS spectrum is free to choose whatever type of system it wants for providing service to the public. As a result, North American PCS systems have been developed with three different transmission formats: D-AMPS, GSM, CDMA. The D-AMPS implementation follows EIA/TIA standard IS-136, which is basically a revision of IS-54 that incorporates digital control channels. (IS-54 defines the use of an analog control channel for compatibility with AMPS).