- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Science & Programming»
- Programming Languages
Pointers in C Programming Language

In this tutorial I am going to discuss what pointer is and how to use them in our C program. Many C programmer thinks that pointer is one of the difficult topic in C language but it’s not completely true. It is difficult to understand in comparison of other secondary (array, structure etc.) data types available in C. Pointer in C seems to be difficult because it works directly with computer memory (RAM).
When we declare any variable in C, for example integer variable, it occupies a memory according to its size (here 2 bytes). As it occupies a memory so it’s natural to have an address for this location so that it can be referenced later by CPU for manipulation. But before we begin with Pointer we must have some idea on the operators we are going to use in Pointer programming.
The ‘*’ And ‘&’ Operators
Take a look on the following declaration,
int x=10;
When we make such declaration how C compiler treat this statement:
- Reserve memory space for this integer value.
- Name this memory location as x.
- Store the value 10 at this location.
This can be illustrated by a simple diagram:
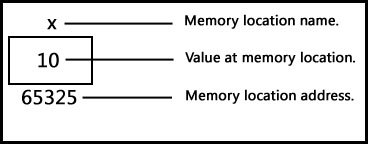
So when we declared an integer variable x and assigned value 10 then compiler occupied a 2 byte memory space at memory address 65325 and stored value 10 at that location. Compiler named this address x so that we can use x instead of 65325 in our program. But we can use address or variable in our program and both will point to the same value (example given below).
The memory address of a variable could differ from PC to PC and entirely depends on available free space in memory at time of program execution. As this differs from PC to PC thus we cannot rely on that address (numeric value representing variable address) and we cannot use this address in our program. But have you noticed one thing that address is an integer.
We can print address of any variable or function, following program shows how we can do that:
Address of variable example.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int i=9;
clrscr();
printf("Value of i : %d\n",i);
printf("Address of i : %u",&i);
getch();
}This is a very simple c program which prints value and address of an integer. But did you notice line no. 10 in above program? This line output the address of i variable and to get address of i variable we have used ampersand (&) operator. This operator is known as "Address of" operator and we already used this operator many times in our program, just recall scanf statement which is used to accept input from computer keyboard. So when we use ampersand operator (&i) before any variable then we are instructing c compiler to return its address instead of value.
Another operator we going to deal with in this entire pointer tutorial is "*" called "Value at address" operator. It is the same operator which we use for multiplication of numbers. As the name suggest, "value at address" operator returns value stored at particular address. The "value at address" operator also called indirection operator. Following example extends above C program and puts "value at address" operator in action.
Value at address (*) example
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int i=9;
clrscr();
printf("Value of i : %d\n",i);
printf("Address of i : %u\n",&i);
printf("Value at address of i : %d",*(&i));
getch();
}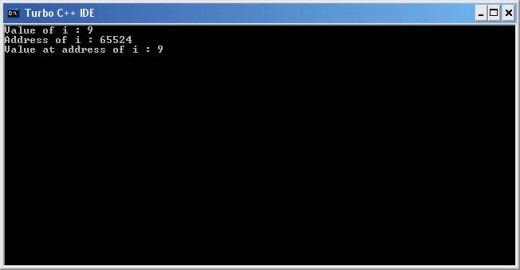
Now in this program notice line no. 11 and use of ‘&’ and ‘*’ operators also see the output of program which prints value of variable i and *(&i) same. This is how these two operator works.
You must have clear idea of ‘&’ and ‘*’ operator usage before you jump into pointer because pointer deals with these to operator. If you find any difficulty then post your doubts and I will try to clear your doubts.What is Pointers in C Programming?
A pointer is a secondary data type (also known as derived data type) in C. It is built from one of the primary data types available in C language. Basically pointer contains memory address of other variable or function as their value. As pointer deals with memory address, it can be used to access and manipulate data stored in memory.
Benefits of using Pointer in C Program
Pointer is one of the most exciting features of C language and it has added power and flexibility to the language. Pointer is in C language because it offers following benefits to the programmers:
- Pointers can handle arrays and data table efficiently.
