Robotics Mechanism
Automatica 2018 Munich Germany (Robotics Engineering Exhibition)
Do you think Robots are essential (where Humans can not work ) ?
Robotics
Entertainment robo AIBO

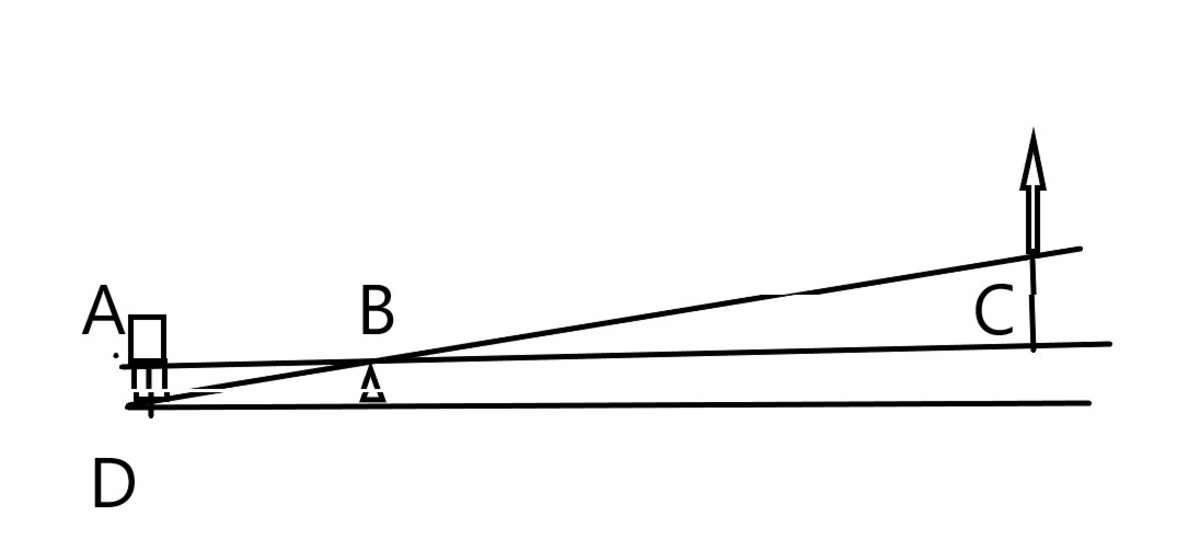
Robot Arm Kinematics
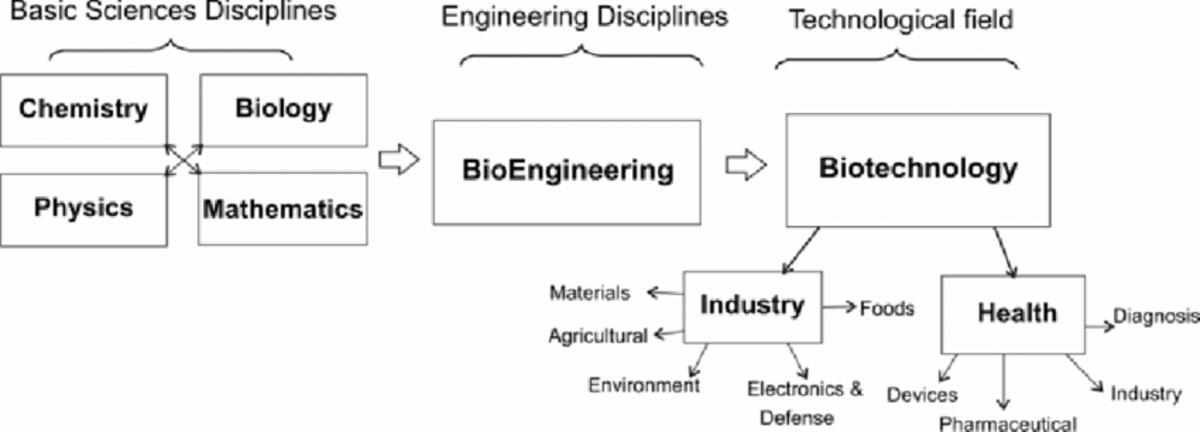
A system that contains sensors, control systems, manipulators, power supplies and software all working together to perform a task. Designing, building, programming and testing a robots is a combination of physics, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, structural engineering, mathematics and computing.
A mechanical manipulator can modeled as an open-loop articulated chain with several rigid bodies (links) connected in series by either revolute or prismatic joints driven by actuators.One end of the chain is attached to a supporting base while teh other end attached with a tool (end -effector) to manipulate objects or perform assembly tasks.The relative motion of the joints results in the motion of the links that positions the hand in desired orientation.In most ofthe robotics applications ,one is interested inthe spatial description of the end-effector of the manipulator with respect to a fixed co-ordinate system.
Robot Arm kinematics deals with the analytical study of the geometry of motion of a robot arm with respect to a fixed reference coordinate system as a function of time without regards to the forces/moments that cause the motion.Thus, it deals with the analytical description of the spatial displacement of the robot as a function of time, in particular the relations between the joint-variable space and the position and orientation of the robot arm. This chapter addresses two fundamental questions of both theoretical and practical interests in robot arm mechanism
Robotic main applications
1 – Robotic handling operations
Material handling is the most popular application with 38% of operational stock of industrial robots worldwide. This includes machine machine tending, palatalizing and various operations for metal machining and plastic moulding.
2 – Robotic Processing
Processing is not a big segment of industrial robots (only 2%) and this is probably because a lot of automated machines are available on the market to do specifically these applications. The main application areas are mechanical, laser and water jet cutting.
3 – Robotic Welding
This segment mostly includes spot welding and arc welding which is mainly used by the automotive industry. Spot welding is still more popular than arc welding but not for long; as arc welding is becoming very popular in the metal industry.
4 – Robotic Dispensing
Here we are talking about painting, gluing, applying adhesive sealing, spraying, etc. Only 4% of the operational robots are doing dispensing.
5 – Robotic Assembly
Assembly operations include: fixing, press-fitting, inserting, disassembling, etc. This category of robotic applications seems to have decreased over the last few years, even while other robotic applications have increased.
© 2009 Apeksha Waychal