- Pointers support dynamic memory management.
- Pointer helps to return multiple values from a function through function argument.
- Pointer increases program execution speed.
- Pointer is an efficient tool for manipulating structures, linked lists, queues stacks etc.
We can achieve these and much more benefits from pointer only if we can use it properly.
Pointer with an example
Since this tutorial is already become lengthy so I am going to give a small example on how we can use pointer in our C program. Of course we will discuss remaining part in my next pointer tutorial.
Syntax: datatype *pointer_name;
Example : int *iPtr;
float *fPtr;
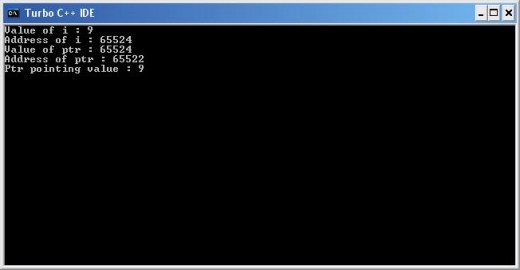
Pointer Example
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int i=9, *ptr;
ptr=&i;
clrscr();
printf("Value of i : %d\n",i);
printf("Address of i : %u\n",&i);
printf("Value of ptr : %u\n",ptr);
printf("Address of ptr : %u\n",&ptr);
printf("Ptr pointing value : %d", *ptr);
getch();
}In the above example in line no. 6 we have declared an integer i and assigned 9 to it. Along with variable i, we have also declared an integer pointer. To declare a pointer of any data type we just need to put an * (asterisk) before variable name or identifier. In our example ptr is an integer variable and is capable of holding address of any integer variable.
Remember one thing integer pointer can hold only integer variable address, you cannot use integer pointer to hold address of float or char variable. To hold char or float variable address in a pointer you need to declare char or float pointer respectively.
In line no. 7 we assigned integer variable i’s address to ptr, now ptr is pointing to i. Line no 10 prints value of i and line no. 11 prints address of i. Next line prints value stored in ptr pointer variable, line no. 13 prints address of ptr pointer. As pointer is different entity so it also requires space in memory. Memory occupied by a pointer depends on its data type. Integer pointer will occupy 2 bytes whereas character pointer will occupy 1 byte. Finally line no. 14 prints the value of address stored in ptr pointer i.e. value of i. And to print value of stored address in a pointer we need write *pointer variable name (in our example *ptr). A memory map will help you to understand this.
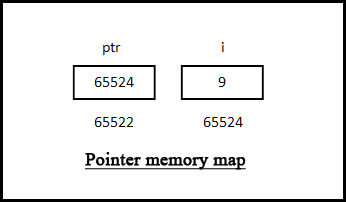
Reader's Feedback
Is this tutorial helpful to understand basic C Pointer concept?
If you find any difficulty or error in this article then please let me know through comment box.
Thank you for visiting my free C pointer tutorial.
C Programming Other Tutorial Links
- Functions in C Programming Language
A function in C language is a block of code that performs a specific task. It has a name and it is reusable i.e. it can be executed from as many different parts in a C Program as required. It also optionally returns a value to the calling program So - Types of Function in C Programming Language
In my previous c programming tutorial I tried to explain what the function, its advantages is and how to declare a C function. And I told you that there are five types of functions and they are: Functions with no arguments and no return values. Func - Function Pointer in C Programming Language
Like C variables, function too has address and we can use this address to invoke function. So this tutorial is entirely devoted to function-pointer. But before we can call a function using we need to find out its address. So first we will see how to - What Is an Array in C Programming Language
what is an array in c programming, this tutorial explains it with example and line by line explanation. - 2d Array in C Programming Language
We know how to work with an array (1d array) with one dimension. In C language it is possible to have more than one dimension in an array. This tutorial explains how we can use two dimensional arrays (2D array or matrix array) to store values with ex
© 2009 RAJKISHOR SAHU